In this paper, we are concerned with the physically engaging pseudo-relativistic Schrödinger system:
\[ \begin{cases} \left(-\Delta+m^{2}\right)^{s}u(x)=f(x,u,v,\nabla u) & \hbox{in } \Omega,\\ \left(-\Delta+m^{2}\right)^{t}v(x)=g(x,u,v,\nabla v) & \hbox{in } \Omega,\\ u>0,v>0 & \hbox{in } \Omega, \\ u=v\equiv 0 & \hbox{in } \mathbb{R}^{N}\setminus\Omega, \end{cases} \]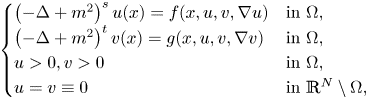
where $s,t\in (0,1)$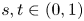 and the mass $m>0.$
and the mass $m>0.$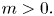 By using the direct method of moving plane, we prove the strict monotonicity, symmetry and uniqueness for positive solutions to the above system in a bounded domain, unbounded domain, $\mathbb {R}^{N}$
By using the direct method of moving plane, we prove the strict monotonicity, symmetry and uniqueness for positive solutions to the above system in a bounded domain, unbounded domain, $\mathbb {R}^{N}$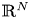 , $\mathbb {R}^{N}_{+}$
, $\mathbb {R}^{N}_{+}$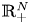 and a coercive epigraph domain $\Omega$
and a coercive epigraph domain $\Omega$ in $\mathbb {R}^{N}$
in $\mathbb {R}^{N}$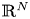 , respectively.
, respectively.