The polydisperse coagulation equation
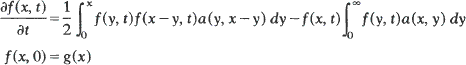 models irreversible aggregation of particles with varying masses. This paper uses a one-parameter family of discrete-time continuous multitype branching processes to solve the polydisperse coagulation equation when
models irreversible aggregation of particles with varying masses. This paper uses a one-parameter family of discrete-time continuous multitype branching processes to solve the polydisperse coagulation equation when 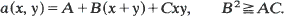
The critical time tc when 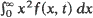 diverges corresponds to a critical branching process, while post-critical times t> tc correspond to supercritical branching processes.
diverges corresponds to a critical branching process, while post-critical times t> tc correspond to supercritical branching processes.