Congenital heart defects occur in approximately 1/100 live birthsReference Hoffman and Kaplan 1 and represent the major cause of infant death due to birth defects.Reference Boneva, Botto, Moore, Yang, Correa and Erickson 2 Early studies in rats indicated that heart defects are among the folate-sensitive birth defects, which include neural tube defects and cleft lip and palate.Reference Baird, Nelson, Monie and Evans 3 More recent human studies suggest that periconceptional folate supplementation reduces the incidence of heart defects, in particular conotruncal defects and ventricular septal defect.Reference Bailey and Berry 4 , Reference van Beynum, Kapusta, Bakker, den Heijer, Blom and de Walle 5 In Canada, fortification of grain products with folic acid has been linked to a significant decrease in heart defects, particularly conotruncal defects.Reference Ionescu-Ittu, Marelli, Mackie and Pilote 6 Increased folate intake may prevent heart defects by lowering maternal homocysteine levels, as maternal hyperhomocysteinaemia is associated with a greater than fourfold increase in risk for heart defects.Reference Verkleij-Hagoort, Bliek, Sayed-Tabatabaei, Ursem, Steegers and Steegers-Theunissen 7 However, it is possible that homocysteine as such does not cause heart defects, but that it acts as a biomarker of disturbed folate metabolism or cellular methylation reactions that may disrupt embryonic development.
The link between low folate/high homocysteine and heart defect incidence implies that single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the folate pathways may be genetic risk factors for these disorders. A number of polymorphisms in folate pathway genes have been identified that appear to affect protein function and/or folate metabolism and thus may affect the risk for heart defects (for a review, see Christensen and RozenReference Christensen and Rozen 8 ). On this basis, we selected four variants to examine in a cohort of congenital heart defect patients and their mothers: methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) c.677C > T and c.1298A > C, methionine synthase reductase (MTRR) c.66A > G and reduced folate carrier (SLC19A1) c.80A > G. These polymorphisms were selected on the basis of their reported associations with risk for neural tube defects, and observations of cardiac defects in mouse models.
MTHFR catalyses the reduction of methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, which is required for the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine. The MTHFR c.677C > T variant (p.Ala222Val, dbSNP ID: rs1801133) results in a thermolabile protein associated with reduced enzyme activity in vivo.Reference Frosst, Blom and Milos 9 , Reference Weisberg, Tran, Christensen, Sibani and Rozen 10 This variant has been found to increase plasma homocysteine, particularly in combination with low folate levels,Reference Jacques, Bostom and Williams 11 and is a risk factor for neural tube defects.Reference van der Put, Steegers-Theunissen and Frosst 12 The MTHFR c.1298A > C variant (p.Glu429Ala, rs1801131) has been reported to modestly reduce MTHFR activity in vivo,Reference Weisberg, Tran, Christensen, Sibani and Rozen 10 although it may not influence homocysteine levelsReference Fredriksen, Meyer, Ueland, Vollset, Grotmol and Schneede 13 , Reference Yang, Botto and Gallagher 14 or neural tube defect risk.Reference Relton, Wilding and Pearce 15 The c.1298A > C variant is in linkage disequilibrium with the c.677C > T variant (the 677TT/1298CC genotype is rarely observed), which complicates the analysis of its effects.Reference Brown, Pratt and Buller 16 In mice, MTHFR-deficient females have greater numbers of offspring with heart defects than wild-type mice; the majority of observed defects were ventricular septal defects.Reference Li, Pickell, Liu, Wu, Cohn and Rozen 17
MTRR catalyses the regeneration of the cobalamin cofactor of methionine synthase and may also help stabilise and activate methionine synthase.Reference Yamada, Gravel, Toraya and Matthews 18 Methionine synthase uses the 5-methyltetrahydrofolate generated by MTHFR to remethylate homocysteine, producing methionine. If MTRR activity is disrupted, it results in a functional deficiency of methionine synthase.Reference Gulati, Chen, Brody, Rosenblatt and Banerjee 19 The MTRR c.66A > G variant (p.Ile22Met, rs1801394) has been reported to have different biochemical properties from the wild-type residue in vitro;Reference Olteanu, Munson and Banerjee 20 however, the effect of the mutation in vivo is not clear. Although this variant protein does not appear to independently affect homocysteine levels,Reference Fredriksen, Meyer, Ueland, Vollset, Grotmol and Schneede 13 , Reference Yang, Botto and Gallagher 14 the 66GG genotype has been reported to significantly decrease homocysteine levels in MTHFR 677TT individuals.Reference Yang, Botto and Gallagher 14 This variant has also been reported to influence risk for neural tube defects, although results of these studies have been mixed.Reference Relton, Wilding and Pearce 15 , Reference Wilson, Platt and Wu 21 – Reference O'Leary, Mills and Pangilinan 23 In mouse models, MTRR deficiency causes increased plasma homocysteineReference Elmore, Wu and Leclerc 24 and has been found to increase the incidence of ventricular septal defect.Reference Deng, Elmore, Lawrance, Matthews and Rozen 25
Reduced folate carrier (gene name: SLC19A1) is a bidirectional transporter that carries reduced folates such as methyltetrahydrofolate. The effect of the SLC19A1 c.80A > G variant (p.His27Arg, rs1051266) on the protein is not clear; one study found no effect,Reference Whetstine, Gifford and Witt 26 whereas another found that it decreased transport of the folate analog methotrexate.Reference Baslund, Gregers and Nielsen 27 This variant does not appear to affect plasma homocysteine or folate levels.Reference Fredriksen, Meyer, Ueland, Vollset, Grotmol and Schneede 13 The SLC19A1 c.80A > G variant may be a folate-responsive risk factor for neural tube defects in some populations, although reports are inconsistent.Reference Pei, Zhu and Ren 28 , Reference Shaw, Lammer, Zhu, Baker, Neri and Finnell 29 In mice, reduced folate carrier-deficient embryos die before implantation in the absence of maternal folate supplementation; heart defects such as conotruncal defects and ventricular septal defect have been reported in folate-supplemented reduced folate carrier-deficient embryos at later stages of development.Reference Taparia, Gelineau-van Waes, Rosenquist and Finnell 30
The aim of this study is to assess the impact of these polymorphisms on heart defect risk in a Canadian cohort born before mandatory folate fortification. This is the first investigation of the impact of the MTHFR c.677C > T, MTHFR c.1298A > C, MTRR c.66A > G, and SLC19A1 c.80A > G variants in a Canadian cohort.
Materials and methods
Human subjects
The subjects in this study are a subset of a previously described cohort.Reference Christensen, Rohlicek and Andelfinger 31 DNA from patients and control subjects was obtained from blood spots and stored as reported.Reference Christensen, Rohlicek and Andelfinger 31 Informed consent was obtained from all study participants before sample collection. The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki with approval from the Institutional Review Boards at the Montreal Children's Hospital and CHU Sainte-Justine. The subjects were from the province of Quebec, Canada, of Northern European background, born before December 31, 1996, before the introduction of mandatory folic acid fortification in Canada in 1998. Demographic information and use of folic acid supplements during pregnancy was obtained using a questionnaire administered at sample collection. As in other studies,Reference van Beynum, Kapusta and den Heijer 32 – Reference Hobbs, Cleves, Karim, Zhao and MacLeod 34 mothers were considered unsupplemented if use of supplements began only after the pregnancy was known. Congenital heart defects were diagnosed by echocardiography, as described.Reference Christensen, Rohlicek and Andelfinger 31 Only patients and mothers of children with non-syndromic heart defects were included in this study. Control samples were collected from mothers and children unaffected by heart defects who presented at the Montreal Children's Hospital for outpatient blood sampling.
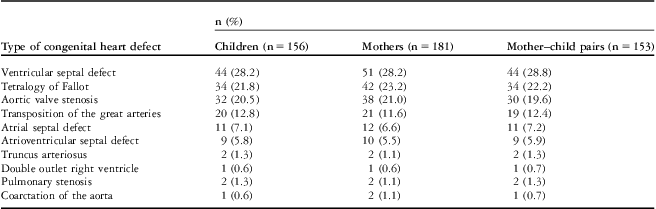
The subjects include 156 children with congenital heart defects, 181 mothers of children with congenital heart defects, 69 control children, and 65 control mothers (Table 1). There were 216 mother–child pairs within the cohort, that is, 153 patients and 63 controls. Congenital heart defects in the patients were aortic valve stenosis, atrial septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, coarctation of the aorta, double-outlet right ventricle, pulmonary stenosis, transposition of the great arteries, tetralogy of Fallot, truncus arteriosus, and ventricular septal defect (Table 1).
Table 1 Congenital heart defect diagnoses in patients and mothers.

Genotyping
Genotypes were determined by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis at the Research Institute of the Montreal Children's Hospital. Genotyping of MTHFR c.677C > T was carried out using the sense primer 5′-TGAAGGAGAAGGTGTCTGCGGGA-3′ and the antisense primer 5′-GATGCCCATGTCGGTTCATGCCTT-3′. Following 35 cycles of polymerase chain reaction amplification (94°C, 1 minute; 68°C, 1 minute; 72°C, 2 minutes), the 104 base-pair amplicon was digested with Hinf1 to generate the 104 base-pair 677C or 79 base-pair 677T fragments. Genotyping for MTHFR c.1298A > C, MTRR c.66A > G, and SLC19A1 c.80A > G was carried out as described, except that the restriction enzyme Hinp1I was used for SLC19A1.Reference Leclerc, Sibani and Rozen 35 – Reference Shaw, Zhu, Lammer, Yang and Finnell 37 One case mother could not be genotyped for MTRR c.66A > G or SLC19A1 c.80A > G, and thus was excluded from the analysis of those polymorphisms.
Statistical methods
Case–control tests of single-nucleotide polymorphism association without controlling for covariates were first used to compare the frequency of polymorphism alleles in two well-defined cohorts of patients diagnosed with the heart defects under study and unaffected controls. Case–control tests were performed for mother and child cohorts separately. Polymorphism impact on heart defect risk was analysed by diagnosis; owing to small numbers, coarctation of the aorta, double-outlet right ventricle, pulmonary stenosis, and truncus arteriosus were not analysed separately. Single-nucleotide polymorphism association with heart defect risk overall was analysed by grouping all diagnoses together.
Case–control association tests included the chi-square test on genotype, the chi-square test on alleles and the Cochran–Armitage trend test on genotypes. A total of 100,000 permutations were used to obtain the exact p-values by the Monte Carlo method.Reference Westfall and Young 38 Single-nucleotide polymorphisms were tested for Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium using an exact testReference Guo and Thompson 39 based on the conditional probability of genotype counts given allelic counts and the hypothesis of allelic independence using 100,000 permutations to get the exact p-values by Monte Carlo permutation.
A logistic regression model was used to evaluate the genotypic effect for the homozygous, heterozygous, dominant, and recessive models for each polymorphism. MTHFR 677T, MTHFR 1298C, MTRR 66G, and SLC19A1 80G were set as the risk alleles. All statistical analyses were conducted with SAS 9.1 including SAS genetics. Results with p-values less than or equal to 0.05 were considered to be of interest; to correct for multiple testing, the significance threshold was adjusted to less than or equal to 0.0125 using the Bonferroni correction.
Results
Descriptive data
Cohort Demographics
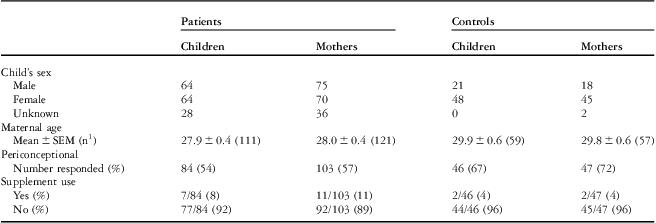
Demographic information for the cohort – maternal age at birth of index child, child's sex, multivitamin use – is shown in Table 2. Maternal age in the control group was significantly higher than that in the case groups, p is equal to 0.0121 for heart defects overall. Although significant, this approximately 1-year increase in maternal age would not be expected to affect heart defect risk. The proportion of female children is also higher in the control groups than that in the case groups.
Table 2 Demographic description of the cohort.
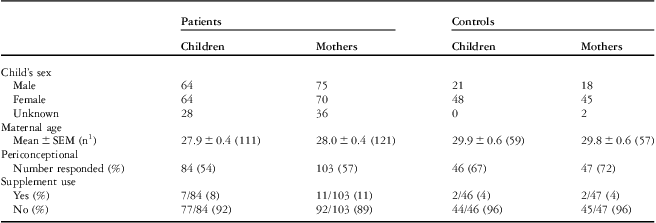
1Number of mothers that provided maternal age at birth of index child
In the mothers’ cohort, supplemental vitamin use questions were completed by 57% of patients’ mothers and 72% of control mothers (Table 2). Of those, only 11% of patients’ mothers and 4% of control mothers reported using multivitamins containing folic acid before conception. Owing to these small numbers, a separate analysis of supplemented and unsupplemented mothers was not performed. The majority of mothers in this study did not use folic acid supplements during the periconceptional period. Of those that responded, 50% of patients’ mothers and 68% of control mothers reported using multivitamins only after the pregnancy was discovered; as in other studies, we consider these mothers to be unsupplemented.Reference van Beynum, Kapusta and den Heijer 32 – Reference Hobbs, Cleves, Karim, Zhao and MacLeod 34 Materna was the most commonly named supplement in all groups. As the majority of participants were mother–child pairs, reported use of multivitamins containing folic acid was not meaningfully different in the children's cohort. Given that all of the participants in this study were born before folic acid supplementation in Canada, and the majority of mothers used folic acid supplements only after the periconceptional period, this study is more likely to detect folate-responsive single-nucleotide polymorphism associations than post-fortification cohorts.
Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium and linkage
In the mothers’ cohort, no significant deviations from the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium were observed; frequency of polymorphisms and Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium results are reported in Supplementary Table S1. In the children, there were no deviations from the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium for any polymorphism or diagnosis except for MTHFR c.677C > T in children with ventricular septal defect and tetralogy of Fallot, which results in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium deviation for heart defects overall for this polymorphism – frequency of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium results in Supplementary Table S2. These deviations could be due to genetic associations with heart defects; however, they were not significant after correction for multiple testing.
As expected, the MTHFR c.677C > T and c.1298A > C variants were in linkage disequilibrium with a D′ value of 1. The 677TT/1298CC genotype was not observed in this cohort.
Association of folate-related single-nucleotide polymorphisms with risk for congenital heart defects
The associations between heart defect risk and the variant allele, homozygous variant genotype and heterozygous variant genotype were evaluated for each of the four polymorphisms. The associations of heart defect risk using recessive and dominant effect models were also assessed by logistic regression. No significant associations were observed for atrial septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, transposition of the great arteries, and tetralogy of Fallot in either mothers or children. Complete results including calculated odds ratios, upper and lower 95% confidence limits, and p-values for the four polymorphisms in the mothers are reported in Supplementary Tables S3 and S4; complete results for the children in Supplementary Tables S5 and S6. Tables 3–6 show the results for the diagnosis groups for which there were findings of interest (overall heart defect risk, aortic valve stenosis, and ventricular septal defect).
The maternal MTHFR 1298AC genotype was associated with increased odds ratios for aortic valve stenosis (odds ratio (AC versus CC): 2.90 (1.22–6.86), p = 0.0157; odds ratio (AC and CC versus AA): 2.39 (1.04–5.47), p = 0.0398) (Tables 3 and 4). However, these associations did not meet the higher threshold for significance (p = 0.0125) after correction for multiple testing. No maternal effect on heart defect risk was observed for MTHFR c.677C > T, MTRR c.66A > G, and SLC19A1 c.80A > G.
Table 3 Association of maternal folate-related single-nucleotide polymorphisms with risk of congenital heart defects in children.

AS = aortic valve stenosis; CHD = congenital heart defects; CL = 95% confidence limit; MTHFR = methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; MTRR = methionine synthase reductase; OR = odds ratio; SLC19A1 = reduced folate carrier; SNP = single-nucleotide polymorphism; VSD = ventricular septal defect
Table 4 Association of maternal folate-related single-nucleotide polymorphisms with risk of congenital heart defects in children, recessive and dominant effects.

AS = aortic valve stenosis; CHD = congenital heart defects; CL = 95% confidence limit; MTHFR = methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; MTRR = methionine synthase reductase; OR = odds ratio; SLC19A1 = reduced folate carrier; SNP = single-nucleotide polymorphism; VSD = ventricular septal defect
In children, the MTRR c.66A > G variant was associated with decreased risk for heart defects. The G allele, the GG and the AG genotypes decreased odds ratios for heart defects overall (odds ratio (G versus A): 0.66 (0.44–0.98), p = 0.0532; odds ratio (GG versus AA): 0.42 (0.18–0.97), p = 0.0423; odds ratio (AG versus AA): 0.39 (0.18–0.84), p = 0.0168) (Table 5). When genotypes were combined using the dominant model (AG and GG versus AA), the odds ratio was 0.40 (0.19–0.83), p = 0.0140 (Table 6). None of these models met the higher threshold for significance after correction for multiple testing. The relationship of MTRR c.66A > G and heart defect risk appears to be driven by associations with risk for aortic valve stenosis and ventricular septal defect. Decreased odds ratios for aortic valve stenosis were found for both the AG genotype (odds ratio (AG versus AA): 0.27 (0.09–0.79), p = 0.0162) (Table 5) and the dominant model (odds ratio (AG and GG versus AA): 0.32 (0.12–0.83), p = 0.0191) (Table 6); these associations did not meet the threshold of p = 0.0125 for significance after correction for multiple testing. The c.66A > G variant appears to be linked with ventricular septal defect risk at both the allele and genotype levels: odds ratio (G versus A): 0.54 (0.32–0.93), p = 0.0295; odds ratio (GG versus AA): 0.32 (0.11–0.91), p = 0.0329; odds ratio (AG versus AA): 0.25 (0.09–0.65), p = 0.0044) (Table 5). Consistent with these observations, the dominant model was highly significant for ventricular septal defect (odds ratio (AG and GG versus AA): 0.27 (0.11–0.66), p = 0.0040) (Table 6). The association of ventricular septal defect risk with the AG genotype and the dominant model were significant after correction for multiple testing. The MTHFR c.677C > T, MTHFR c.1298A > C, and SLC19A1 c.80A > G polymorphisms were not associated with heart defect risk in the children.
Table 5 Association of folate-related single-nucleotide polymorphisms in children with risk of congenital heart defects.

AS = aortic valve stenosis; CHD = congenital heart defects; CL = 95% confidence limit; MTHFR = methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; MTRR = methionine synthase reductase; OR = odds ratio; SLC19A1 = reduced folate carrier; SNP = single-nucleotide polymorphism; VSD = ventricular septal defect
Table 6 Association of folate-related single-nucleotide polymorphisms in children with the risk of congenital heart defects, recessive and dominant effects.

AS = aortic valve stenosis; CHD = congenital heart defects; CL = 95% confidence limit; MTHFR = methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; MTRR = methionine synthase reductase; OR = odds ratio; SLC19A1 = reduced folate carrier; SNP = single-nucleotide polymorphism; VSD = ventricular septal defect
Discussion
Studies of animal models suggest that heart defects associated with low folate/high homocysteine may result from abnormal differentiation, migration, and apoptosis in neural crest cells affecting primarily the interventricular septum and the conotruncal region.Reference Boot, Steegers-Theunissen, Poelmann, Van Iperen, Lindemans and Gittenberger-de Groot 40 , Reference Tang, Wlodarczyk, Santillano, Miranda and Finnell 41 Several studies of the effects of folic acid/multivitamin supplementation also suggest an association between folate deficiency and conotruncal defects/ventricular septal defect.Reference Bailey and Berry 4 , Reference Czeizel 42 In this cohort, we found potential associations of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in enzymes of folate metabolism with ventricular septal defect and aortic valve stenosis. Aortic valve stenosis has not been commonly reported to be a folate-responsive heart defect; however, patients with aortic valve stenosis have not been included in many of these studies.
In this study, a significant association between the MTRR c.66A > G variant in children and risk for certain types of heart defects was observed. After correction for multiple testing, the MTRR 66AG genotype and the dominant model (AG and GG versus AA) were found to significantly decrease risk for ventricular septal defect. Maternal c.66A > G genotype had no effect on heart defect risk in this population. The results of published studies of this variant and heart defect risk have been mixed. This variant, in either the mother or child, was found to have no impact on heart defect risk in mixed pre- and post-fortification American cohorts – grouped conotruncal and left-sided cardiac defects, respectivelyReference Goldmuntz, Woyciechowski, Renstrom, Lupo and Mitchell 43 , Reference Mitchell, Long, Garbarini, Paluru and Goldmuntz 44 – or in children with conotruncal defects in a pre-fortification American cohort.Reference Shaw, Lu and Zhu 45 In contrast to our findings, in the Dutch population, which is not folic acid fortified, maternal MTRR 66GG was found to increase risk for non-conotruncal heart defects – including aortic valve stenosis, pulmonary stenosis, coarctation of the aorta, atrial septal defect and others – when combined with vitamin B12 deficiency.Reference van Beynum, Kouwenberg and Kapusta 46 However, in a second Dutch cohort, consisting primarily of conotruncal and septal defects, there was no association between either maternal or inherited 66GG genotype and heart defects, regardless of B12 status.Reference Verkleij-Hagoort, van Driel and Lindemans 47 Similarly conflicting results have been obtained from investigations of this variant and neural tube defect risk.Reference Relton, Wilding and Pearce 15 , Reference Wilson, Platt and Wu 21 – Reference O'Leary, Mills and Pangilinan 23 These contrasting results suggest that the effect of the MTRR variant may depend on other factors – for example, genetic, nutritional, environmental – within the population, or that this variant may only affect risk for specific subtypes of heart defects. In mice, both maternal and embryonic MTRR deficiency were found to increase ventricular septal defect incidence in offspring.Reference Deng, Elmore, Lawrance, Matthews and Rozen 25 However, it is not clear that the 66G variant causes in vivo MTRR deficiency.Reference Olteanu, Munson and Banerjee 20 , Reference Olteanu, Wolthers, Munro, Scrutton and Banerjee 48
We did not find an association between heart defect risk and MTHFR c.677C > T genotype in this pre-fortification Canadian cohort. The results of studies of this variant and heart defects in other non-fortified populations have been mixed. Some groups have reported increased risk for certain subtypes of heart defects associated with maternalReference van Beynum, Kapusta and den Heijer 32 or inheritedReference Junker, Kotthoff and Vielhaber 49 , Reference Lee, Su and Cheng 50 TT genotype, whereas others have not observed these effects.Reference Shaw, Lu and Zhu 45 , Reference Shaw, Iovannisci and Yang 51 – Reference Xu, Xu and Xue 53 In the Dutch population, the risk for conotruncal defects associated with maternal MTHFR 677TT genotype was increased in those who did not consume folic acid supplements during the periconceptional period.Reference van Beynum, Kapusta and den Heijer 32 Consistent with those findings, studies of MTHFR c.677C > T in folic acid fortified populations have found no link with heart defect risk,Reference Goldmuntz, Woyciechowski, Renstrom, Lupo and Mitchell 43 , Reference Mitchell, Long, Garbarini, Paluru and Goldmuntz 44 , Reference Hobbs, James and Parsian 54 , Reference McBride, Fernbach and Menesses 55 except in combination with maternal obesity.Reference Hobbs, Cleves, Karim, Zhao and MacLeod 34
In this cohort, maternal MTHFR 1298AC genotype was associated with a possible increase in risk for aortic valve stenosis. This contrasts with the findings from a pre-fortification American cohort that did not observe any association between this variant and aortic valve stenosis risk.Reference McBride, Fernbach and Menesses 55 In other non-fortified populations, this variant was not linked to risk for conotruncal defectsReference Shaw, Lu and Zhu 45 , Reference Storti, Vittorini and Lascone 52 or a mixed group of heart defects.Reference Xu, Xu and Xue 53 In a Dutch study, non-fortified population, the 1298AC and CC genotypes in children were reported to decrease risk for a mixed group of heart defects, compared with those with the 1298AA genotype, unless their mothers consumed folic acid supplements;Reference van Driel, Verkleij-Hagoort and de Jonge 33 maternal genotype had no effect on risk in unsupplemented mothers, but the 1298AC and CC genotypes increased heart defect risk relative to the 1298AA genotype in mothers that were folic acid supplemented. However, the 1298AC and CC genotypes in children were also associated with a decreased risk for heart defects in a folic acid fortified cohort,Reference Hobbs, James and Parsian 54 and the 1298CC genotype in children was found to protect against conotruncal defects in a mixed pre- and post-fortification American cohort.Reference Goldmuntz, Woyciechowski, Renstrom, Lupo and Mitchell 43 No association between this variant and risk for left-sided cardiac defects was found in a second mixed pre- and post-fortification American cohort.Reference Mitchell, Long, Garbarini, Paluru and Goldmuntz 44 Clearly, the impact of this variant on heart defect risk, particularly in combination with folic acid intake, requires further investigation.
In this study, the SLC19A1 c.80A > G variant was also not associated with heart defects. In contrast, the 80GG and AG genotypes showed an increase in risk for conotruncal defects in a Californian populationReference Shaw, Zhu, Lammer, Yang and Finnell 37 and heart defects in general – predominantly ventricular septal defect – in a Chinese population.Reference Pei, Zhu, Zhu, Ren, Finnell and Li 56 In those studies, low folate levels increased the risk attributed to the variant. However, this association was not observed in a second study of the Californian population.Reference Shaw, Lu and Zhu 45
The associations with heart defect risk for the MTHFR c.1298A > C variant in mothers and MTRR c.66A > G variants in children may reflect the metabolic role of these enzymes. MTHFR produces the major circulating form of folate supplied to embryos during development;Reference Henderson, Perez, Schenker, Mackins and Antony 57 therefore, maternal MTHFR deficiency may cause foetal folate deficiency resulting in abnormalities, whereas MTHFR deficiency in the child may be compensated for by the supply of methyltetrahydrofolate from the mother. MTRR supports the folate-dependent remethylation of homocysteine within cells and tissues. Therefore, MTRR could have a greater role in one-carbon metabolism within developing embryonic tissues, leading to metabolic changes that affect heart defect incidence.
The largely unsupplemented nature of this cohort provides the opportunity to identify folate-responsive relationships between these polymorphisms and heart defect risk that may not be evident in more recent North American cohorts. Clearly, gene–nutrient interactions may play an important role in the impact of variants of folate metabolism on heart defect risk, and should be considered in future studies. In this study, the number of patients was small when subdivided by diagnosis; despite this limitation, we observed some associations. Nonetheless, our findings should be considered preliminary and further investigation of these gene variants should be performed in larger cohorts.
In conclusion, we identified possible associations between certain types of congenital heart defects and single-nucleotide polymorphisms in genes of folate metabolism. The MTRR c.66A > G variant in children may protect against specific heart defects, such as ventricular septal defect. Additional studies of folate-related variants and heart defect risk in larger cohorts should be focused on specific classes of defects, with particular emphasis on the potential for genetic interactions between mother and child.
Acknowledgements
We thank Qing Wu, Liyuan Deng, and Roxanne Gendron for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, grant number GMHD-79045 (GUA, AR, RR) and a Fellowship from the Montreal Children's Hospital Research Institute (KEC).
Supplementary materials
For supplementary material referred to in this article, please visit http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1017/S1047951112000431