Article contents
ON SKEWNESS AND DISPERSION AMONG CONVOLUTIONS OF INDEPENDENT GAMMA RANDOM VARIABLES
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 November 2010
Abstract
Let {x(1)≤···≤x(n)} denote the increasing arrangement of the components of a vector x=(x1, …, xn). A vector x∈Rn majorizes another vector y (written  ) if
) if 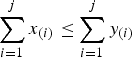 for j = 1, …, n−1 and
for j = 1, …, n−1 and  . A vector x∈R+n majorizes reciprocally another vector y∈R+n (written
. A vector x∈R+n majorizes reciprocally another vector y∈R+n (written  ) if
) if  for j = 1, …, n. Let
for j = 1, …, n. Let  , be n independent random variables such that
, be n independent random variables such that  is a gamma random variable with shape parameter α≥1 and scale parameter λi, i = 1, …, n. We show that if
is a gamma random variable with shape parameter α≥1 and scale parameter λi, i = 1, …, n. We show that if  , then
, then  is greater than
is greater than 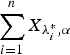 according to right spread order as well as mean residual life order. We also prove that if
according to right spread order as well as mean residual life order. We also prove that if 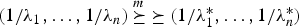 , then
, then 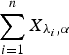 is greater than
is greater than 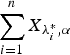 according to new better than used in expectation order as well as Lorenze order. These results mainly generalize the recent results of Kochar and Xu [7] and Zhao and Balakrishnan [14] from convolutions of independent exponential random variables to convolutions of independent gamma random variables with common shape parameters greater than or equal to 1.
according to new better than used in expectation order as well as Lorenze order. These results mainly generalize the recent results of Kochar and Xu [7] and Zhao and Balakrishnan [14] from convolutions of independent exponential random variables to convolutions of independent gamma random variables with common shape parameters greater than or equal to 1.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences , Volume 25 , Issue 1 , January 2011 , pp. 55 - 69
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2011
References
- 13
- Cited by


