Let 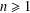 $n\geq 1$ be an integer and
$n\geq 1$ be an integer and 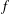 $f$ be an arithmetical function. Let
$f$ be an arithmetical function. Let 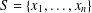 $S=\{x_{1},\ldots ,x_{n}\}$ be a set of
$S=\{x_{1},\ldots ,x_{n}\}$ be a set of  $n$ distinct positive integers with the property that
$n$ distinct positive integers with the property that 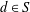 $d\in S$ if
$d\in S$ if 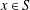 $x\in S$ and
$x\in S$ and 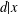 $d|x$. Then
$d|x$. Then  $\min (S)=1$. Let
$\min (S)=1$. Let  $(f(S))=(f(\gcd (x_{i},x_{j})))$ and
$(f(S))=(f(\gcd (x_{i},x_{j})))$ and  $(f[S])=(f(\text{lcm}(x_{i},x_{j})))$ denote the
$(f[S])=(f(\text{lcm}(x_{i},x_{j})))$ denote the  $n\times n$ matrices whose
$n\times n$ matrices whose 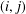 $(i,j)$-entries are
$(i,j)$-entries are  $f$ evaluated at the greatest common divisor of
$f$ evaluated at the greatest common divisor of  $x_{i}$ and
$x_{i}$ and 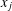 $x_{j}$ and the least common multiple of
$x_{j}$ and the least common multiple of 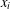 $x_{i}$ and
$x_{i}$ and  $x_{j}$, respectively. In 1875, Smith [‘On the value of a certain arithmetical determinant’, Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 7 (1875–76), 208–212] showed that
$x_{j}$, respectively. In 1875, Smith [‘On the value of a certain arithmetical determinant’, Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 7 (1875–76), 208–212] showed that 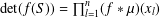 $\det (f(S))=\prod _{l=1}^{n}(f\ast \unicode[STIX]{x1D707})(x_{l})$, where
$\det (f(S))=\prod _{l=1}^{n}(f\ast \unicode[STIX]{x1D707})(x_{l})$, where  $f\ast \unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$ is the Dirichlet convolution of
$f\ast \unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$ is the Dirichlet convolution of 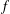 $f$ and the Möbius function
$f$ and the Möbius function 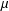 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$. Bourque and Ligh [‘Matrices associated with classes of multiplicative functions’, Linear Algebra Appl. 216 (1995), 267–275] computed the determinant
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$. Bourque and Ligh [‘Matrices associated with classes of multiplicative functions’, Linear Algebra Appl. 216 (1995), 267–275] computed the determinant  $\det (f[S])$ if
$\det (f[S])$ if  $f$ is multiplicative and, Hong, Hu and Lin [‘On a certain arithmetical determinant’, Acta Math. Hungar. 150 (2016), 372–382] gave formulae for the determinants
$f$ is multiplicative and, Hong, Hu and Lin [‘On a certain arithmetical determinant’, Acta Math. Hungar. 150 (2016), 372–382] gave formulae for the determinants 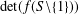 $\det (f(S\setminus \{1\}))$ and
$\det (f(S\setminus \{1\}))$ and  $\det (f[S\setminus \{1\}])$. In this paper, we evaluate the determinant
$\det (f[S\setminus \{1\}])$. In this paper, we evaluate the determinant  $\det (f(S\setminus \{x_{t}\}))$ for any integer
$\det (f(S\setminus \{x_{t}\}))$ for any integer  $t$ with
$t$ with 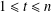 $1\leq t\leq n$ and also the determinant
$1\leq t\leq n$ and also the determinant  $\det (f[S\setminus \{x_{t}\}])$ if
$\det (f[S\setminus \{x_{t}\}])$ if  $f$ is multiplicative.
$f$ is multiplicative.