Introduction
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are biochemical changes of amino acid residues that alter the charge state, hydrophobicity, conformation or stability of the proteins. These modifications act as molecular switches regulating the interaction of proteins with nucleic acids, cofactors, lipids and other proteins (Venne et al., Reference Venne, Kollipara and Zahedi2014). PTMs can be ‘read’ by specific effectors to regulate several cellular processes in response to extracellular and intracellular stimuli. To date, >450 unique protein modifications have been identified, including phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, SUMOylation and methylation, among others (Venne et al., Reference Venne, Kollipara and Zahedi2014).
Protein methylation occurs at different amino acids and it has been estimated that from 0.6 to 1.6% of the eukaryote genomes encode methyltransferases, the enzymes that perform this PTM (Katz et al., Reference Katz, Dlakić and Clarke2003). Although initially the studies had been largely focused on lysine and arginine methylation of histones, which impact the transcription regulation (Jambhekar et al., Reference Jambhekar, Dhall and Shi2019), nowadays it is known that methylation on non-histone proteins regulates other molecular mechanisms, including RNA stability, splicing and translation (Lanouette et al., Reference Lanouette, Mongeon, Figeys and Couture2014; Blanc and Richard, Reference Blanc and Richard2017; Al-Hamashi et al., Reference Al-Hamashi, Diaz and Huang2020).
Arginine contains in its side chain an aliphatic sequence of three carbon atoms, ending with a guanidino group, which is protonated and positively charged at physiological pH, with five potential hydrogen-bonds donors to interact with other molecules (Bedford and Clarke, Reference Bedford and Clarke2009). The addition of one or two methyl groups to arginine creates a bulkier and more hydrophobic residue that does not alter the global cationic charge of the amino acid, but disperses it towards the methyl groups (Bedford and Richard, Reference Bedford and Richard2005; Bedford and Clarke, Reference Bedford and Clarke2009). Arginine methylation increases the affinity for specific proteins such as those containing aromatic cages, including the Tudor domain (Tripsianes et al., Reference Tripsianes, Madl, Machyna, Fessas, Englbrecht, Fischer, Neugebauer and Sattler2011), which interpret specific methylation marks to regulate several molecular events such as epigenetics, mRNA splicing, mRNA translation, DNA damage and stress response, among others (Blanc and Richard, Reference Blanc and Richard2017).
Infections with protozoan parasites are responsible for high morbidity and mortality in humans worldwide. The diseases produced by these microorganisms depend on the expression and activity of their virulence factors as well as the response of parasites to host immunity and the transition to different stages and hosts, events that require changes in gene expression and activation of specific signalling pathways that could be regulated by arginine methylation. Some advances have been made regarding the role of arginine methylation and the enzymes that perform this PTM, named as protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs), in the biology of certain protozoan parasites, mainly in Trypanosoma brucei; however, in others, such as Trypanosoma cruzi, many Leishmania and Plasmodium species as well as Trichomonas vaginalis, the arginine methylation and PRMTs have not yet been studied. Here, current knowledge on arginine methylation and PRMTs in protozoan parasites is reviewed.
Protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs)
The addition of methyl groups to the guanidino nitrogen atoms of arginine residues is catalysed by the PRMTs, which use S-adenosyl-L-Methionine (AdoMet or SAM) as the donor of the methyl groups (Blanc and Richard, Reference Blanc and Richard2017). According to their activity, there are three main types of PRMTs, type I catalyses monomethylarginine (MMA) and asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA); type II yields MMA and symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA); and type III produces MMA only (Fig. 1); additionally, yeasts have a type IV PRMT, which monomethylates the delta (δ) nitrogen atom of arginine (Bedford and Clarke, Reference Bedford and Clarke2009). Most PRMTs substrates contain glycine- and arginine-rich (GAR) sequences that include multiple arginines in RGG or RXR contexts (Najbauer et al., Reference Najbauer, Johnson, Young and Aswad1993; Gary and Clarke, Reference Gary and Clarke1998; Feng et al., Reference Feng, Maity, Whitelegge, Hadjikyriacou, Li, Zurita-Lopez, Al-Hadid, Clark, Bedford, Masson and Clarke2013).
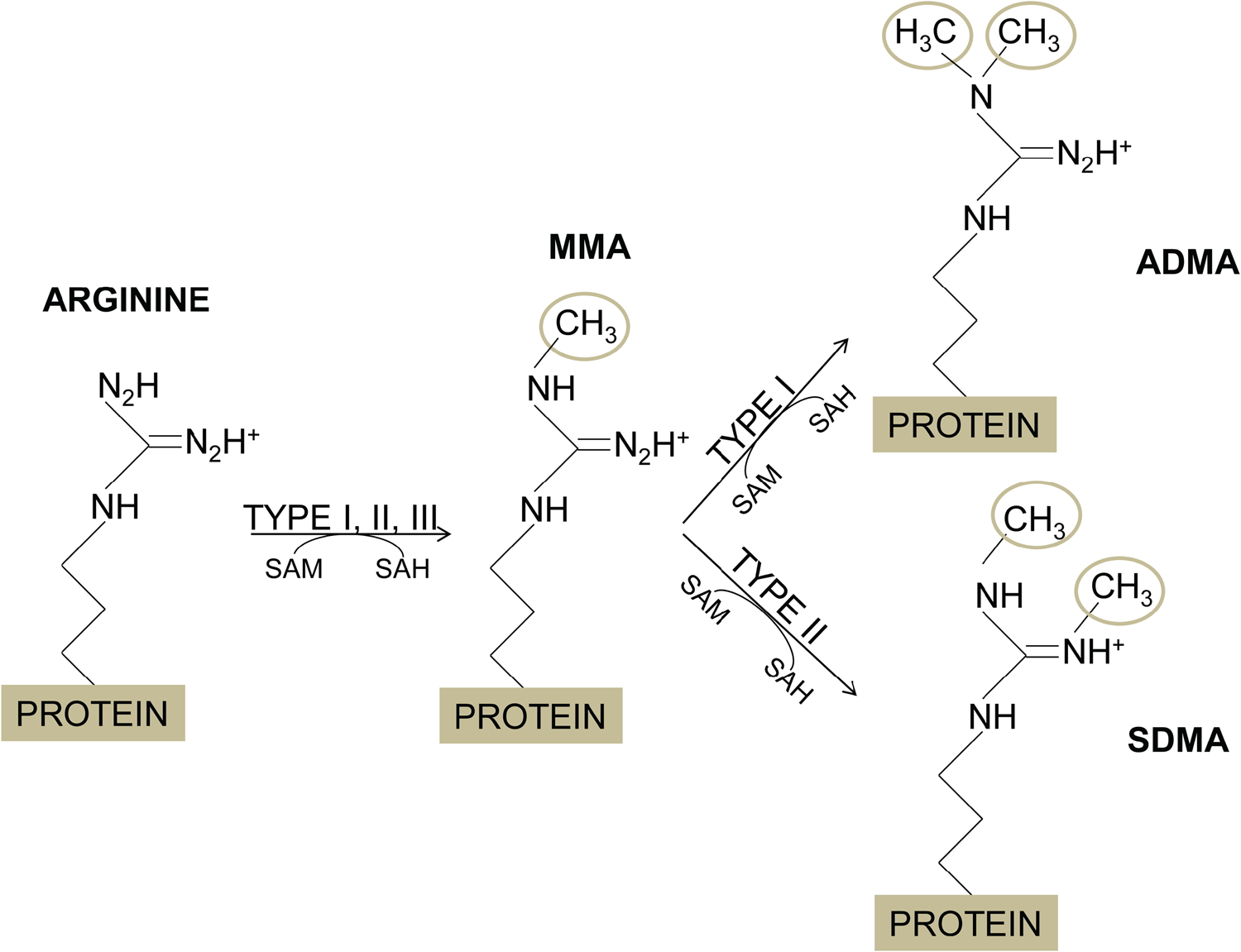
Fig. 1. Arginine methylation. The methylation of arginine residues is catalysed by the protein arginine methyltrnasferases (PRMTs), which transfer a methyl group from the S-adenosylmethionone (SAM or AdoMet), resulting in the arginine methylation and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). PRMTs of type I, II and III produce monomethylarginine (MMA). In addition, PRMTs of type I add other methyl groups to the same nitrogen atom to yield asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), while PRMTs of type II attach the second methyl group to the other N-terminal nitrogen of the arginine residue, forming symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA).
PRMTs contain a conserved core region of approximately 310 amino acids comprising the characteristic methyltransferase motif for the binding of the AdoMet cofactor, formed by a seven-strand twisted beta-sheet and the PRMT-specific ‘double E’ and ‘THW’ loops (Cheng et al., Reference Cheng, Collins and Zhang2005). In addition, different studies demonstrated that the dimerization of PRMTs facilitates their AdoMet-binding and their catalytic activity (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Zhou and Cheng2000; Zhang and Cheng, Reference Zhang and Cheng2003; Xu, Reference Xu2004; Li et al., Reference Li, Gong, Zhou, Liu, Cao, He, Chen and Zhou2015; Zhou et al., Reference Zhou, Xie, Hu, Hu, Patel, Zhang, Yu, Huang, Jiang, Liang, Zheng and Luo2015).
Nine PRMTs have been characterized in humans (PRMT1-9). PRMT1, 2, 3, 4 (also known as CARM1), 6 and 8 are type I, PRMT5 and 9 are type II, and PRMT7 is type III (Bedford and Clarke, Reference Bedford and Clarke2009). Some of these proteins contain specific domains, PRMT2 has an SH3 domain, PRMT3 a Zn-finger domain (Frankel and Clarke, Reference Frankel and Clarke2000) and PRMT8 is myristoylated at its N-terminus (Frankel et al., Reference Frankel, Yadav, Lee, Branscombe, Clarke and Bedford2002). It has been demonstrated that most of type I PRMTs are active as homodimers (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Zhou and Cheng2000; Zhang and Cheng, Reference Zhang and Cheng2003; Xu, Reference Xu2004; Li et al., Reference Li, Gong, Zhou, Liu, Cao, He, Chen and Zhou2015; Zhou et al., Reference Zhou, Xie, Hu, Hu, Patel, Zhang, Yu, Huang, Jiang, Liang, Zheng and Luo2015), while that PRMT5 forms a hetero-octameric complex (methylosome) with MEP50 (four subunits of each), in which MEP50 binds to the substrate and stimulates PRMT5 activity (Ho et al., Reference Ho, Wilczek, Bonanno, Xing, Seznec, Matsui, Carter, Onikubo, Kumar, Chan, Brenowitz, Cheng, Reimer, Almo and Shechter2013). PRMT1 is responsible for most of the total monomethylation and asymmetric dimethylation of arginine, whereas PRMT5 has the major type II activity (Bedford and Clarke, Reference Bedford and Clarke2009).
Most of these enzymes are ubiquitously expressed, with exception of PRMT8, which is localized only in the central nervous system (Lee et al., Reference Lee, Sayegh, Daniel, Clarke and Bedford2005). In general, PRMTs are found in the nucleus and cytoplasm, but PRMT3 is located principally in the cytoplasm, PRMT6 is concentrated mainly in the nucleus and PRMT8 is linked to the plasma membrane (Frankel and Clarke, Reference Frankel and Clarke2000; Frankel et al., Reference Frankel, Yadav, Lee, Branscombe, Clarke and Bedford2002; Lee et al., Reference Lee, Sayegh, Daniel, Clarke and Bedford2005). Arginine methylation on histones is involved in the co-activation or co-repression of gene transcription and the effects on transcription of specific residues modified by different PRMTs have been determined (reviewed by Rakow et al., Reference Rakow, Pullamsetti, Bauer and Bouchard2020). PRMT1 and PRMT4/CARM1 are the main co-activators (Bedford and Clarke, Reference Bedford and Clarke2009), PRMT2 and PRMT7 function as co-repressors (Ganesh et al., Reference Ganesh, Yoshimoto, Moorthy, Akahata, Boehm, Nabel and Nabel2006; Karkhanis et al., Reference Karkhanis, Wang, Tae, Hu, Imbalzano and Sif2012), whereas PRMT5 and PRMT6 have been reported to have both functions (Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Rank, Tan, Li, Moritz, Simpson, Cerruti, Curtis, Patel, Allis, Cunningham and Jane2009; Migliori et al., Reference Migliori, Müller, Phalke, Low, Bezzi, Mok, Sahu, Gunaratne, Capasso, Bassi, Cecatiello, De Marco, Blackstock, Kuznetsov, Amati, Mapelli and Guccione2012; Casadio et al., Reference Casadio, Lu, Pollock, LeRoy, Garcia, Muir, Roeder and Allis2013; Cheng et al., Reference Cheng, Gao, Di Lorenzo, Jayne, Hottiger, Richard and Bedford2020). In addition, PRMTs also methylate several non-histone proteins such as transcription factors and protein involved in RNA metabolism, DNA damage repair and many signalling pathways (reviewed by Al-Hamashi et al., Reference Al-Hamashi, Diaz and Huang2020).
PRMTs have also been identified in non-mammalian animals, filamentous fungi, yeasts, plants and protozoan parasites (McBride et al., Reference McBride, Zurita-Lopez, Regis, Blum, Conboy, Elf and Clarke2007; Ahmad et al., Reference Ahmad, Dong and Cao2011; Fisk and Read, Reference Fisk and Read2011; Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Zhang, Ni, Wu, Yan and Li2016; Hadjikyriacou and Clarke, Reference Hadjikyriacou and Clarke2017; Plett et al., Reference Plett, Raposo, Bullivant, Anderson, Piller and Plett2017; Wang et al., Reference Wang, Wang, Lin, Tsai, Chang, Lee, Lin and Li2017; Bauer et al., Reference Bauer, Lechner, Pidroni, Petrone, Merschak, Lindner, Kremser, Graessle, Golderer, Allipour and Brosch2019). Enzymes similar to mammalian PRMT1, 3 and 5 are present in different eukaryotic organisms, whereas other PRMTs, such as PRMT2 and 8, are less conserved and it has been suggested that they could have evolved in the multicellular organisms as a requirement for tissue-specific functions (Bachand, Reference Bachand2007).
Arginine methylation and PRMTs in protozoan parasites
Protozoan parasites, except Giardia intestinalis, have several PRMTs that were named according to their similarity with the human enzymes [reviewed by Fisk and Read (Reference Fisk and Read2011)], although they have structural differences with their mammalian homologues (see below). All protozoan parasites have two or more PRMTs of type I and at least one of type II; interestingly, trypanosomatids also contain a type III enzyme (Fisk and Read, Reference Fisk and Read2011). They also possess the canonical histones, suggesting that the arginine methylation observed in histones of other eukaryotes, as well as their effects in gene expression, are preserved in these microorganisms. In addition, arginine methylation in non-histone proteins may also be important in the biology of protozoan parasites. However, most of the non-histone protein targets in these pathogens remain to be identified.
Phylogenetic analysis shows that there is no strong relationship of PRMT3, PRMT4/CARM1 and PRMT6 of the parasites with their respective human enzymes (Fig. 2). Furthermore, this analysis clearly separates the PRMTs of parasites into four main clades, one of them grouped PRMTs of type I, most of them with a higher relationship with the human PRMTs 1, 3 and 8; the other clade comprises PRMTs of type II similar to human PRMT5; the third clade is present only in trypanosomatids and corresponds to type III (PRMT7); and the last clade includes the PRMT3 of T. brucei and the atypical PRMT of E. histolytica (Fig. 2).

Fig. 2. Phylogenetic relationship of protozoan parasites PRMTs. The predicted amino acid sequences of PRMTs from human, protozoan parasites and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (types I and IV) were aligned by MUSCLE. Then, data were submitted to phylogenetic analysis by UPGMA using MEGA version 5.05. Accession numbers for the protein sequences of T. vaginalis are indicated. The other PRMTs used for this analysis were: Human: HsPRMT1 (NP_938074.2), Hs PRMT2 (NP_001526.2), HsPRMT3 (NP_005779.1), HsPRMT4/CARM1 (NP_954592.1), HsPRMT5 (NP_006100.2); HsPRMT6 (NP_060607.2), HsPRMT7 (NP_061896.1), HsPRMT8 (NP_062828.3). HsPRMT9 (NP_612373.2); S. cereviciae: ScRMT2 (NP_010753.1), ScHMT1 (NP_009590.1); T. brucei: TbPRMT1 (Tb927.1.4690), TbPRMT3 (Tb927.10.3560), TbPRMT5 (Tb927.10.640), TbPRMT6 (Tb927.5.3960), TbPRMT7 (Tb927.7.5490); P. falciparum: PfPRMT1 (PF14_0242), PfPRMT4/CARM1 (PF14_0242), PfPRMT5 (PF13_0323), T. gondii: TgPRMT1 (GT1_030400), Tg PRMT3 (GT1_001320), TgPRMT4/CARM1 (GT1_074560), TgPRMT5 (GT1_126490); E. histolytica: EhPRMT1a (EHI_105780), EhPRMT1b (EHI_152460), EhPRMT1c (EHI_202470), EhPRMTA (EHI_159780), EhPRMT5 (EHI_158560). The numbers at the nodes of the branches indicate the confidence percentages of the tree topology from the bootstrap analysis of 1000 replicates. Proteins are grouped into type I, II, III, IV and atypical.
Arginine methylation and PRMTs in trypanosomatids
The causative agents of African trypanosomiasis (T. brucei), Leishmaniasis (Leishmania spp.) and Chagas disease (T. cruzi) belong to the kinetoplastids group (trypanosomatids). The main mechanisms implicated in the regulation of gene expression in these parasites are the post-transcriptional processes, including RNA turnover, translation and editing, involving multiple RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), which are common targets of arginine methylation (Campagnaro et al., Reference Campagnaro, Nay, Plevin, Cruz and Walrad2021). These microorganisms contain five PRMTs, which are homologues to the mammalian PRMT1, 3, 5, 6 and 7 (Fisk and Read, Reference Fisk and Read2011); the studies related to these enzymes have been performed on the five enzymes of T. brucei and on the PRMT7 of Leishmania major, whereas there are no reports about the role of PRMTs in other Leishmania species or in T. cruzi.
Although the number of annual cases of African trypanosomiasis has been progressively decreasing, it has been estimated that approximately 1.8 million people live in high or very high-risk areas and 11.3 million people in moderate-risk zones (Simarro et al., Reference Simarro, Cecchi, Franco, Paone, Diarra, Priotto, Mattioli and Jannin2015). T. brucei life cycle consists of bloodstream trypomastigotes into the vertebrate host and procyclic trypomastigotes, epimastigotes and metacyclic trypomastigotes into the tsetse fly (Glossina spp.).
A recent global proteomic analysis identified 1332 methylarginines in 676 proteins (approximately 10% of the proteome) (Lott et al., Reference Lott, Li, Fisk, Wang, Aletta, Qu and Read2013), demonstrating that arginine methylation is a common PTM in this parasite. In addition, both type I and type II PRMT activities have been detected in cell extracts of T. brucei (Pelletier et al., Reference Pelletier, Xu, Wang, Zahariev, Pongor, Aletta and Read2002). TbPRMT1 catalyses the majority of the ADMA modification in vivo (Pelletier et al., Reference Pelletier, Pasternack and Read2005). It is expressed in all stages of the parasite life cycle and synthetic peptides containing GAR sequences are methylated by the recombinant protein (Pelletier et al., Reference Pelletier, Pasternack and Read2005). The TbPRMT1 knockdown does not produce defects in the in vitro growth of the procyclic or bloodstream forms, but its knockout downregulates enzymes involved in glycolysis and upregulates enzymes participating in proline degradation, reduces the cytoplasmic mRNA granules in the insect stage under starvation and decreases the virulence of T. brucei in mice (Pelletier et al., Reference Pelletier, Pasternack and Read2005; Kafková et al., Reference Kafková, Debler, Fisk, Jain, Clarke and Read2017; Kafková et al., Reference Kafková, Tu, Pazzo, Smith, Debler, Paul, Qu and Read2018). Interestingly, TbPRMT1 directly binds to RNA and to a lipin homologue that possesses activity of phosphatidic acid phosphatase (Pelletier et al., Reference Pelletier, Frainier, Munini, Wiemer, Karpie and Sattora2013; Kafková et al., Reference Kafková, Tu, Pazzo, Smith, Debler, Paul, Qu and Read2018). All these results indicate that TbPRMT1 participates in carbohydrates metabolism, RNA biology, phospholipid biosynthesis and virulence (Table 1).
Table 1. Functions of characterized PRMTs in protozoan parasites

Based on the homology to human PRMT3, TbPRMT3 was predicted to be a type I enzyme (Fisk and Read, Reference Fisk and Read2011); however, most of the conserved amino acids involved in PRMT activity are absent in TbPRMT3, where both glutamate residues in the double E loop are changed to aspartate and tryptophan is the only conserved residue in the THW loop; concordantly, its recombinant protein has no enzymatic activity (Kafková et al., Reference Kafková, Debler, Fisk, Jain, Clarke and Read2017). In fact, TbPRMT3 functions as a proenzyme that stabilizes the TbPRMT1 enzyme, producing an active heterotetramer formed by two enzyme-proenzyme pairs (TbPRMT1/TbPRMT3, also named TbPRMT1ENZ/TbPRMT1PRO) (Kafková et al., Reference Kafková, Debler, Fisk, Jain, Clarke and Read2017). Our phylogenetic analysis suggested that TbPRMT3 is more related to the atypical enzyme of Entamoeba histolytica EhPRMTA than to other PRMT members (Fig. 2).
TbPRMT5 is constitutively expressed in procyclic and bloodstream forms, it is found mainly in the cytoplasm forming high-molecular-weight complexes that do not include to MEP50, but that contain a DEAD box protein and two kinetoplast-specific proteins involved in RNA editing (Pasternack et al., Reference Pasternack, Sayegh, Clarke and Read2007). Interestingly, genes encoding MEP50 homologue have not been found in the genome database of T. brucei and recombinant TbPRMT5 displays enzymatic activity on broad substrates that includes the RNA-binding protein 16 (Pasternack et al., Reference Pasternack, Sayegh, Clarke and Read2007). Thus, this enzyme participates in the processing or translation of RNA (Table 1).
TbPRMT6 was named based on its higher homology to human PRMT6 than to another type I enzymes, but in the parasite, protein lacks the N-terminal nuclear localization signal detected in the human enzyme and its chrystal structure revealed several features that are distinct from previously characterized type I PRMTs, including four stretches of insertion, the absence of the β15 strand and a unique dimerization arm (Fisk et al., Reference Fisk, Zurita-Lopez, Sayegh, Tomasello, Clarke and Read2010; Wang et al., Reference Wang, Zhu, Chen, Li, Peng, Chen, Zou, Zhang, Jin, Yang, Wu, Niu, Gong, Teng and Yunyu2014a). It methylates bovine H4R3, components of the nuclear pore complex and flagellar proteins, but it does not methylate several parasite proteins that contain GAR sequences (Fisk et al., Reference Fisk, Zurita-Lopez, Sayegh, Tomasello, Clarke and Read2010; Wang et al., Reference Wang, Zhu, Chen, Li, Peng, Chen, Zou, Zhang, Jin, Yang, Wu, Niu, Gong, Teng and Yunyu2014a). Remarkably, the TbPRMT6 knockdown reduces the growth rate of procyclic and bloodstream stages and yields aberrant morphologies in both forms (Fisk et al., Reference Fisk, Zurita-Lopez, Sayegh, Tomasello, Clarke and Read2010). Therefore, this enzyme participates in epigenetics, cell growth and cell morphology of T. brucei (Table 1).
TbPRMT7 is expressed in the bloodstream and procyclic stages, but is apparently dispensable (Fisk et al., Reference Fisk, Sayegh, Zurita-Lopez, Menon, Presnyak, Clarke and Read2009). Unlike human PRMT7, the trypanosomatid homologue is localized only in the cytoplasm and lacks the second AdoMet binding-like domain, which is required for the activity of mammalian PRMT7; however, the parasite enzyme showed a robust monomethylation activity on several targets (Fisk et al., Reference Fisk, Sayegh, Zurita-Lopez, Menon, Presnyak, Clarke and Read2009). Homodimerization of TbPRMT7 is due to the interaction between a dimerization arm of one subunit with the AdoMet-binding domain of the other and consequently, mutations on the dimerization arm remove dimerization and significantly reduce the methyltransferase activity (Wang et al., Reference Wang, Zhu, Caceres, Liu, Peng, Wang, Chen, Chen, Zhang, Zuo, Gong, Teng, Hevel, Wu and Shi2014b; Debler et al., Reference Debler, Jain, Warmack, Feng, Clarke, Blobel and Stavropoulos2016). In addition, the change of a glutamate residue to aspartate in the double E loop (E181D) confers to TbPRMT7 the ability to perform ADMA, whereas an additional change of glutamine residue to alanine in the THW loop (E181D/Q329A double mutant) generated SDMA (Jain et al., Reference Jain, Warmack, Debler, Hadjikyriacou, Stavropoulos and Clarke2016), indicating that specific residues in the double E and THW loops are responsible for the product formed by different PRMTs.
An study analysing single and double TbPRMTs knockdowns (Lott et al., Reference Lott, Zhu, Fisk, Tomasello and Read2014) showed that: (i) the reduction of TbPRMT1 induces a decrease in TbPRMT3 protein levels and similarly, the TbPRMT3 knockdown reduced the TbPRMT1 expression; (ii) the knockdown of TbPRMT1 or TbPRMT3 produced a decrease in ADMA with a concomitant increase in MMA, confirming that TbPRMT1 and TbPRMT3 form functional hetero-oligomers; (iii) in TbPRMT7 knockdown, a very slight reduction of ADMA and unchangeable levels of MMA were observed, but the double TbPRMT1/7 knockdown dramatically reduced ADMA and MMA, proposing that both enzymes can compete for the arginine monomethylation on the same substrates; (iv) in single TbPRMT6 and double TbPRMT6/7 knockdowns no significant changes were observed in ADMA, confirming that TbPRMT6 methylates a relatively narrow group of substrates, but double knockdowns showed a more dramatic growth defect in the procyclic form that single repression of TbPRMT6, indicating that patterns of ADMA and MMA are critical to proliferation of procyclic forms (Lott et al., Reference Lott, Zhu, Fisk, Tomasello and Read2014). All these results indicate that TbPRMTs display a functional interplay at multiple levels.
Leishmaniasis is a group of tropical diseases that affect 12 million people worldwide with 1.5 million new cases diagnosed each year (Alvar et al., Reference Alvar, Vélez, Bern, Herrero, Desjeux, Cano, Jannin and Boer2012). Leishmania spp. has two forms: promastigote in the sand fly vector and amastigote into the infected macrophages of the vertebrate host. The presence of arginine-methylated proteins in Leishmania sp. was demonstrated in 1986 and some of them have been identified (Paolantonacci et al., Reference Paolantonacci, Lawrence, Lederer and Robert-Gero1986). Leshmania sp. has five PRMT homologues to those of T. brucei, but studies showed certain differences, for example, the L. major PRMT3 has an intact double E loop, suggesting that it could be an active enzyme (Campagnaro et al., Reference Campagnaro, Nay, Plevin, Cruz and Walrad2021). The expression of LmPRMT7 is high in the promastigote logarithmic growth phase and intracellular amastigotes, but low in the promastigote stationary phase (Ferreira et al., Reference Ferreira, Alves-Ferreira, Defina, Walrad, Papadopoulou and Cruz2014). Interestingly, the LmPRMT7 knockout augmented infectivity in vitro and in vivo; and in concordance, the overexpression of this enzyme leads to a reduced progression of the lesion; moreover, the LmPRMT7 deletion rescues the pathogenic phenotype of an attenuated strain of L. major (Ferreira et al., Reference Ferreira, Alves-Ferreira, Defina, Walrad, Papadopoulou and Cruz2014; Alcoforado Diniz et al., Reference Alcoforado Diniz, Chaves, Vaselek, Miserani Magalhães, Ricci-Azevedo, de Carvalho, Lorenzon, Ferreira, Zamboni, Walrad, Volf, Sacks and Cruz2021). The absence of LmPRMT7 also impairs parasite development within the sand fly vector Phlebotomus duboscqi (Alcoforado Diniz et al., Reference Alcoforado Diniz, Chaves, Vaselek, Miserani Magalhães, Ricci-Azevedo, de Carvalho, Lorenzon, Ferreira, Zamboni, Walrad, Volf, Sacks and Cruz2021). The proteome comparison of wild-type and Δprmt7 parasites allowed the identification of 40 hypomethylated proteins in the mutant cells, including 17 RBPs (Ferreira et al., Reference Ferreira, Dowle, Parry, Alves-Ferreira, Hogg, Kolokousi, Larson, Plevin, Cruz and Walrad2020). Interestingly, the half-life of the RBP16 protein was reduced in the stationary phase of Δprmt7 cells compared to wild-type parasites, whereas the half-life of Alba3 was similar between both populations, although the absence of PRMT7 diminished the binding of Alba3 to the mRNA of the virulence-factor δ-amastin, affecting its stability (Ferreira et al., Reference Ferreira, Dowle, Parry, Alves-Ferreira, Hogg, Kolokousi, Larson, Plevin, Cruz and Walrad2020), suggesting that LmPRMT7 may regulate the protein stability or the affinity of RBPs for their mRNA targets, impacting in the life cycle progression and virulence of L. major (Table 1).
Arginine methylation and PRMTs in Plasmodium falciparum
Parasites of the genus Plasmodium are the causative agents of malaria. The World Health Organization estimated about 229 million malaria cases and 409 000 malaria-related deaths in 2019 (World Health Organization, 2020). The major species infecting humans are P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale and P. knowlesi, although the majority of the malaria cases are produced by P. falciparum, which is associated with the most severe morbidity and mortality in Africa, whereas P. vivax is the specie more widely distributed (Jong et al., Reference Jong, Tebeje, Meerstein-Kessel, Tadesse, Jore, Stone and Bousema2020). Parasites of the genus Plasmodium have several stages in the life cycle: gametes, zygotes, ookynetes, oocysts and sporozoites in the insect vector (females mosquitoes of the genus Anopheles) and schizonts, merozoites, ring, trophozoites and gametocytes in the vertebrate hosts. In addition, in P. vivax and P. ovale infections, some parasites become in dormant forms called ‘hypnozoites’.
Immunoprecipitation assays in blood stages of P. falciparum using anti-methyl arginine antibodies showed the presence of 843 proteins with this PTM involved in several functions such as protein synthesis, chromatin organization and haemoglobin metabolic processes, among others, indicating that arginine methylation may play an important regulatory role in the parasite biology, including host–parasite interactions (Zeeshan et al., Reference Zeeshan, Kaur, Joy, Saini, Paul, Kaushik, Dabral, Mohmmed, Gupta and Malhotra2017). P. falciparum encodes three PRMTs: PfPRMT1, PfPRMT4/CARM1 and PfPRMT5 (Fisk and Read, Reference Fisk and Read2011). Recombinant PfPRMT1 methylates histones H4 and H2A and several conserved substrates involved in RNA metabolism, such as fibrillarin, poly(A)-binding protein II, ribosomal protein S2 and a splicing factor; in concordance, this enzyme is localized in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus (Fan et al., Reference Fan, Miao, Cui and Cui2009). In summary, these studies indicate that PfPRMT1 may play important roles in epigenetics and RNA metabolism (Table 1).
A study about the organization and assembly of the Sm core complex in the P. falciparum spliceosome suggested that its proteins form a heptameric ring, in which the methylation of PfSmD1, catalysed by PfPRMT5, allows the interaction of this Sm protein with two proteins containing the Tudor domain: PfSMN (survival of motor neurons) and PfTSN (Tudor Staphylococcal nuclease) (Hossain et al., Reference Hossain, Sharma, Korde, Kanodia, Chugh, Rawat and Malhotra2013), indicating that PfPRMT5 has an important role in splicing (Table 1).
At the moment, neither the role of PfPRMT4/CARM1 in the biology of P. falciparum nor the function of PRMTs in the other Plasmodium species has been investigated.
Arginine methylation and PRMTs in Toxoplasma gondii
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite that produces a disease called toxoplasmosis. It has been estimated that this microorganism infects 16–40% of the population in the USA and up to 80% of the population in other countries (Hill and Dubey, Reference Hill and Dubey2002). Members of the cat family are its final hosts, whereas various warm-blooded animals including humans, are intermediate hosts (Montoya and Liesenfeld, Reference Montoya and Liesenfeld2004). The T. gondii life cycle consists of two stages, the replicating tachyzoite and the latent bradyzoite. Bradyzoites can remain in host tissues for its lifetime without health consequences, but when host immunity is attenuated, bradyzoites can differentiate into actively replicating tachyzoites, causing life-long chronic infection.
This parasite has four PRMTs similar to PRMT1, PRMT3, PRMT4/CARM1 and PRMT5 (Fisk and Read, Reference Fisk and Read2011). Approximately 50% of the MMA-proteins found in wild-type parasites do not exhibit this modification in TgPRMT1 knockout cells, indicating that they are putative substrates for this enzyme (Yakubu et al., Reference Yakubu, Simon de Moterri, Nieves, Kim and Weiss2017). TgPRMT1 substrates include the H4 histone, two ApiAP2 transcription factors, several RBPs, a lysine methyltransferase containing a SET domain, myosin E and SPM2 (a component of the subpellicular microtubules that regulate cell division) and, interestingly, most of them are also susceptible to phosphorylation, suggesting a relationship between both PTMs (Saksouk et al., Reference Saksouk, Bhatti, Kieffer, Smith, Musset, Garin, Sullivan, Cesbron-Delauw and Hakimi2005; Yakubu et al., Reference Yakubu, Simon de Moterri, Nieves, Kim and Weiss2017). The fact that myosin E and SPM2 are putative substrates of TgPRMT1 could explain why this enzyme is detected concentrated in the centrosome and in a pericentriolar material during the replication of tachyzoites (El Bissati et al., Reference El Bissati, Suvorova, Xiao, Lucas, Upadhya, Ma, Hogue Angeletti, White, Weiss and Kim2016). Another target of TgPRMT1 is the Argonaute protein (TgAgo), a component of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) that in T. gondii displays low RNA slicer activity, but its methylation by TgPRMT1 induces the recruitment of the Tudor Staphylococcal Nuclease (TgTSN), making it a second potent RNA slicer for RISC (Musiyenko et al., Reference Musiyenko, Majumdar, Andrews, Adams and Barik2012). Parasites lacking TgPRMT1 grow slower than wild-type ones and show abnormal daughter buds, perturbed centrosome stoichiometry and loss of synchronous replication (Musiyenko et al., Reference Musiyenko, Majumdar, Andrews, Adams and Barik2012; El Bissati et al., Reference El Bissati, Suvorova, Xiao, Lucas, Upadhya, Ma, Hogue Angeletti, White, Weiss and Kim2016). Thus, TgPRMT1 participates in epigenetics, RNA metabolism and splicing, mechanisms that may control cell duplication (Table 1).
TgPRMT4/CARM1 catalyses the methylation of H3R17, an epigenetic mark for gene activation that is present in genes specifically expressed by tachyzoites; concordantly, inhibition of TgPRMT4/CARM1 induces conversion to bradyzoites, as well as a decrease of H3R17 methylation (Saksouk et al., Reference Saksouk, Bhatti, Kieffer, Smith, Musset, Garin, Sullivan, Cesbron-Delauw and Hakimi2005). On the other hand, TgPRMT5 produces MMA and SMDA on H3R26 and H4R3 and is expressed in both tachyzoites and bradyzoites, but it has different localization in both stages, in tachyzoites, it is found in the cytoplasm, while in bradyzoites it is located mainly in the nucleus (Liu et al., Reference Liu, Li, Li, Li, Chen, Wu, Yang, Lai, Liu, Sullivan, Cui and Chen2019). Therefore, TgPRMT4/CARM1 and TgPRMT5 participate in epigenetics, which in turn regulates the stage conversion (Table 1).
Arginine methylation and PRMTs in Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica is the microorganism that causes human amebiasis. This parasite infects up to 50 million people worldwide each year, producing intestinal and extra-intestinal diseases that cause between 40 000 and 100 000 deaths annually (Walsh, Reference Walsh1986). Its life cycle consists of two stages, the infective cysts and the invasive trophozoites.
The E. histolytica chromatin is organized in nucleosomes, but the distance of the DNA linker is irregular (Torres-Guerrero et al., Reference Torres-Guerrero, Peattie and Meza1991). Moreover, its histone H4 is longer than the consensus due to the insertion at the N-terminus of three amino acid segments, one of them adds three lysine residues that could be susceptible to being modified by acetylation and/or methylation (Binder et al., Reference Binder, Ortner, Plaimauer, Födinger, Wiedermann, Scheiner and Duchêne1995; Lozano-Amado et al., Reference Lozano-Amado, Herrera-Solorio, Valdés, Alemán-Lazarini, Almaraz-Barrera, Luna-Rivera, Vargas and Hernández-Rivas2016). Regarding the arginine methylation of histones, the antibodies against MMA- and ADMA-H4R3 recognized nuclear proteins of amoeba, indicating the presence of this epigenetic mark in E. histolytica, although the alignment of the amino acid sequence of its H4 histone with the eukaryotic consensus sequence, showed that the modified arginine corresponds to position 8 (H4R8) (Borbolla-Vázquez et al., Reference Borbolla-Vázquez, Orozco, Betanzos and Rodríguez2015; Lozano-Amado et al., Reference Lozano-Amado, Herrera-Solorio, Valdés, Alemán-Lazarini, Almaraz-Barrera, Luna-Rivera, Vargas and Hernández-Rivas2016).
This parasite contains five PRMTs, four of them show similarity to type I enzymes, whereas the other is related to the PRMT5 family (type II) (Fisk and Read, Reference Fisk and Read2011) (Fig. 2). The amino acid sequences of the four type I PRMTs display higher similarity to human PRMT1 and do not contain the specific signatures for other type I PRMTs; therefore, they were initially classified as PRMT1 homologues (Fisk and Read, Reference Fisk and Read2011). However, our phylogenetic analysis suggested that one of these EhPRMTs does not show significant homology with any PRMT family (Borbolla-Vázquez et al., Reference Borbolla-Vázquez, Orozco, Betanzos and Rodríguez2015) (Fig. 2), therefore, we named it as atypical PRMT (EhPRMTA), whereas the other three type I enzymes were termed EhPRMT1a, EhPRMT1b and EhPRMT1c (Borbolla-Vázquez et al., Reference Borbolla-Vázquez, Orozco, Betanzos and Rodríguez2015). An antibody against human PRMT1 recognized these EhPRMT1 proteins and they were localized in the nucleus and the cytoplasm, suggesting that they could methylate both histones and non-histone proteins (Borbolla-Vázquez et al., Reference Borbolla-Vázquez, Orozco, Betanzos and Rodríguez2015). In fact, the recombinant protein of EhPRMT1a catalysed the asymmetric dimethylation of H4R3 in commercial histones (Borbolla-Vázquez et al., Reference Borbolla-Vázquez, Orozco, Betanzos and Rodríguez2015), indicating that it may be involved in epigenetics (Table 1); however, until now it is unknown whether the three EhPRMT1 proteins have redundant or different functional roles.
EhPRMTA is the type I enzyme that shows the lowest similarity to PRMT1 (Fisk and Read, Reference Fisk and Read2011). In concordance, this protein was not recognized by an antibody against human PRMT1 (Borbolla-Vázquez et al., Reference Borbolla-Vázquez, Orozco, Betanzos and Rodríguez2015). In addition, it does not contain several of the canonical amino acid residues of type I PRMTs (Medina-Gómez et al., Reference Medina-Gómez, Bolaños, Borbolla-Vázquez, Munguía-Robledo, Orozco and Rodríguez2021) and a phylogenetic analysis grouped this protein with the inactive PRMT3 of T. brucei (Fig. 1), although the EhPRMTA recombinant protein displayed enzymatic activity on commercial histones (Medina-Gómez et al., Reference Medina-Gómez, Bolaños, Borbolla-Vázquez, Munguía-Robledo, Orozco and Rodríguez2021). On the other hand, EhPRMTA interacts with the EhTSN protein, which is a transcription factor of E. histolytica (Cázares-Apátiga et al., Reference Cázares-Apátiga, Medina-Gómez, Chávez-Munguía, Calixto-Gálvez, Orozco, Vázquez-Calzada, Martínez-Higuera and Rodríguez2017) and its homologues in other protozoan parasites participate in RNA metabolism (Hossain et al., Reference Hossain, Korde, Singh, Mohmmed, Dasaradhi, Chauhan and Malhotra2008; Musiyenko et al., Reference Musiyenko, Majumdar, Andrews, Adams and Barik2012), suggesting that this EhPRMT is involved in transcription regulation and in RNA metabolism; moreover, the EhPRMTA-knockdown increased cell growth and phagocytosis, but decreased cell migration and survival of trophozoites submitted to heat shock (Medina-Gómez et al., Reference Medina-Gómez, Bolaños, Borbolla-Vázquez, Munguía-Robledo, Orozco and Rodríguez2021), indicating that this PRMT participates in these events (Table 1), although the identification of its protein targets remains to be determined.
Discussion
Because there is a correlation between the expression level of some PRMTs and cancer (Yang and Bedford, Reference Yang and Bedford2013), investigation in both academic laboratories and the pharmaceutical industry has been leading to the discovery of several small molecules targeting different PRMTs that at micromolar and submicromolar concentrations display anti-tumour effects in cellular assays (Hu et al., Reference Hu, Qian, Ho and Zheng2016; Zhang and Zheng, Reference Zhang and Zheng2016; Guccione and Richard, Reference Guccione and Richard2019). In fact, three specific inhibitors for PRMT5 (GSK3325695, JNJ-64619178 and EPZ015938) and one for type I PRMTs (GSK3368715) have been analysed in phase I clinical trials (Rakow et al., Reference Rakow, Pullamsetti, Bauer and Bouchard2020). As PRMTs of protozoan parasites play important roles in their cell growth, virulence, conversion stages and response to stress conditions (Table 1), anti-PRMT drugs could also be effective for the treatment of diseases produced by those pathogenic microorganisms. In fact, several small molecules that inhibit the activity of PfPRMT1 also restrict the P. falciparum growth (Fan et al., Reference Fan, Miao, Cui and Cui2009). Moreover, a study analysing the antiplasmodial activity of several compounds that inhibit epigenetic modifiers in cancer cells, showed that sinefungin, a pan-inhibitor of AdoMet-dependent methyltransferases, affected the asexual stage of P. falciparum, whereas the ellagic acid, a PRMT inhibitor, was 10-fold more potent against the asexual stage and early gametocytes than against mammalian cells (Coetzee et al., Reference Coetzee, von Grüning, Opperman, van der Watt, Reader and Birkholtz2020). In addition, the structural differences shown by the PRMTs of the parasites with respect to their human homologues could be used to design specific anti-parasitic drugs.
Conclusions
Methylation of arginine residues is involved in the regulation of several molecular processes, such as transcription, RNA processing and signal transduction pathways, which in parasites may control pathogenesis-related events. Although most PRMTs from protozoan parasites have not been characterized, current research on some of these enzymes shows that they participate in cell growth, metabolism, stress response, stage transitions and virulence. Thus, the PRMTs of protozoan parasites are attractive targets to develop new therapeutic strategies that could help in the control of the public health problems generated by these pathogens. Actually, the considerable advances in the identification of clinically relevant PRMT inhibitors for cancer therapy could be extended to find effective drugs against the protozoan parasites.
Financial support
This work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT, Mexico) Grant FORDECYT-PRONACES/194163/2020.
Conflict of interest
The author declares there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
Not applicable.