Introduction
In vitro production (IVP) can produce many embryos over a short time interval, providing more embryos compared with in vivo production (Pontes et al., Reference Pontes, Nonato-Junior, Sanches, Ereno-Junior, Uvo, Barreiros, Oliveira, Hasler and Seneda2009). Therefore, IVP is a robust tool to enhance genetic gain (Vieira et al., Reference Vieira, Rodrigues, Castro Netto, Guerreiro, Silveira, Freitas, Bragança, Marques, Sá Filho, Bó, Mapletoft and Baruselli2016), contributing to the livestock economy (Blondin, Reference Blondin2017). In 2018, Brazil was responsible for 33.5% of global numbers of in vitro produced bovine embryos (Viana, Reference Viana2019).
Despite the advantages and widespread use of IVP, bull effects contribute to considerable variation in embryo rates, even under similar conditions (Otoi et al., Reference Otoi, Tachikawa and Kondo1993; Palma and Sinowatz, Reference Palma and Sinowatz2004; Alomar et al., Reference Alomar, Tasiaux, Remacle, George, Paul and Donnay2008). Differences in in vitro fertility have been associated with the sperm trait profile of samples used for in vitro fertilization (IVF) (Tanghe et al., Reference Tanghe, Van Soom, Sterckx, Maes and De Kruif2002; Tartaglione and Ritta, Reference Tartaglione and Ritta2004; Alomar et al., Reference Alomar, Mahieu, Verhaeghe, Defoin and Donnay2006, Reference Alomar, Tasiaux, Remacle, George, Paul and Donnay2008; Simões et al., Reference Simões, Feitosa, Siqueira, Nichi, Paula-Lopes, Marques, Peres, Barnabe, Visintin and Assumpção2013; Siqueira et al., Reference Siqueira, de Castro, de Assis, Bicudo, Mendes, Nichi, Visintin and Assumpção2018) and it has been shown convincingly that sperm oxidative stress impairs fertilization ability, embryo development, fetal growth and offspring health (Silva et al., Reference Silva, Gadella, Colenbrander and Roelen2007; Lane et al., Reference Lane, McPherson, Fullston, Spillane, Sandeman, Kang and Zander-Fox2014; de Castro et al., Reference de Castro, de Assis, Siqueira, Hamilton, Mendes, Losano, Nichi, Visintin and Assumpção2016).
During IVF, sperm are exposed to higher oxygen concentrations (approximately 20%) when compared with in vivo conditions (1.5–8%) (Fischer and Bavister, Reference Fischer and Bavister1993). The effects of high oxygen concentrations in the in vitro environment have also been correlated with the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Goto et al., Reference Goto, Noda, Mori and Nakano1993; Takahashi, Reference Takahashi2012). Although ROS are free radicals and highly reactive oxidizing agents with critical roles in physiological functions such as sperm capacitation, acrosome reaction and oocyte binding (Ford, Reference Ford2001), any imbalance between ROS production and antioxidant levels has a negative influence on sperm capacity, as a result of oxidative stress (Sikka et al., Reference Sikka, Rajasekaran and Hellstrom1995).
Mammalian sperm are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, increasing their susceptibility to ROS-mediated damage. These free radicals react with unsaturated fatty acids, initiating a cascade of lipid peroxidation (Lenzi et al., Reference Lenzi, Gandini, Picardo, Tramer, Sandri and Panfili2000). Furthermore, by-products of lipid peroxidation are also harmful for sperm, damaging their membranes, DNA and proteins (Agarwal et al., Reference Agarwal, Virk, Ong and Plessis2014).
The main source of sperm for in vitro fertilization is frozen–thawed semen, which has a higher lipid peroxidation index compared with fresh semen (Chatterjee and Gagnon, Reference Chatterjee and Gagnon2001; Kadirvel et al., Reference Kadirvel, Kumar and Kumaresan2009). Lipid peroxidation in frozen–thawed semen occurs due to the collapse of antioxidant enzyme defences, coupled with the generation of ROS during cryopreservation (Alvarez and Storey, Reference Alvarez and Storey1992). Furthermore, dilution of seminal plasma, in addition to temperature reduction (Medeiros et al., Reference Medeiros, Forell, Oliveira and Rodrigues2002), may exacerbate the oxidative environment, due to removal of seminal proteins that prevent sperm membrane changes and inhibit lipid peroxidation (Del Valle et al., Reference Del Valle, Casao, Pérez-Pé, Holt, Cebrián-Pérez and Muiño-Blanco2017).
Selection of a viable and motile sperm population is usually performed before IVF (Tanghe et al., Reference Tanghe, Van Soom, Sterckx, Maes and De Kruif2002; Suzuki et al., Reference Suzuki, Geshi, Yamauchi and Nagai2003; Samardzija et al., Reference Samardzija, Karadjole, Matkovic, Cergolj, Getz, Dobranic, Tomaskovic, Petric, Surina, Grizelj and Karadjole2006; Machado et al., Reference Machado, Carvalho, Filho, Caixeta, Franco, Rumpf and Dode2009). Different methods, such as swim up, centrifugation and Percoll® gradient, are used to select viable and motile sperm, as well as to remove seminal plasma and cryoprotectant. Percoll is the most widely used density separation reagent in bovine IVF, and is use is related to sperm quality, increasing the proportion of motile sperm (Henkel and Schill, Reference Henkel and Schill2003; Suzuki et al., Reference Suzuki, Geshi, Yamauchi and Nagai2003; Machado et al., Reference Machado, Carvalho, Filho, Caixeta, Franco, Rumpf and Dode2009). Although selection methods improve sperm traits, it has not been well established whether Percoll gradient selection removes cells damaged by cryopreservation-induced oxidative stress. Trait profiles of frozen–thawed sperm used for IVF and their oxidative potential could strongly affect IVP yields. Therefore, the hypothesis of this study was that the level of native oxidative stress in semen straws could affect sperm traits and the oxidative potential of sperm samples during IVF, despite the use of sperm selection and preparation (Percoll centrifugation). To test this hypothesis, we evaluated the influence of native lipid peroxidation index of commercial cryopreserved semen on sperm traits after Percoll gradient selection and also, the lipid peroxidation index of the sperm samples when kept under IVF conditions.
Materials and methods
Ethics Committee approval for animal use was granted by the School of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science of University of São Paulo (protocol CEUA 7246170117).
Reagent and solutions
All chemical reagents and solutions used were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), unless otherwise stated.
Semen preparation
In total, 48 semen batches from 14 Nellore bulls donated from two commercial artificial insemination centres in Brazil were used. The cryopreservation procedure was performed according to standard protocols from each centre and both centres used egg yolk-based extenders. For each one of the 48 batches, five semen straws from the same batch/ejaculate were used. Each straw was thawed, processed and analyzed independently for all variables in an independent replicate. Each straw was considered as a technical replicate of the same biological sample (batch/ejaculate). The mean of five replicates was determined and used for ranking, comparisons between groups and correlations (n = 48).
In this study, for the sperm preparation protocol, including centrifugation force and mediums, we tested the most commonly used protocol in IVP laboratories in Brazil (Machado et al., Reference Machado, Carvalho, Filho, Caixeta, Franco, Rumpf and Dode2009; Ramos-Deus et al., Reference Ramos-Deus, Santos Nascimento, Vieira, Chaves, Albuquerque, Ferreira-Silva, Grázia, Santos Filho, Batista, Teixeira and Oliveira2020). Therefore, after thawing (37ºC; 30 s), straws were evaluated for visual motility. Samples were subjected to a Percoll density gradient (400 µl Percoll 45% over 400 µl Percoll 90%) and centrifuged at 6600 g for 5 min. After centrifugation, the extender in the supernatant was collected to assess lipid peroxidation, whereas the pellet containing motile sperm was washed at 1100 g for 3 min in 1 ml Fert-TALP without inducers of sperm capacitation (Parrish et al., Reference Parrish, Susko-Parrish, Winer and First1988). The selected population was then assessed for motility, and its concentration analyzed using a Neubauer chamber and diluted in an appropriate volume of Fert-TALP to a final concentration of 25 × 106 motile sperm/ml. Samples were then analyzed using fluorescent probes under flow cytometry [FITC-PSA with propidium iodide (PI), tetraethylbenzimidazolycarbocyanine iodide (JC-1) and acridine orange] and incubated under IVF conditions (with Fert-TALP with capacitation agents for 20 h under mineral oil at 38.5ºC, 5% CO2 in air, and high humidity) to evaluate oxidative potential.
Experimental design, based on ranking and selection of bulls by lipid peroxidation
To evaluate the influence of lipid peroxidation on cryopreserved samples, spermatozoa trait profiles were analyzed after Percoll gradient selection and the samples were grouped based on native lipid peroxidation index in the extender. The 48 semen straws were divided retrospectively into four groups, with median and quartiles used to determine the limiting values for each group. Group 1 included semen straws that were between the maximum value of lipid peroxidation and the upper quartile (highest, n = 13); Group 2 included semen straws between upper quartile and median (high, n = 11); Group 3 included the median and the lower quartile (average, n = 12); and Group 4 included lower quartile and the minimum value of lipid peroxidation (low, n = 12).
Lipid peroxidation
To analyze lipid peroxidation, the TBARS test was used for two samples: (1) supernatant recovered after Percoll centrifugation containing the remaining semen extender fraction; and (2) sperm selected using Percoll and incubated under the same in vitro fertilization conditions. Sperm in this group (25 × 106 motile sperm/ml) were incubated with 475 µl of Fert-TALP with capacitation agents for 20 h under mineral oil at 38.5ºC, in 5% CO2 in air, and high humidity.
The TBARS reaction evaluates malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations as products of lipid peroxidation. This analysis was performed as described earlier by Hamilton et al. (Reference Hamilton, de Castro, Delgado Jde, de Assis, Siqueira, Mendes, Goissis, Muiño-Blanco, Cebrián-Pérez, Nichi, Visintin and D'Ávila Assumpção2016). Samples were analyzed to evaluate the spontaneous lipid peroxidation content by the production of TBARS. Initially, ice-cold trichloroacetic acid 10% (ratio 2:1) was added. Samples were then centrifuged at 20,800 g for 15 min (5°C) to precipitate proteins and debris. The supernatant was recovered and transferred to cryotubes, 1% thiobarbituric acid was added (ratio 1:1) and the sample incubated at 95°C in a water bath for 15 min. In this assay, thiobarbituric acid reacts with MDA to produce a pink-coloured complex. Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances were quantified using a cuvette and a spectrophotometer (Ultrospec 3300 pro®, Amersham Biosciences) at a wavelength of 532 nm and lipid peroxidation index reported as nanograms of TBARS/ml. The values obtained were compared with a standard curve for MDA concentration.
Motility
Total sperm motility was subjectively estimated by examination using phase contrast microscopy at ×100 magnification by placing 5 µl of semen sample on a warmed slide (37ºC) overlaid with a coverslip. Sperm motility was estimated at two time points: immediately after thawing (Motility post thaw) and after selection using Percoll (Motility post Percoll).
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry analyses were performed with a Guava EasyCyte™ Mini System (Guava® Technologies, Hayward, CA, USA) with a blue laser (488 nm) that emitted 20 mW visible laser radiation and three channels for fluorescence detection (525, 583 and 680 nm). We assessed 20 × 103 gated cells per sample, with data from each assay analyzed using FlowJo software v.10.2 (Flow Cytometry Analysis Software, Tree Star Inc., Ashland, OR, USA). Cells were identified and selected excluding debris, probe particles and non-single sperm events by applying a gate on forward scatter (FSC) versus a green fluorescence dot plot. The data corresponding to each fluorescence signal were given as arbitrary fluorescence units, recorded after logarithmic amplification, and the selected population was represented by percentage (%). Control samples, in addition to negative and positive samples, were used to elaborate thresholds and gates for each analysis to achieve the highest determination coefficient. This set-up for gain and voltage of channels used was applied to all samples. More details for control samples and fluorescent probes are available in a previous report (Siqueira et al., Reference Siqueira, de Castro, de Assis, Bicudo, Mendes, Nichi, Visintin and Assumpção2018).
In total, 187.5 × 103 events were used for fluorescein-conjugated Pisum sativum agglutinin (FITC-PSA) with PI and JC-1 stains, and 375 × 103 sperm were used for chromatin resistance to acid denaturation. To assess the acrosome integrity and plasma membrane integrity, FITC-PSA was used in conjunction with PI to produce a simultaneous evaluation. Sperm samples were incubated for 5 min with 7 µg/ml PI and 24 µg/ml FITC while protected from light. The FITC fluorescence emission was detected at 515–520 nm and PI fluorescence emission was detected at 630–650 nm. Emission of green fluorescence using FITC-PSA indicates a damaged acrosome, whereas emission of red fluorescence using PI indicates a damaged plasma membrane.
JC-1 was used to assess sperm mitochondrial membrane potential, and cells were incubated for 5 min with 1 µM JC-1 while protected from light. Fluorescence detection was performed at 590 nm. Sperm with a high mitochondrial membrane potential emit greater intensities of yellow fluorescence compared with sperm with low mitochondrial membrane potential (Uribe et al., Reference Uribe, Villegas, Boguen, Treulen, Sánchez, Mallmann, Isachenko, Rahimi and Isachenko2017).
Chromatin resistance analysis was based on a sperm chromatin structure assay (SCSA) (Evenson et al., Reference Evenson, Larson and Jost2002), modified as described previously (Castro et al., Reference Castro, Siqueira, Hamilton, Mendes, Visintin and Assumpção2018). The assay evaluates the susceptibility of chromatin to fragmentation and uses an acid detergent challenge to denature double-stranded DNA. This method allows acridine orange (AO) dye to bind to DNA, emitting either red fluorescence for single-stranded denatured chromatin or green fluorescence for double-stranded DNA, indicating resistant chromatin.
Samples with high motility were selected as a negative control for acrosome and membrane damage and high mitochondrial membrane potential. For positive controls (damaged acrosome and membrane and reduced mitochondrial membrane potential), a subset of the negative control sample was subjected to five cycles of freezing (liquid nitrogen) and thawing (water bath at 60ºC).
For the AO positive control, sperm were incubated with an acid solution (hydrochloric acid and acid detergent 1.2 M; pH 0.1) for 5 min to induce total sperm DNA denaturation (Castro et al., Reference Castro, Siqueira, Hamilton, Mendes, Visintin and Assumpção2018).
Statistical analyses
Statistical analysis was performed using Statistical Analysis System 9.3 software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) for Windows. All data were tested for normality of residues and homogeneity of variance. Group and bull effects were included in the statistical model. Comparisons of means among experimental groups were performed using a Tukey test. The GLM procedure was used to evaluate the effects of lipid peroxidation groups on dependent variables. A correlation test (Spearman) was performed between sperm traits and lipid peroxidation on sperm samples. Results are presented as mean ± standard error (SEM). A 5% significance level was used to reject the null hypothesis.
Results and Discussion
Ranking by lipid peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation is an important marker of oxygen-induced damage (Aitken et al., Reference Aitken, Clarkson and Fishel1989). In aerobic conditions, as during cryopreservation, sperm undergo spontaneous lipid peroxidation that may lead to complete loss of motility (Alvarez et al., Reference Alvarez, Storey and Touchstone1978). In this study, we verified whether the level of lipid peroxidation in the extender of cryopreserved semen influenced sperm traits of Percoll-selected populations or the oxidative potential of samples subjected to IVF conditions.
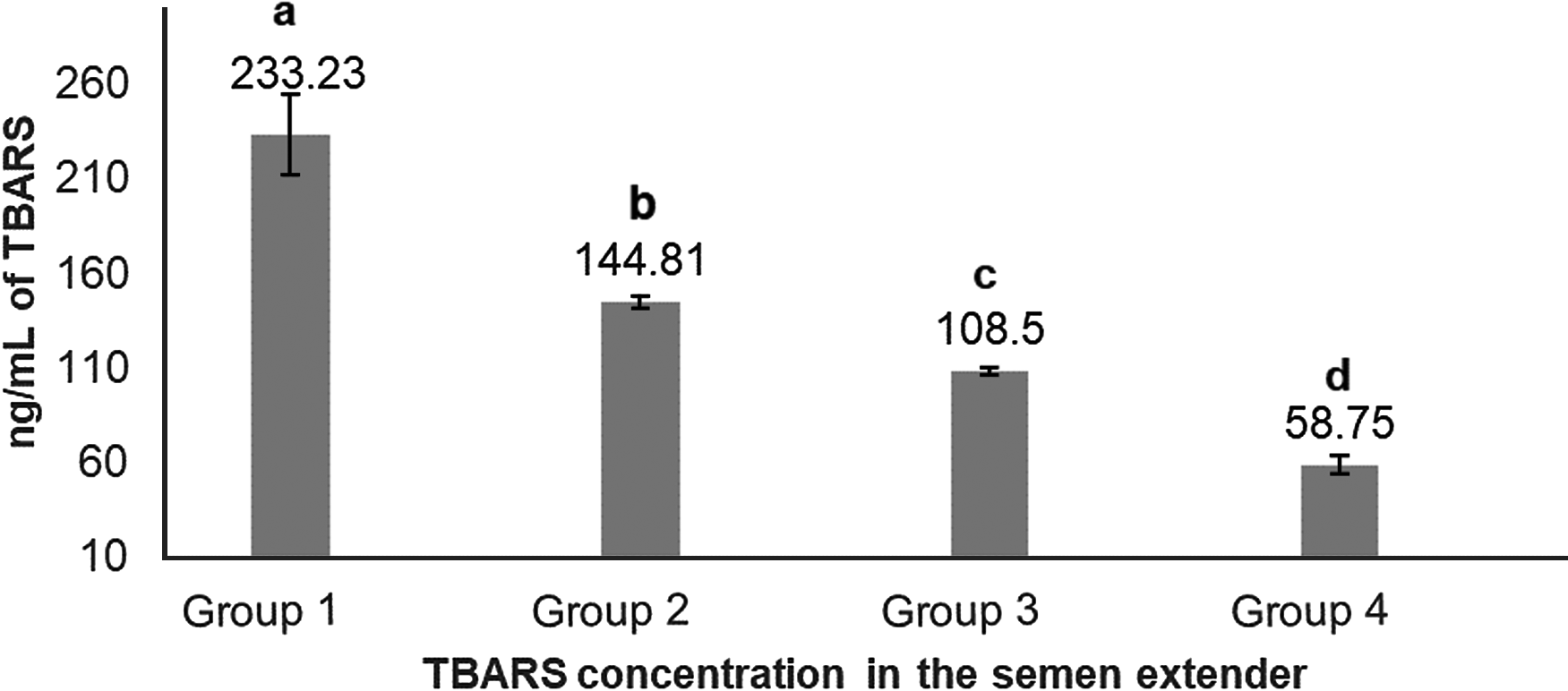
Ranking of samples according to lipid peroxidation index (TBARS) in semen extender generated four treatment groups, based on quartiles (233.23 ± 21.46; 144.81 ± 2.69; 108.50 ± 1.84; 58.75 ± 4.69 ng/ml for Groups 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively; Fig. 1).

Figure 1. Means (+SEM) TBARS concentration (ng/ml) in extender from Percoll® supernatant, ranked from highest to lowest concentrations and allocated into four lipid peroxidation groups. a–dGroups without a common superscript differed (P < 0.05).
The aim of this study was to evaluate the native lipid peroxidation of commercial semen straws, without any induction, to better represent commercial IVF laboratory conditions. The determination of native lipid peroxidation index of each straw was possible only after thawing, precluding a prospective grouping. Therefore we used retrospective grouping in this study. Retrospective grouping of samples based on lipid peroxidation index has previously been used successfully to evaluate the effects of oxidative stress on sperm quality and fertility (Simões et al., Reference Simões, Feitosa, Siqueira, Nichi, Paula-Lopes, Marques, Peres, Barnabe, Visintin and Assumpção2013; Hamilton et al., Reference Hamilton, de Castro, Delgado Jde, de Assis, Siqueira, Mendes, Goissis, Muiño-Blanco, Cebrián-Pérez, Nichi, Visintin and D'Ávila Assumpção2016). However, the retrospective division of groups had some limitations, such as not controlling the distribution of samples, bulls and centres among groups. We also performed correlation analysis as a post-test to analyze the behaviour of these variables in datasets independently of group division.
Sperm evaluations
Plasma membrane integrity and mitochondrial membrane potential
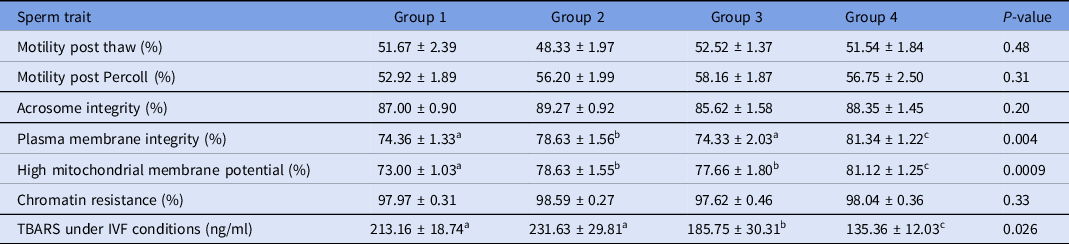
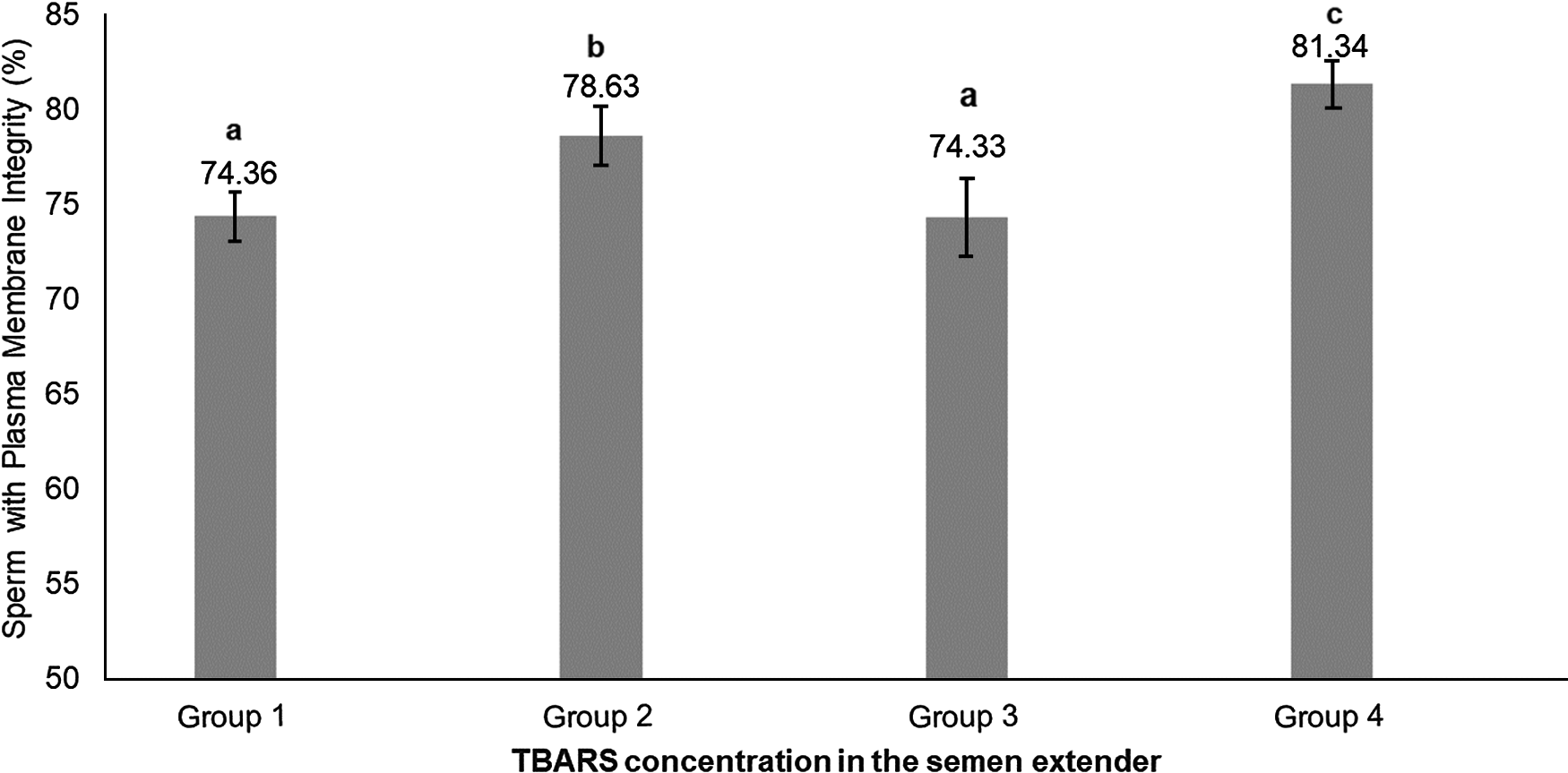
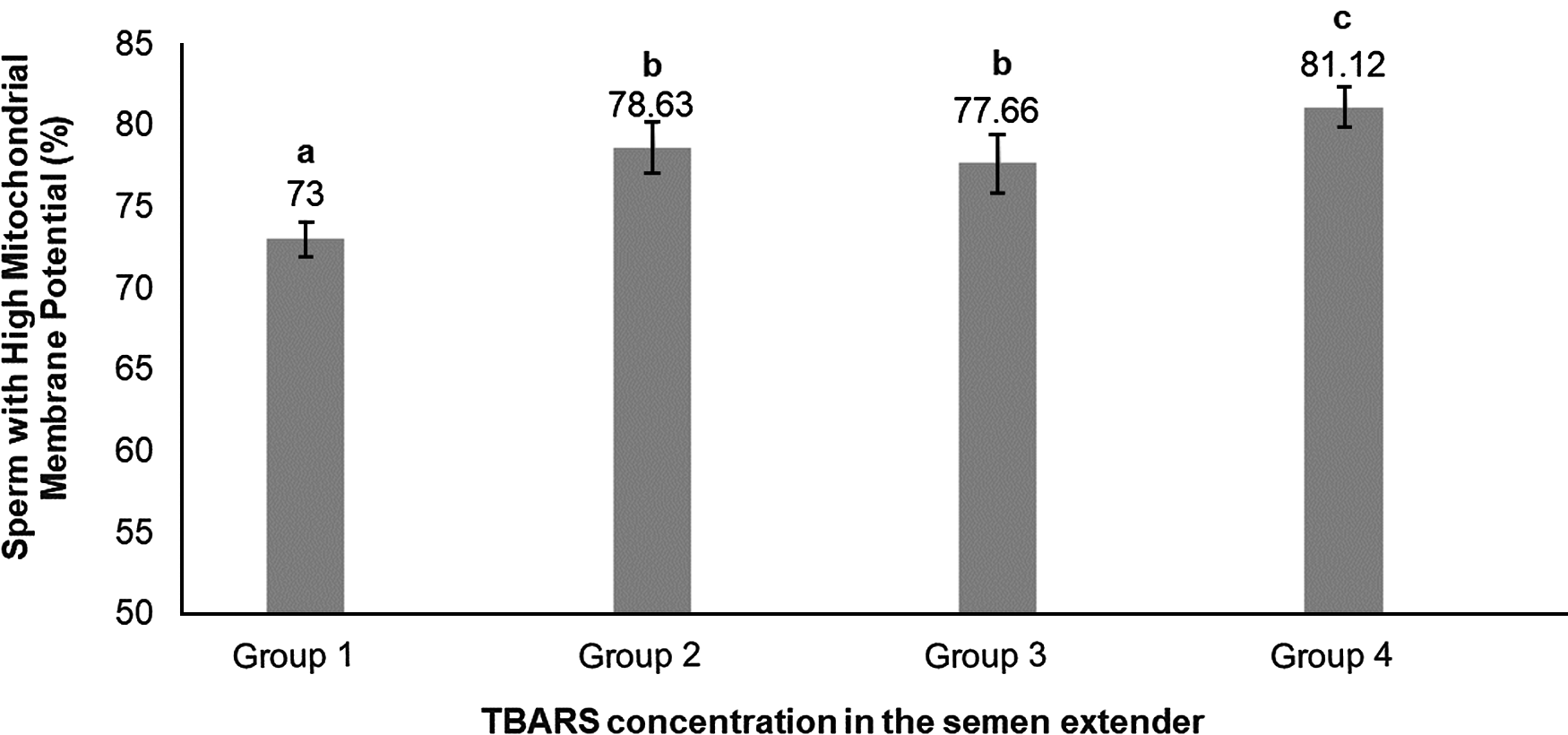
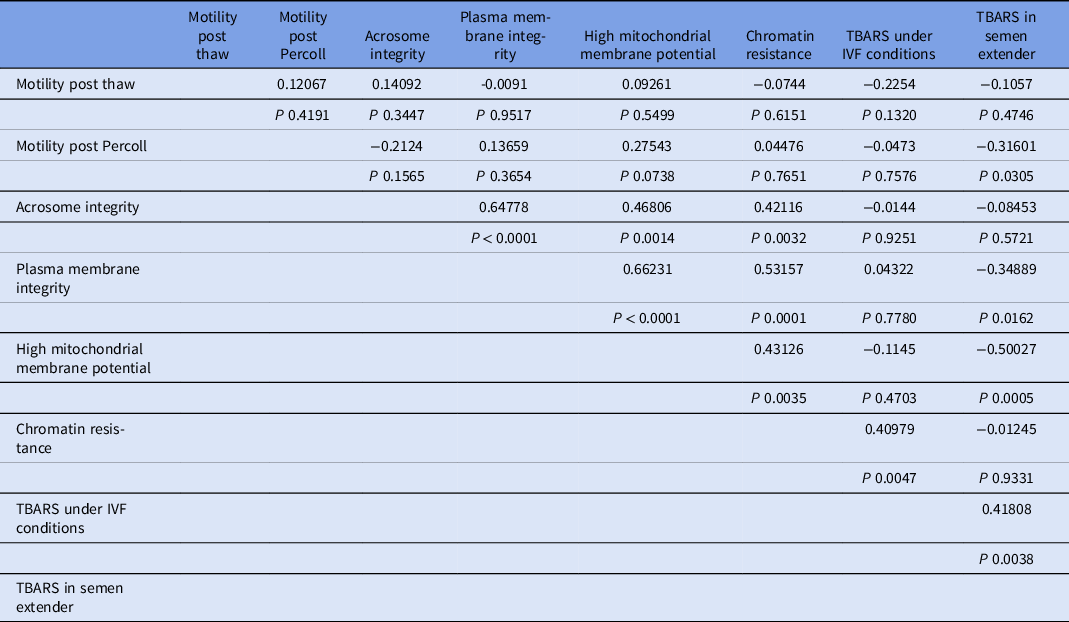
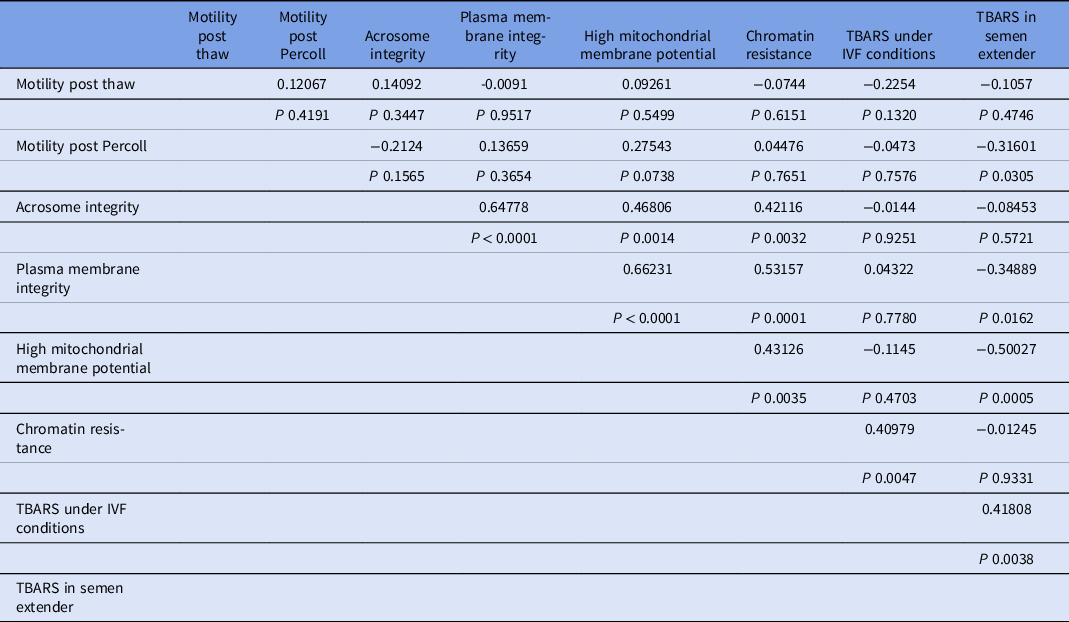
Percoll selection provides a highly motile sperm population with resistant chromatin and intact acrosomes and plasma membranes (Tanghe et al., Reference Tanghe, Van Soom, Sterckx, Maes and De Kruif2002; Suzuki et al., Reference Suzuki, Geshi, Yamauchi and Nagai2003; Samardzija et al., Reference Samardzija, Karadjole, Matkovic, Cergolj, Getz, Dobranic, Tomaskovic, Petric, Surina, Grizelj and Karadjole2006; Machado et al., Reference Machado, Carvalho, Filho, Caixeta, Franco, Rumpf and Dode2009), making it a useful tool for IVF. In our study, Percoll selection did not select solely the population with an intact plasma membrane. Group 1 (highest level of lipid peroxidation in semen extender after Percoll) had a lower plasma membrane integrity sperm population and lowest percentage of sperm with high mitochondrial membrane potential (Table 1 and Figs 2 and 3) when compared with the other groups based on the content of lipid peroxidation in the semen extender. Additionally, Group 4 (lowest lipid peroxidation content in extender) had a higher percentage of sperm with intact plasma membranes and a higher percentage of sperm with high mitochondrial membrane potential. Furthermore, there was a negative linear correlation in semen extender between percentage of sperm with plasma membrane integrity, high mitochondrial membrane potential and TBARS index (Table 2: Rho = −0.3; P = 0.01; Rho = −0.5; P = 0.0005, respectively).
Table 1. Means (± SEM) sperm traits separated into groups on the basis of TBARS levels in semen extender (ranked from Groups 1 to 4, highest to lowest lipid peroxidation levels, respectively)
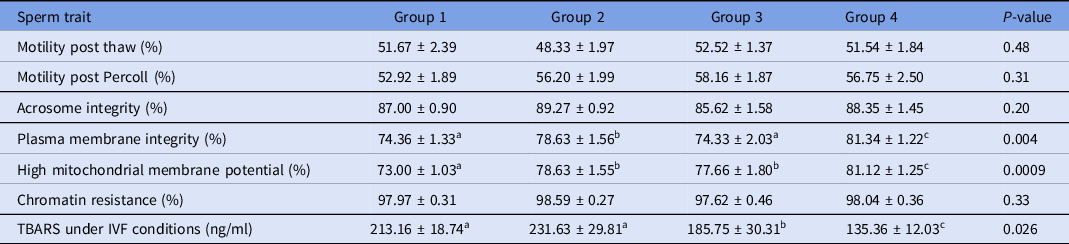
a-cWithin a row, means without a common superscript differed (P < 0.05).
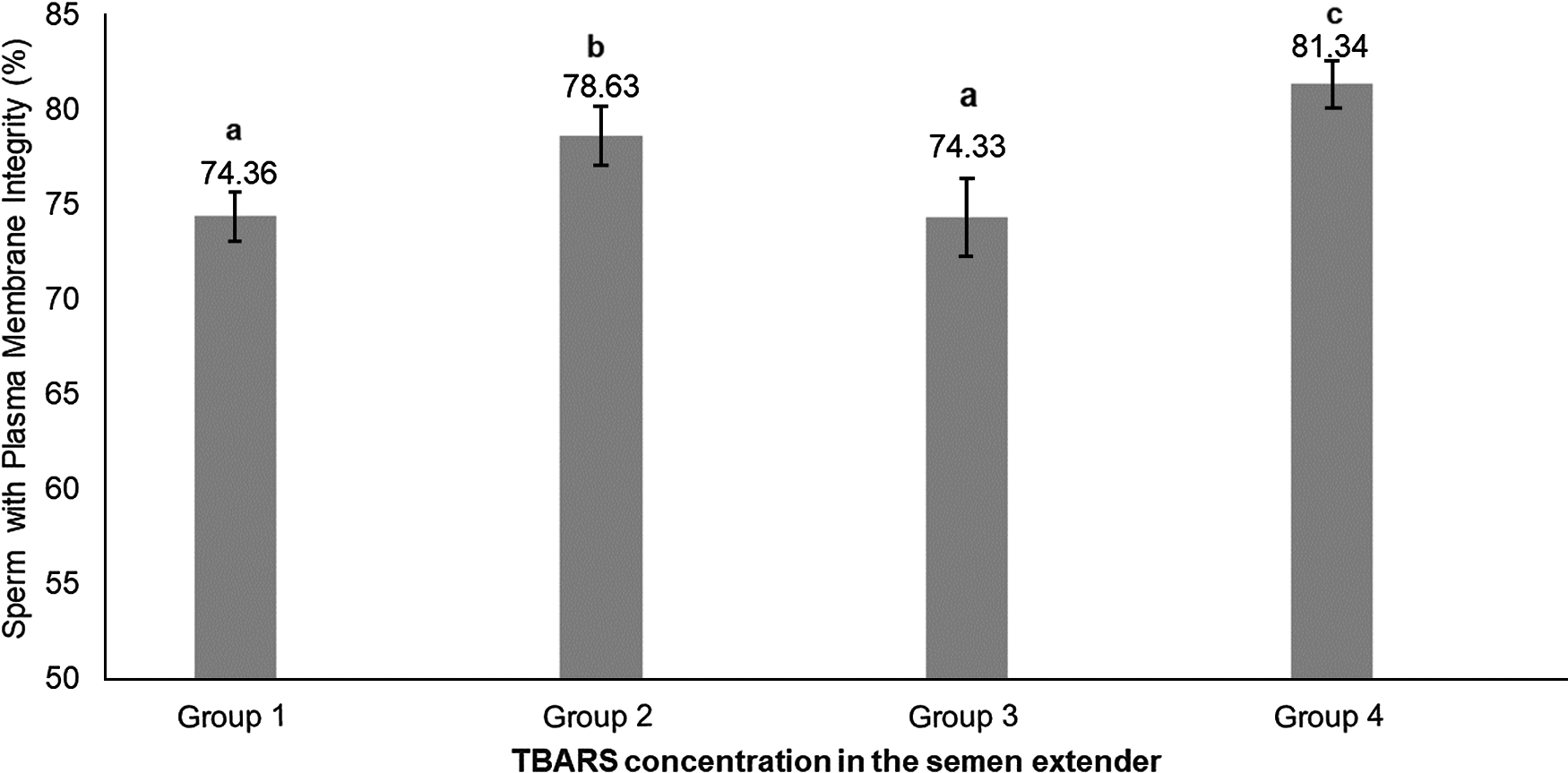
Figure 2. Means (+ SEM) percentage of sperm with plasma membrane integrity in four lipid peroxidation groups, ranked from highest to lowest (Group 1 to Group 4, respectively).a–cGroups without a common superscript differed (P = 0.004).
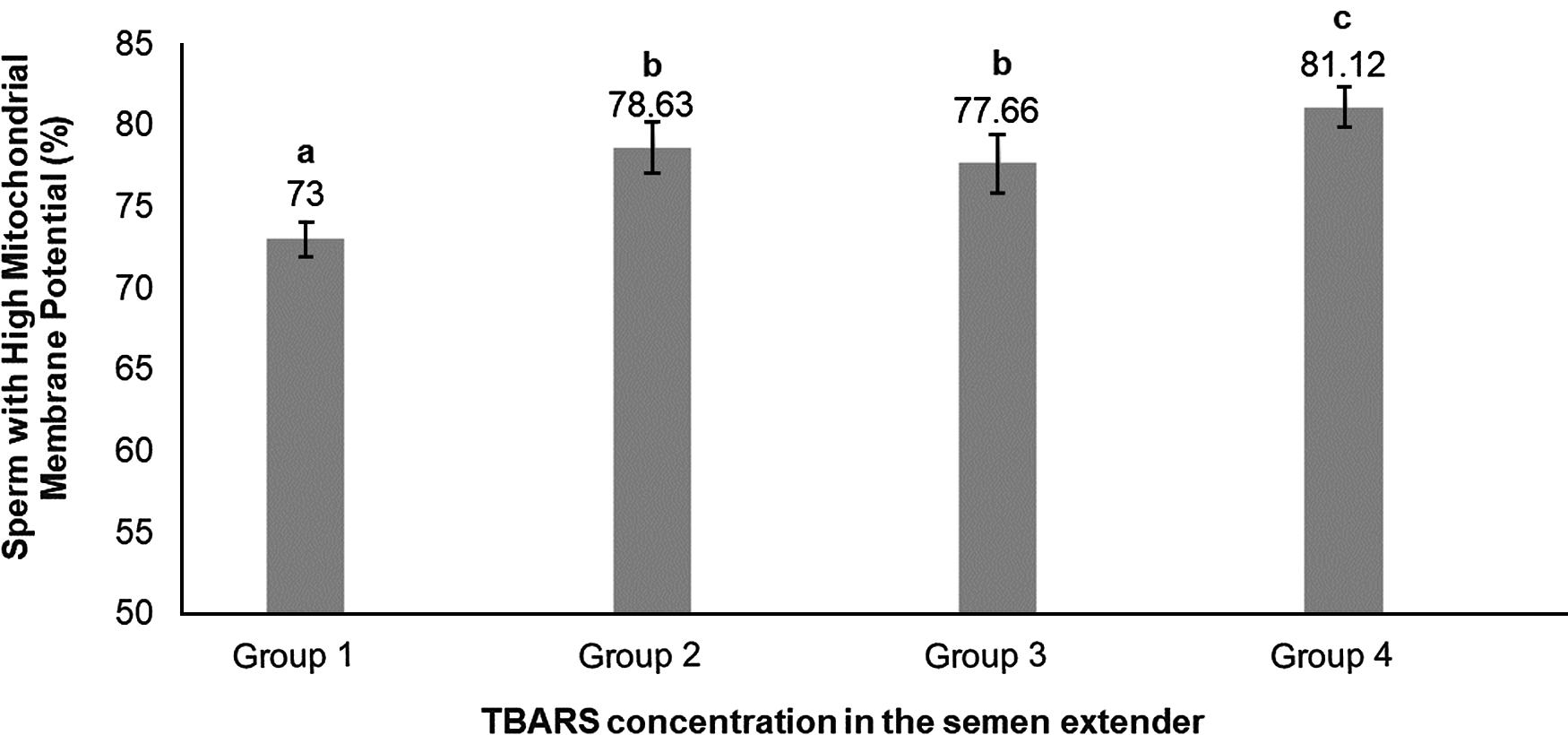
Figure 3. Means (+ SEM) percentage of sperm with high mitochondrial membrane potential in four lipid peroxidation groups, ranked from highest to lowest (Group 1 to Group 4, respectively). a–cGroups without a common superscript differed (P = 0.0009).
Table 2. Correlation coefficients (Rho) and probability (P) values between sperm traits and lipid peroxidation
Similarly, there was increased oxidation in plasma membranes and mitochondria in sperm exposed to pro-oxidative conditions (Silva et al., Reference Silva, Gadella, Colenbrander and Roelen2007). It is well known that sperm are very susceptible to oxidative stress, as a result of their relative lack of cytoplasm that limits enzymatic antioxidant protection (Aitken et al., Reference Aitken, Gordon, Harkiss, Twigg, Milne, Jennings and Irvine1998; Chatterjee and Gagnon Reference Chatterjee and Gagnon2001). This situation would allow free radicals to attack lipids in the sperm membrane and mitochondria (Aitken et al., Reference Aitken, Jones and Robertson2012). Disruption to the electron transport chain could lead to a decrease in proton pumping with consequent impairment to membrane potential (Ricci et al., Reference Ricci, Muñoz-Pinedo, Fitzgerald, Bailly-Maitre, Perkins, Yadava, Scheffler, Ellisman and Green2004).
Despite some studies not reporting changes to the sperm plasma membrane (Silva et al., Reference Silva, Gadella, Colenbrander and Roelen2007), and mitochondrial membrane potential (de Castro et al., Reference de Castro, de Assis, Siqueira, Hamilton, Mendes, Losano, Nichi, Visintin and Assumpção2016), or DNA (Silva et al., Reference Silva, Gadella, Colenbrander and Roelen2007) as a consequence of induced oxidative stress, all these studies reported decreased fertility as a result of lipid peroxidation or oxidative stress. Therefore, lipid peroxidation could decrease sperm fertility, even without some detectable changes in these sperm traits.
In our study, Percoll did not completely remove sperm with oxidative damage. Corroborating our results, although Percoll selected sperm with greater motility and viability, this selection did not increase fertility rates (Suzuki et al., Reference Suzuki, Geshi, Yamauchi and Nagai2003; Machado et al., Reference Machado, Carvalho, Filho, Caixeta, Franco, Rumpf and Dode2009). Also, the level of lipid peroxidation within the sperm plasma membrane negatively influenced blastocyst rates (Silva et al., Reference Silva, Gadella, Colenbrander and Roelen2007). Taken together, these findings could explain why Percoll selection described in previously studies failed to improve fertility.
Another consideration is that all straws used in this study were extended in egg yolk-based extender, this type of extender remains the one most often used in Brazil (Leite et al., Reference Leite, do Vale Filho, de Arruda, de Andrade, Emerick, Zaffalon, Martins and de Andrade2010), and it is an enriched source of aromatic amino acids, substrates for production of H2O2 by membrane-bound aromatic amino acid oxidase (AAAO) released from dead sperm (Vishwanath and Shannon, Reference Vishwanath and Shannon2000). In this context, in Group 1, high levels of cells with damaged plasma membranes could be considered a cause of higher levels of lipid peroxidation. Therefore, we inferred that changes recorded in this study were likely to be a consequence of oxidative stress rather than a cause.
Lipid peroxidation under IVF conditions
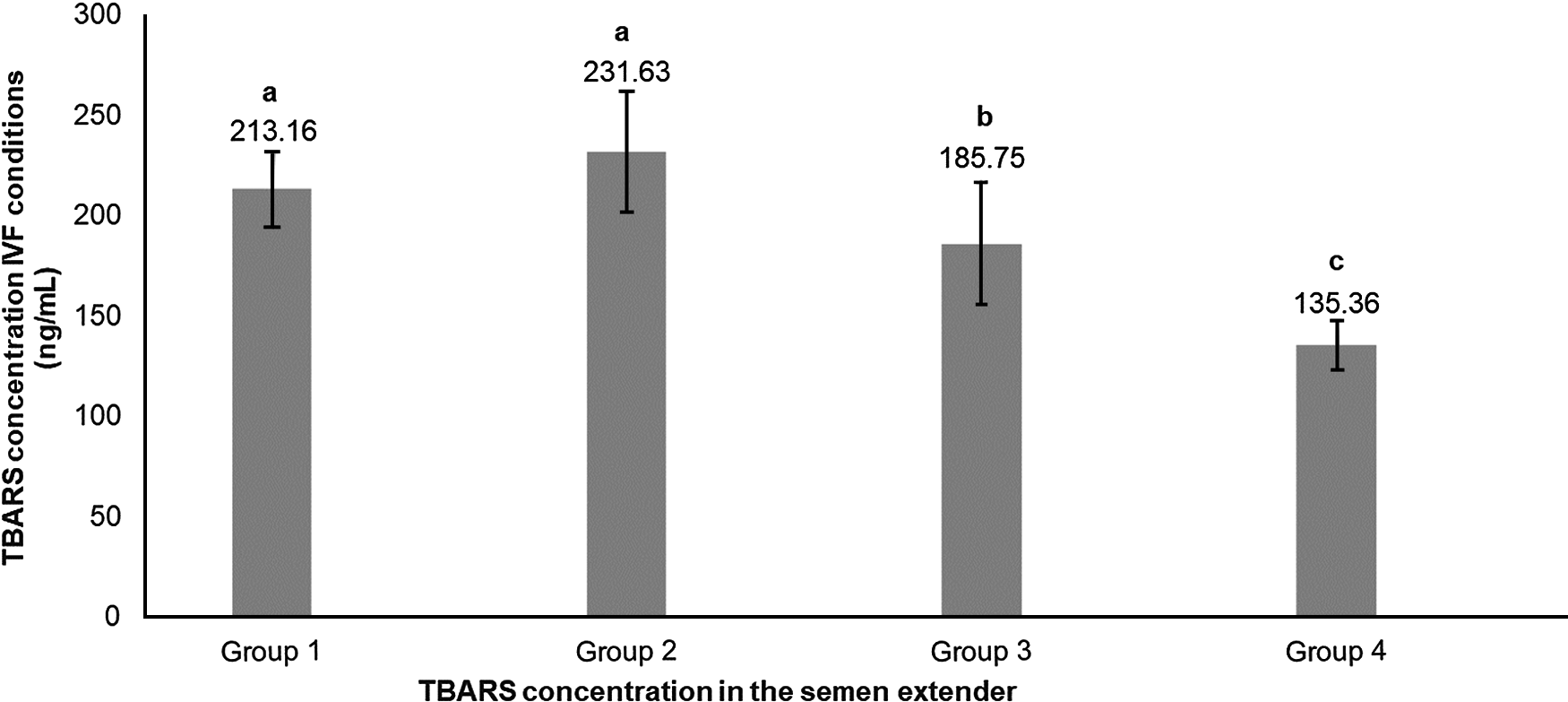
For the TBARS index under IVF conditions, Groups 1 and 2 (higher index of TBARS in semen extender) also had higher values for lipid peroxidation under IVF conditions (Table 1 and Fig. 4). Moreover, there was also a significant positive linear correlation in semen extender between TBARS under IVF conditions and TBARS index (Rho = 0.4, P = 0.0038, Table 2).
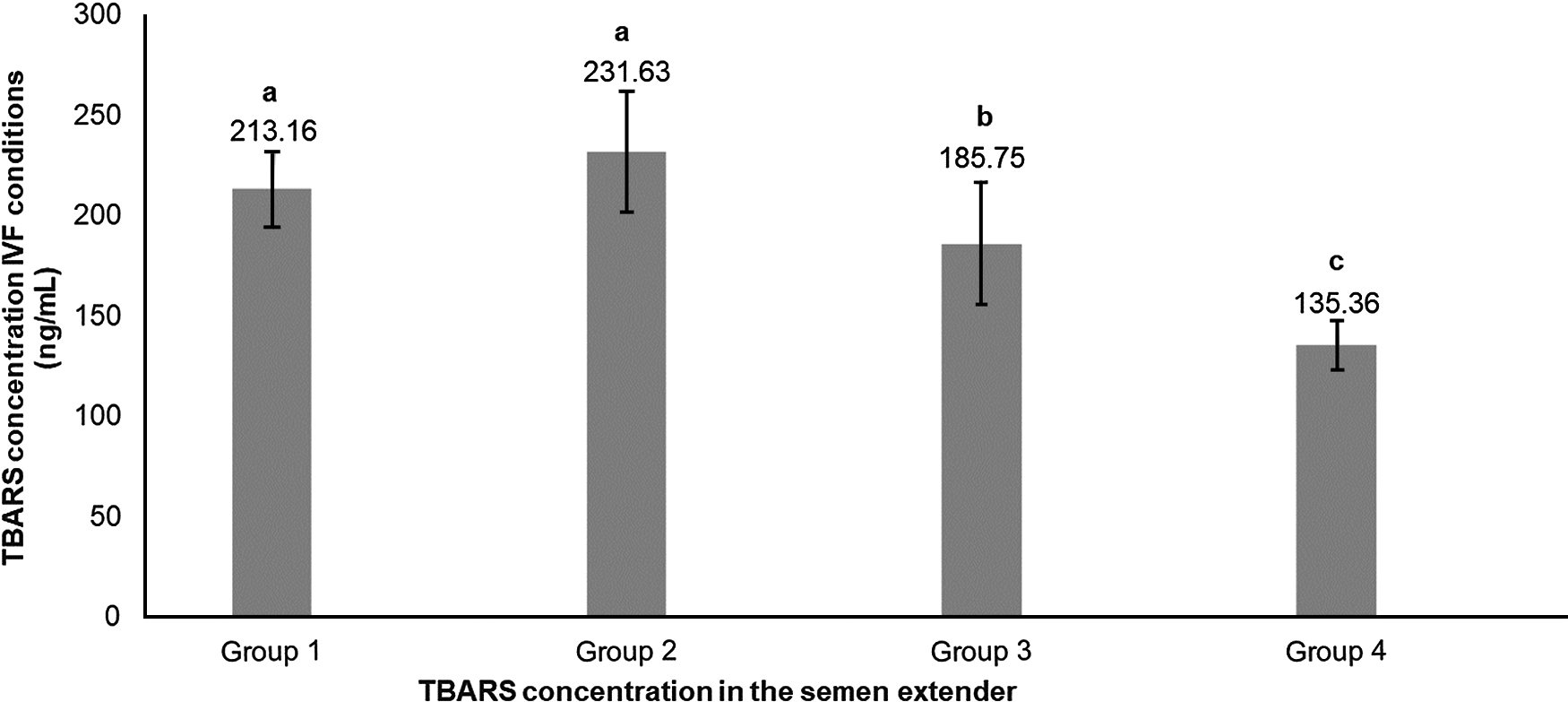
Figure 4. Means (+SEM) lipid peroxidation produced under in vitro fertilization conditions in four lipid peroxidation groups, ranked from highest to lowest (Group 1 to Group 4, respectively). a–cGroups without a common superscript differed (P = 0.0026).
Similar to our study, sperm previously exposed to oxidative conditions had an increased capacity for generating ROS after induction of capacitation (Aitken et al., Reference Aitken, Clarkson and Fishel1989). Following this reasoning, the level of oxidative stress present in the cryopreserved samples would influence ROS production and consequently lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress of sperm after Percoll selection for IVF. Current results have highlighted the importance of semen handling during cryopreservation with implications pertaining to the oxidative potential of samples during IVF, despite the higher quality of cells recovered after Percoll selection. Several studies have been undertaken to demonstrate that colloid centrifugation improves the quality and fertilizing ability of cryopreserved sperm, as well as reduce the ROS amount (Martinez-Alborcia et al., Reference Martinez-Alborcia, Morrell, Gil, Barranco, Maside, Alkmin, Parrilla, Martinez and Roca2013; Morrell et al., Reference Morrell, Lagerqvist, Humblot and Johannisson2017; Nongbua et al., Reference Nongbua, Johannisson, Edman and Morrell2017). Our results do not contradict these earlier studies, as we did not compare lipid peroxidation in the sperm samples before and after colloid centrifugation. This centrifugation is effective for removing extender, and we can assume that it is effective in removing ROS contained in the extender. However, the higher oxidative potential was observed in sperm selected from straws with a higher lipid peroxidation index, and suggested that oxidative stress markers, such as intracellular ROS and those linked to the plasma membrane, remain on the selected sperm samples, affecting later IVP conditions and rates.
Motility, acrosome membrane integrity and chromatin resistance
Sperm motility, acrosome integrity and chromatin resistance were not significantly different between groups of lipid peroxidation on the basis of TBARS levels in the semen extender obtained from supernatants after Percoll centrifugation (Table 1).
Although we did not observe any significant difference among groups regarding motility, we observed a significantly negative correlation between lipid peroxidation index and motility after Percoll selection. Lipid peroxidation levels correlated with loss of motility have been observed previously (Alvarez et al., Reference Alvarez, Storey and Touchstone1978). Probably, we were not able to detect significant differences among groups because a subjective method is less accurate than objectives methods, making the comparison less sensitive to differences. Unfortunately, in this study, it was not feasible to use a more objective motility assessment.
There was no significant effect of lipid peroxidation index of extender on acrosome integrity or chromatin resistance. It is possible that these two sperm traits are less susceptible to oxidative damage compared with plasma membrane integrity and mitochondrial membrane potential. Consistent with these results, oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide strongly impaired sperm motility but, even at higher doses, this resulted in only 2% of sperm with damaged chromatin, indicating that bull sperm chromatin is relatively resistant to damage and that changes in this sperm trait were relatively rare in this species (Simões et al., Reference Simões, Feitosa, Siqueira, Nichi, Paula-Lopes, Marques, Peres, Barnabe, Visintin and Assumpção2013; de Castro et al., Reference de Castro, de Assis, Siqueira, Hamilton, Mendes, Losano, Nichi, Visintin and Assumpção2016).
Chromatin resistance was positively correlated with lipid peroxidation under IVF conditions. Relationship analysis also detected positive correlations among acrosome integrity, membrane integrity, mitochondrial potential, and chromatin resistance (Table 2).
This study evaluated and found that the oxidative index of the extender of commercial semen straws was associated with the sperm trait profile after sperm selection and oxidative potential under IVF conditions. However, this study focused on evaluating this effect in sperm cells. Further studies are necessary to evaluate the effect of lipid peroxidation in bull semen straws and the oxidative potential of these samples on IVP rates.
Conclusion
Oxidative status of cryopreserved semen is associated with plasma membrane integrity and mitochondrial membrane potential of sperm selected for IVF and could also be associated with their oxidative potential under IVF conditions. Percoll selection did not completely remove sperm with oxidative markers.
Ethical approval
Ethics Committee approval for animal use was granted by the School of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science of University of São Paulo (protocol CEUA 7246170117).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank John Kastelic for paper reviewing and English corrections. Also, the Department of Animal Reproduction of University of São Paulo for the scientific support.
Financial support
The authors thank Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq process number 152574/2016-6), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) for financial support.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.