Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 August 2017
We study factor of i.i.d. processes on the d-regular tree for d ≥ 3. We show that if such a process is restricted to two distant connected subgraphs of the tree, then the two parts are basically uncorrelated. More precisely, any functions of the two parts have correlation at most 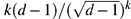 $k(d-1) / (\sqrt{d-1})^k$, where k denotes the distance between the subgraphs. This result can be considered as a quantitative version of the fact that factor of i.i.d. processes have trivial 1-ended tails.
$k(d-1) / (\sqrt{d-1})^k$, where k denotes the distance between the subgraphs. This result can be considered as a quantitative version of the fact that factor of i.i.d. processes have trivial 1-ended tails.