Although there are large assemblages of both Crow rock art (Conner Reference Conner1980, Reference Conner1984; Conner and Conner Reference Conner and Lu Conner1971; Keyser Reference Keyser2010, Reference Keyser2012, Reference Keyser2014, Reference Keyser2018; Keyser and Cowdrey Reference Keyser and Cowdrey2008; Keyser and Klassen Reference Keyser and Klassen2001; Keyser and Minick Reference Keyser and Minick2018; Keyser and Poetschat Reference Keyser and Poetschat2009; Keyser and Renfro Reference Keyser and Renfro2017; Loendorf Reference Loendorf2012; McCleary Reference McCleary2008a, Reference McCleary2016) and portable biographic art in the form of painted robes and ledger drawings (Brownstone Reference Brownstone and Feest2001; Cowles Reference Cowles1982; Heidenreich Reference Heidenreich1985; Keyser Reference Keyser1996; Logan and Schmittou Reference Logan and Schmittou1995; Lowie Reference Lowie1935; Wildschut Reference Wildschut1926), scholars have long lamented the absence of a strong connection—both chronological and stylistic—between these two datasets that would aid in interpreting the petroglyphs. Conner expressed this gap most succinctly: “Missing in the chain of evidence is a stylistic link between the rock drawings attributed to the Crow and the known Historic Crow hide paintings. This link will probably never be found” (Reference Conner1984:136).
The picture is further complicated because rock art does not have documented “dates of collection” such as those that often fortuitously accompany portable artworks, nor does rock art generally become part of the stratigraphic record as occurs typically with other archaeological data. Hence, although the growing application of direct and chronometric methods to rock art has made considerable contributions in the Plains and elsewhere (e.g., Dorn Reference Dorn and Whitley2001; Rowe Reference Rowe and Whitley2001; Ruiz and Rowe Reference Ruiz, Rowe and Smith2014), rock art of the Historic period (post-1730) often can still only be attributed to quite broad time spans (Keyser Reference Keyser and Whitley2001; Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2017). This is especially frustrating, because to truly draw rock art into the fine-grained historical and ethnohistorical context of documented key events that took place over the course of the nineteenth century, a scale of resolution on the order of a decade or so is often desirable for biographic artworks (Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2019).
Recent research, however, has provided a method for relatively easy seriation dating of painted Blackfoot bison robes (Lycett Reference Lycett2017; Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2017). Moreover, through the building of such seriations we have established stylistic trends and identifications for Blackfoot artworks that would not otherwise be possible (e.g., Bouma and Keyser Reference Bouma and Keyser2004; Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2018). Taking the next step, we have also begun applying these research results to various Blackfoot rock art sites and images (e.g., Keyser and Lycett Reference Keyser and Lycett2019; Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2017). Although this effort is in its infancy, the utility of the method is self-evident, and its relative ease of use is obvious. With this in mind, and given Keyser's recent research involving Crow rock art at several key sites, we began discussing the possibility of developing such a seriation for Crow biographic art that could serve as a basis not only for helping date particular examples (including both rock art and portable pieces) but also for showing stylistic trends within the corpus of Crow art itself (Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2019). In this article we report on our use of this comparative framework and statistical seriation methodology to establish a more accurate chronology for five Crow rock art sites.
Crow Rock Art
Scattered throughout central Montana and north-central Wyoming are dozens of petroglyph sites with images of horses, humans, tipis, weapons, and other items of material culture that show the Crow Indians' movement out onto the Northwestern Plains and their adaptation to a nomadic equestrian lifeway. Known as Biographic rock art, the earliest of these images date to the Protohistoric period (c. 1620–1730; cf. Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2018:772): they show heavily armed men riding caparisoned horses decked out with a broad array of horse trappings, including painted and feather-covered leather armor, Spanish chain bits, feather war bonnets, and pendant human scalps (Figure 1). Shield-bearing horsemen wield highly decorated spears, swords, and war axes, and one even shoots a gun as they fight similarly equipped mounted and pedestrian enemies. As the Crow made this area of the Plains their homeland—stretching from Montana's Missouri River across the Yellowstone River and south into the Bighorn basin of Wyoming—leather armor was abandoned as guns became more common, and horse tack became even more elaborate. Headstalls, Spanish “jingle bits,” metal cruciform stirrups, Spanish and American military saddles, feather horse bonnets, war paint, and various amulets were added to their accoutrements, while weapons and brave deeds of warfare became the focus of their rock art (Keyser Reference Keyser1987:44–52).
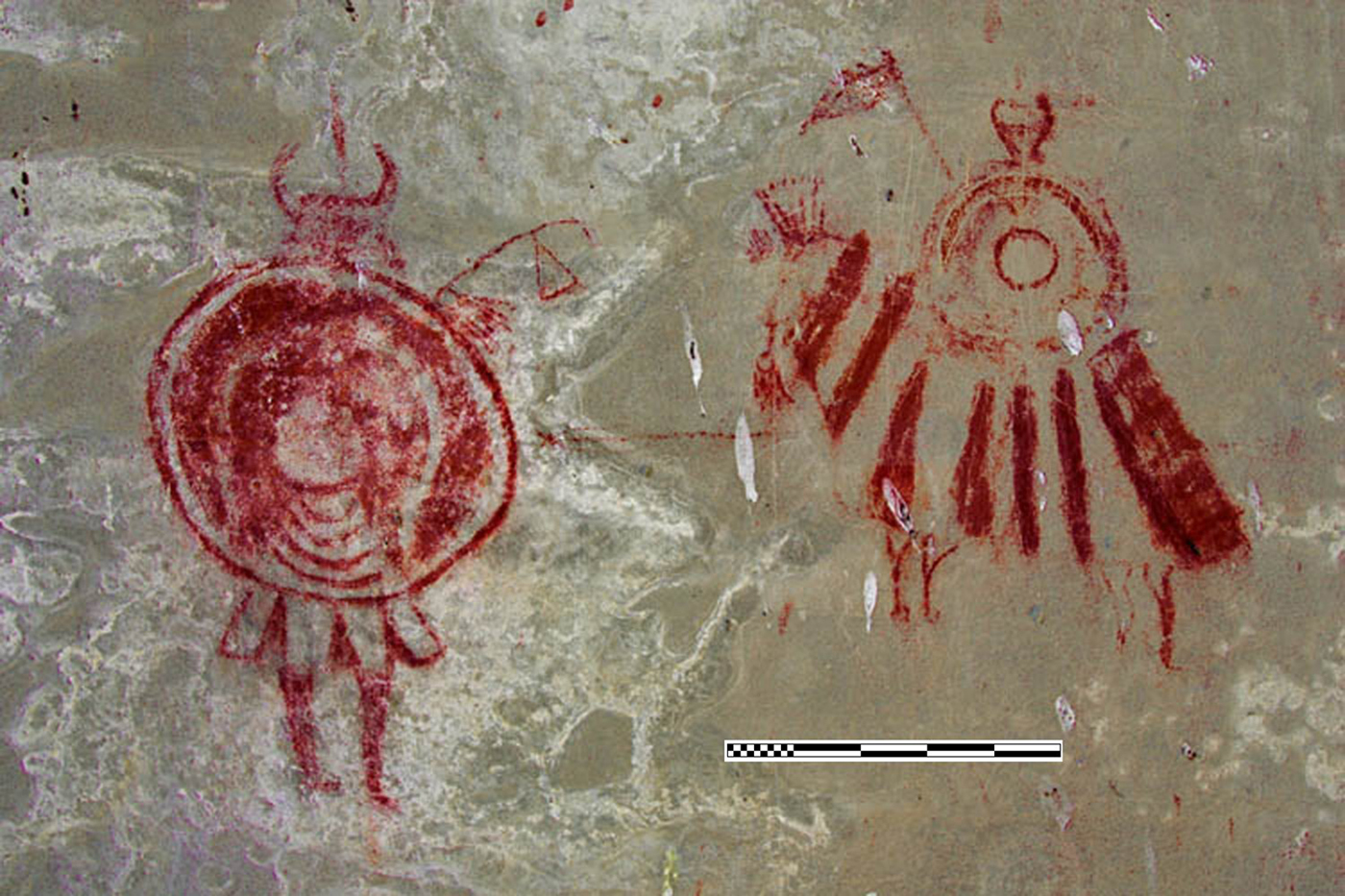

Figure 1. Goffena 24ML408. Armored horse and rider attacking a pedestrian warrior. An early (pre-robe art) example of biographic art circa 1730–1800. Crow attribution hinges on the fact that the horse wears a feather bonnet, since only Crow and Mandan warriors are known to have used such horse war bonnets (Keyser Reference Keyser2012) and the site would have been in the heart of River Crow territory during the Protohistoric era. Scale is 50 cm. (Photograph courtesy of John and Mavis Greer; Photoshop color enhancement by John Greer.) (Color online)
These rock art scenes are detailed narratives with high-quality story content recounting the transition of the Crow from village farmers who broke away from the Hidatsa tribe to the full-fledged Plains equestrian bison hunters, best known from the work of Lowie (Reference Lowie1935) and Wildschut (Reference Wildschut1926; Wildschut and Ewers Reference Wildschut and Ewers1960). Sites such as Joliet (Keyser and Cowdrey Reference Keyser and Cowdrey2008; McCleary Reference McCleary2016), No Water (Keyser and Poetschat Reference Keyser and Poetschat2008), Four Dance Cliff (Conner and Conner Reference Conner and Lu Conner1971), Manuel Lisa (McCleary Reference McCleary2016), Musselshell (Loendorf Reference Loendorf2012), Ellison's Rock (Keyser Reference Keyser2014), and Benjamin Hill (Fredlund Reference Fredlund1976) are recorded in the literature. Dozens of others have equally compelling imagery, yet remain only partially recorded or incompletely studied. Our effort here is directed toward providing one key to help unlock the vast wealth of history present in these hundreds of rock art pictures.
Materials and Methods
Comparative Crow Biographic Artworks
We used 11 portable examples of Crow biographic art to assess rock art chronology (Table 1). These 11 artworks span much of the nineteenth century, include a variety of media (robes, muslins, and ledgers), and have previously been the subject of academic attention. Moreover, these works have been used to establish chronological information on stylistic changes in Crow biographic art and to help better determine the chronology for several undated Crow portable artworks (Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2019). More relevant to this study, however, these biographic artworks—as the portable equivalents of the biographic-style art drawn at the Historic period rock art sites we examine—provide a direct chronological point of comparison that assists us in dating the petroglyphs. Further information and details of these portable artworks are provided in the supplemental information (Supplemental Text 1).
Table 1. Crow Robe/Ledger Art Examples.

Rock Art Sites
We selected imagery from five rock art sites for our analysis, on the basis that notable stylistic differences in their content suggested artworks of different ages (Figures 2–6). Equally important, the artwork from these sites contained sufficient detail of human and/or horse imagery to be a good fit for dating purposes, given our method of comparison with equivalent Crow portable art. Our illustrations of the imagery from these five sites are precisely drawn photo-tracings, made from a combination of original photographs taken by one of us (Keyser), other historic photographs found in the literature, and still other photographs provided by colleagues. Some of these photographs, such as those from Joliet taken in the 1960s, have allowed us to discern many new details; for example, the tapadero stirrup cover on the middle horse in the stacked horse scene in Figure 6b. Others have enabled us to clarify some minor issues of detail currently in the published record (e.g., the shield-bearing warrior in the Joliet combat scene was first apparently drawn as a pedestrian—as we have illustrated it—and then later appears to have been modified into a horseman as per McCleary [Reference McCleary2016:115]). Two of the rock art sites we examined, Joliet and Castle Butte, are well-known in the literature, and images from these sites have been reproduced on several occasions (e.g., Conner and Conner Reference Conner and Lu Conner1971; Keyser Reference Keyser1987; Keyser and Klassen Reference Keyser and Klassen2001; McCleary Reference McCleary2016). Two other sites we examined, Benjamin Hill and 24GV191, are much less well-known, but provide classic examples of Crow rock art. A fifth site, Musselshell (24ML1049), has only recently been recorded (Loendorf Reference Loendorf2012), but the wealth of imagery there, especially of Crow images, has rapidly become important in several Plains rock art projects (Keyser Reference Keyser2012; Keyser and Poetschat Reference Keyser and Poetschat2014; Loendorf Reference Loendorf2012). To provide further context, we briefly discuss each site in turn.

Figure 2. Crow petroglyphs from three separate panels at Castle Butte (24YL418). All scales are 30 cm. Images (a) and (b) adapted from Conner and Conner (Reference Conner and Lu Conner1971); (c) is a photo-tracing by Keyser from a Conner photograph.
Castle Butte (24YL418)
Castle Butte is an extensive rock art site in the southern Bull Mountains between the Yellowstone and Musselshell rivers approximately 65 km (40 miles) northeast of Billings, Montana (Olson Reference Olson1991). Rock art at the site consists of mostly incised petroglyphs with a few red pictographs showing primarily Historic period scenes involving horses, horse tack, warriors, weapons, and tipi village scapes. Combat is a frequent subject, and the general form of both horses and humans clearly identifies most of the petroglyphs as being of Crow manufacture (Brownstone Reference Brownstone and Feest2001:74; Keyser and Renfro Reference Keyser and Renfro2017:12–19).
We used scenes from three different panels at Castle Butte in our analysis (Figure 2). All three are well-known from the Northern Plains archaeological literature, having been published in various forms by multiple authors (Conner and Conner Reference Conner and Lu Conner1971:52–54, 63; Keyser Reference Keyser1987:68; Keyser and Klassen Reference Keyser and Klassen2001:32, 224, 248; McCleary Reference McCleary2016:50).
Benjamin Hill (24RB1027)
Recorded during a “coal-lands survey,” the Benjamin Hill site comprises petroglyphs incised on six panels of a massive south-facing sandstone outcrop overlooking Rosebud Creek about 40 km (25 miles) east of the Little Wolf Mountains and 65 km (40 miles) south of the Yellowstone River (Fredlund Reference Fredlund1976:7). Earlier petroglyphs at the site include a variety of Late Prehistoric period (pre-1620) V-necked-style humans incised on five panels and two groups of fighting warriors and a tipi village scape scratched and incised on two panels.
For our analysis of the site, we selected a single panel of Historic period images containing two separate scenes (Figure 3). This panel shows typical Crow-style fighting warriors juxtaposed with a variety of very detailed weapons characteristic of combat scenes in this region. These weapons include a flintlock gun, a Missouri war axe, a lance, and a broad sword. One combat scene between two warriors grappling over a lance involves an archetypal Crow-style capture hand (Keyser Reference Keyser1996:38–41; Taylor Reference Taylor1994:184–185). Images at this site are published only in one poorly known article (Fredlund Reference Fredlund1976), and as a result they are largely unknown in the professional literature, despite their obvious importance to regional prehistory.

Figure 3. Benjamin Hill (24RBI027). Scale is 30 cm. Two scenes from a single panel. Images are photo-tracings by Keyser from photographs taken by Lynn Fredlund.
24GV191
Painted and carved on the sandstone bluffs bordering the north side of the Musselshell River Valley, approximately 90 km (55 miles) northwest of Billings, Montana, is a vast assemblage of petroglyphs and pictographs recorded as site 24GV191. More than 50 panels of pecked, incised, and scratched petroglyphs and red-painted pictographs provide multiple examples of Protohistoric and Historic period combat and horse-raiding scenes. Exhibiting some of the finest examples of armored horses known in Crow country, the site also documents the actions of both Crow and Blackfoot horse raiders well into the Historic period. Images show dozens of examples of horses, horse tack, warriors, and weapons. At least a dozen panels illustrate vision quest and shamanic imagery relating to Crow ceremonialism and religious life.
Unfortunately, the site has never been formally studied or recorded; the only information comes from photographs taken by a few professional and avocational rock art researchers who have been allowed to visit. Therefore, the imagery is little known, even though it is key to understanding many facets of Crow culture from their earliest entry into the region until the last years of pre-reservation life.
In our analysis we used a single panel from this site, showing a horse and rider facing off against a massed force of enemies (Figure 4). Being able to date this image adds important information to our knowledge of this site and opens a window into other compositions carved there.

Figure 4. Horse and rider imagery at 24GV191 shows rider facing off against massed force of enemies, represented by column of horizontal lines and weapons pointing toward him. Note the arrow wounding the horse in the leg with flowing blood. Scale is 30 cm. Photo-tracing by Keyser from a George Stoll photograph.
Musselshell (24ML1049)
Situated along the north side of the Musselshell Valley about 100 km (60 miles) east of 24GV191 is the Musselshell site (24ML1049). Only recently recorded, the site has a wealth of petroglyphs and pictographs dating from the Late Prehistoric, Protohistoric, and Historic periods (Loendorf Reference Loendorf2012:15–50). Shield-bearing warriors, dancers, nearly two dozen animals, and more than a dozen horses and riders are found on more than 30 panels of rock art carved and painted on the massive sandstone cliffs at the site.
Although only recently investigated, its images promise to yield information crucially important to understanding the history of the Crow in this area and documenting their interaction with neighboring groups. To begin studying the chronology of this site, we selected a single horse and rider from one panel for our analysis (Figure 5).

Figure 5. Horse and rider from Musselshell (24ML1049). Scale is 30 cm. Drawing adapted from Loendorf (Reference Loendorf2012), with photo-tracing modifications by Keyser.
Joliet (24CB402)
Pecked, incised, and scratched on a towering east-facing cliff on the south side of the Rock Creek Valley at Joliet, Montana, is found the region's most intensively studied rock art site. Known in the professional archaeological literature since 1962 (Conner Reference Conner1962), the Joliet site has been the subject of study by at least a dozen scholars since then (Conner and Conner Reference Conner and Lu Conner1971; Gebhard Reference Gebhard1974:44–47; Keyser Reference Keyser1987:57, 65; Keyser and Cowdrey Reference Keyser and Cowdrey2008:25–28; Keyser and Klassen Reference Keyser and Klassen2001:22, 32, 230, 237, 242; Keyser and Poetschat Reference Keyser and Poetschat2014:198–199; Loendorf and Porsche Reference Loendorf and Porsche1985:16–23, 64–68; McCleary Reference McCleary2008a:142–181, Reference McCleary2008b, Reference McCleary2016:113–137). Of primary interest at the site are pecked and incised shield-bearing warriors, six large Timber Creek style grizzly bears, and more than two dozen combat scenes or biographic records of successful warriors. These biographic narrative scenes include depictions of stolen horses, illustrations of hand-to-hand combat, a record of the transfer of the Hot Dance from the Hidatsa to the Crow, and self-portraits of Crow tribal policemen, military scouts, and World War I doughboys.
McCleary, in speaking of both the indigenous and archaeological importance of the site, has stated that of “all the rock art sites known to contemporary Crow people, Joliet looms in their collective consciousness as the rock art site with glyphs containing historic information” (Reference McCleary2016:113; emphasis in original). Furthermore, given that several of the narrative scenes—the exploits of the tribal policeman “Turns Back Plenty,” the tenure of Crow military scouts, the Hot Dance transfer, and World War I—depicted at Joliet are well dated in the historic record, the site provides an important opportunity to measure whether stylistic trends in rock art imagery parallel those documented in portable artworks. Therefore, we analyzed three of the main panels at Joliet: the Hot Dance scene, the “three stacked horses” scene (war honors series), and a warrior on horseback fighting a shield-bearing warrior (Figures 6a–c). While other scenes from this site can also be incorporated, they merely duplicate the specific traits examined for this analysis.

Figure 6. Joliet (24CB402). (a) Hot Dance scene; (b) three stacked horses scene (war honors series); (c) warrior on horseback fights shield-bearing warrior. All scales are 20 cm. Drawings are photo-tracings by Keyser from photographs provided by Conner and Gary Bingham and one published by Gebhard (Reference Gebhard1974).
Stylistic Traits Examined
Building on the work we have undertaken with Blackfoot robe art and rock art, we have previously established that variations in the form of horses and human figures (Table 2) routinely recorded in Crow biographic artworks provide valid information regarding their chronology (Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2019). The presence or absence of specific details in weaponry, tipis, and horse gear also provides important and useful chronological markers in Crow artworks (Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2019).
Table 2. Twenty Stylistic Features Recorded for the Analyses.

The horse-related features we analyzed describe variations in hoof forms, other anatomical details, and specific items of horse tack (Table 2). Recorded variations in the depiction of human forms included the presence or absence of facial features, the overall body and leg form, and the presence of “striped-bodied” humans (Table 2). We also recorded the detached Crow-style “capture hand” convention, the presence of tipis, the presence of “tri-bar ramrod ferrules” on firearms, and the depiction of revolver pistols. Table 2 and Figures 2–6 provide examples of many of these features, and further examples and information can be obtained in Lycett and Keyser (Reference Lycett and Keyser2019).
This protocol provides a list of 20 stylistic traits that were then recorded across the different artworks (Table 2). For the purposes of analysis, these traits were coded as either being present (= 1) or absent (= 0) in each portable artwork example, as well as the five rock art sites. In a very small number of cases (i.e., less than 1% of 320 total data points) there was some ambiguity regarding character identification, and they were coded as missing (?). Also, in the case of one robe (Schoch robe N.A.4) and one of the rock art sites (Benjamin Hill), horses were not illustrated, which means it is ambiguous as to how their authors may have drawn horses had they chosen to do so. Accordingly, the characters relating to horse anatomy in these cases were also, conservatively, treated as missing in these instances. In the multivariate statistical analyses that follow, missing characters were treated by means of pairwise deletion (Hammer Reference Hammer2016). In this conservative procedure for handling such missing cases, if a datum point is recorded as missing for one variable in a pair of artworks, that specific variable is then excluded from the computation of total stylistic “distance” between those two items.
Statistical Methods
We applied two methods of statistical analysis to the dataset. First, using a procedure we have successfully used elsewhere (Keyser and Lycett Reference Keyser and Lycett2019; Lycett Reference Lycett2017; Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2017), we subjected all the artworks to a principal coordinates (PCo) analysis. PCo analysis is a multivariate procedure that can be undertaken on distance matrices (Davis Reference Davis1986; Gower Reference Gower2005) and that (numerically) describes the level of stylistic comparability between all items analyzed. We used Jaccard distances to describe these patterns of similarity and difference between items (Supplemental Table 1), which are particularly suitable for presence–absence data (Jordan and Shennan Reference Jordan and Shennan2003; Shennan Reference Shennan1997). After the distance matrix is calculated and built, PCo analysis then uses these data to compute eigenvalues (measures of variance) and eigenvectors (coordinates). Thereafter, major patterns of variation between items (i.e., artworks) can be graphically illustrated in a scatterplot (Gower Reference Gower2005). The first coordinate describes the major (primary) axis of variation between items based on the inputted data. Thereafter, each coordinate extracted from the matrix describes proportionally less of the original variation between items in percentage terms. We plotted the first two principal coordinates against each other to visualize the major axes of variation between the artworks.
In essence, based on the underlying statistical mechanics, PCo provides a means of readily assessing the stylistic similarity between all of the various artworks in the analysis. This method was shown to be useful in assessing chronological signals in Blackfoot biographic artwork data (Lycett Reference Lycett2017; Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2017, Reference Keyser2018). As has been pointed out elsewhere (e.g., Jensen and Nielsen Reference Jensen, Nielsen, Jensen and Nielsen1997), the use of ordination methods in this manner provides a seriation, with a seriated sequence broadly forming a parabolic arch across the two primary axes of variation (Figure 7). Given that the comparative data (i.e., portable biographic artworks) and the features we recorded provide chronological information (Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2019), ordination methods enable estimation of the chronology of the undated rock art sites. We used PAST v3.21 (Hammer Reference Hammer2016) to undertake this analysis.

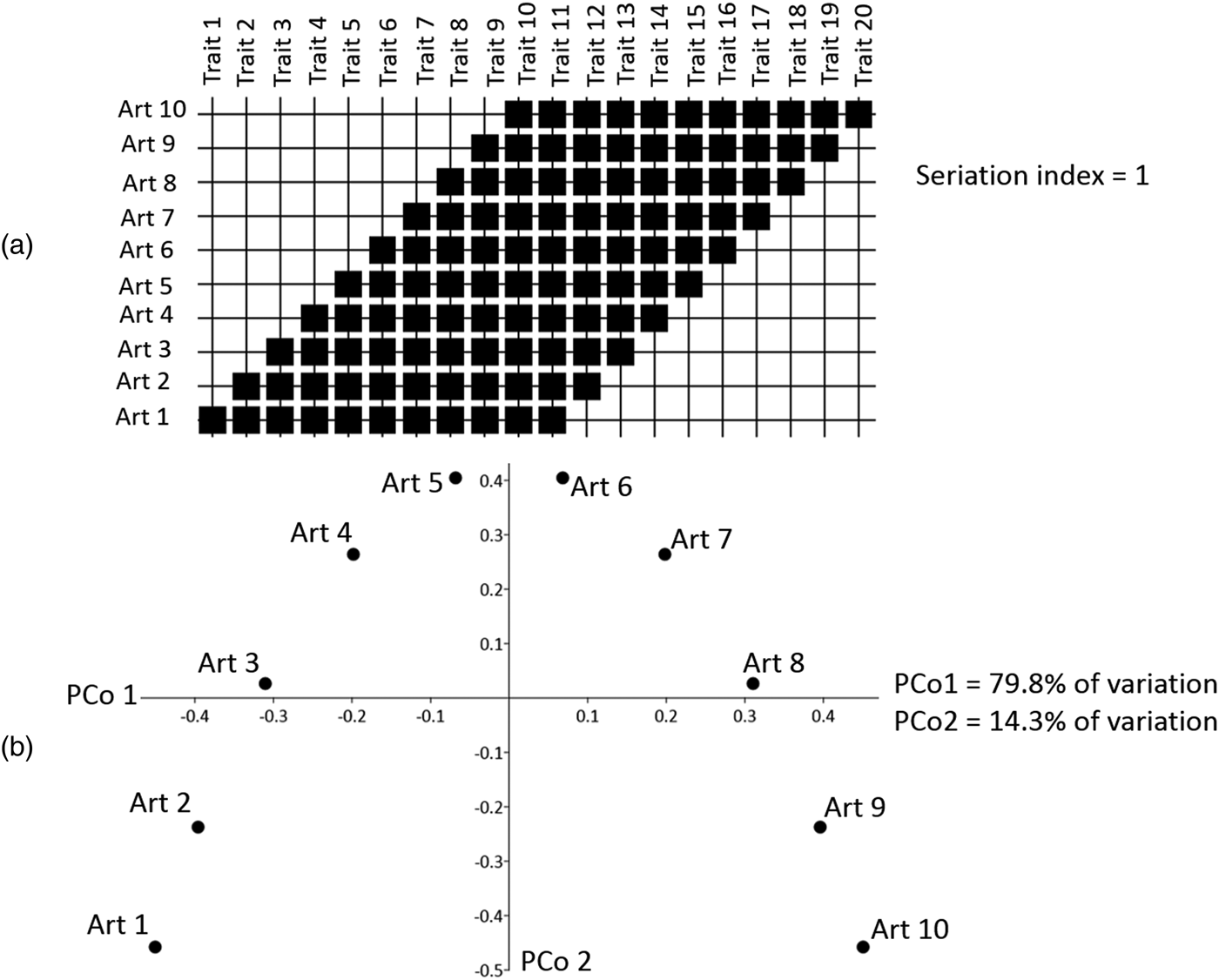
Figure 7. The complementary elements of occurrence seriation and ordination methods, as discussed elsewhere by Jensen and Nielsen (Reference Jensen, Nielsen, Jensen and Nielsen1997). (a) A hypothetical “perfect” seriation for 10 artworks based on 20 traits (note the perfectly diagonal arrangement and lack of gaps with a seriation index = 1); (b) the corresponding PCo analysis using exactly the same methods as we applied to Crow artworks. A seriated sequence broadly forms a parabolic arch, with time distributed across both PCo 1 and PCo 2.
The plotting of time by the (broadly) parabolic arch-shaped results can be cross-checked by reference to the known dated items. We should not expect exact precision in the ordering of items that date to within just a few years of each other, but the arch should clearly plot broad chunks of time, especially in terms of items plotting within each quadrant of the PCo. Assuming that the data we have plot time, this then permits undated items to be placed within a date range by reference to their position on the plot and to the dates of their most closely associated portable artworks. In other words, from the PCo analysis we should be able to construct an estimated chronological ordering for all the Crow biographic artworks in our study. The portable artworks can be positioned according to their known dates, whereas rock art scenes can be positioned according to their estimated date based on their placement in the PCo analysis.
To further assess the statistical validity of this ordering and to visually observe temporal changes in stylistic content of these artworks, we also undertook a statistical occurrence seriation analysis (Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2018). The use of occurrence seriation analysis in archaeology has a long history (reviewed in O'Brien and Lyman Reference O'Brien and Lyman1999): it was initially introduced to overcome certain methodological issues with frequency seriation, which—given its reliance on frequencies of features, rather than the mere presence of absence of a feature—can be more subject to sampling issues (Dempsey and Baumhoff Reference Dempsey and Baumhoff1963; Rowe Reference Rowe1959). When undertaking the statistical occurrence seriation analysis, we used a quantitative algorithm to assess chronology, as first described by Brower and Kile (Reference Brower and Kile1988). Their method was specifically designed to be applied to presence–absence data of the type we use here and so is directly complementary (albeit providing different information) to the PCo analysis performed earlier.
To carry out the occurrence seriation, we constructed a matrix that lists the artworks to be seriated according to their proposed chronology. Artworks are listed in the rows of this matrix, and the stylistic traits are listed in its columns. Trait presences are visually graphed through use of solid squares, and absences are left blank. Brower and Kile's (Reference Brower and Kile1988) quantitative algorithm arranges items in the seriation (as best as the data permit) so that trait presences are arranged along the diagonal and absences are concentrated in the off-diagonal areas of a neatly seriated sequence (note that placing emphasis on a diagonal arrangement in producing a seriation will not necessarily result in the highest overall seriation index for the data). Of course, real-world datasets invariably behave imperfectly, with some presences also located in off-diagonal portions of the plot, thus creating a less-than-perfect seriation. Therefore, Brower and Kile (Reference Brower and Kile1988) also detailed a method for quantifying the extent of “gaps” in a projected seriation. Their “seriation index” ranges from 0 to 1: a perfectly seriated dataset would return a value of 1, whereas “errors” in the sequence push this computed value closer to zero. As has long been noted, such errors or “noise” in a temporal seriation might be caused by a variety of factors such as spatial variation in the data, particular stylistic anachronisms of individual artists, or sampling error (Deetz and Dethlefsen Reference Deetz and Dethlefsen1965; Dempsey and Baumhoff Reference Dempsey and Baumhoff1963; Dunnell Reference Dunnell1970; Hole and Shaw Reference Hole and Shaw1967). Accordingly, real datasets invariably return a seriation index of less than 1. In essence, this index computes the number of “embedded absences” in the seriated sequence, which refers to the number of absences occurring within the range of presences in the columns. Brower and Kile's (Reference Brower and Kile1988:80) method uses the following formula:
 $$1-\left[ {\; \displaystyle{{\mathop \sum \nolimits_{\,j = 1}^n A_j\;} \over {\mathop \sum \nolimits_{\,j = 1}^n R_j\;}}} \right],$$
$$1-\left[ {\; \displaystyle{{\mathop \sum \nolimits_{\,j = 1}^n A_j\;} \over {\mathop \sum \nolimits_{\,j = 1}^n R_j\;}}} \right],$$where A j is the number of embedded absences in a column (j), R j refers to the range of the presences in a column, and n describes the total number of columns.
To test the statistical validity of our proposed chronology for the Crow artworks, we undertook a “constrained” seriation, whereby the characters are free to move, but the sequentially ordered art examples are not (Brower and Kile Reference Brower and Kile1988). Statistical significance is then established by generating 30 random matrices with the same number of occurrences in each row and comparing them to the real matrix through a Monte Carlo simulation (Hammer Reference Hammer2016:99), whereby a resultant p-value < 0.05 indicates that the data are significantly different from random. Since occurrence seriation operates on presence–absence data, we conservatively treated missing cases as absent (i.e., we did not assume their presence) when undertaking this analysis. Note that we did not use occurrence seriation here to derive a temporal sequence; rather, that is done primarily through the PCo, as well as through knowledge of the chronology of the dated artworks and how the rock art plots in comparison to them. Instead, our use of constrained occurrence seriation exploited the statistical properties of Brower and Kile's (Reference Brower and Kile1988) method to provide further statistical examination of the chronology derived, as well as to visually illustrate the pattern of trait change across time in an intuitive manner. This also means that the seriation index we derived for this proposed ordering is not necessarily the absolute highest that might be obtained for these data; it is conservatively low. This means that our statistical evaluation of this ordering is also conservative when comparing this value to the Monte Carlo simulations.
Figure 7 illustrates the complementary nature of occurrence seriation and principal coordinates analysis, which is based on ideas discussed and illustrated previously elsewhere (see, e.g., de Torres and Ruiz-Gálvez Reference de Torres and Ruiz-Gálvez2014; Jensen and Nielsen Reference Jensen, Nielsen, Jensen and Nielsen1997). Figure 7a depicts a hypothetical occurrence seriation for 10 artworks based on 20 traits that show a perfectly diagonal seriation with no gaps in the sequence (i.e., the seriation index = 1). As noted earlier, sampling biases, spatial signal in the data, or the stylistic anachronisms of individual artists might conspire to distort real datasets away from this idealized sequence (see, e.g., Deetz and Dethlefsen Reference Deetz and Dethlefsen1965; Dempsey and Baumhoff Reference Dempsey and Baumhoff1963; Dunnell Reference Dunnell1970; Hole and Shaw Reference Hole and Shaw1967). Figure 7b shows the results of the equivalent PCo analysis employing exactly the same procedures we use here. Two features should be noted about this seriated sequence. First, the seriated items do not plot as a straight line along PCo1; rather the seriated (linear) relationship between items broadly forms a parabolic arch. This is because the two axes of the PCo plot are aiming to describe variation across all items based on the inputted data. Artworks 1 and 10 are most different as illustrated by their relative positions at the extreme ends of PCo1; however, artworks 5 and 6 are also different from both of these items, as illustrated across the second axis of variation (PCo2). The other feature to note is that PCo1 does not describe 100% of the variation, even though this is a perfectly seriated sequence. Indeed, even the cumulative percent of PCo1 and PCo2 does not account for 100% of all variation. This is because the method has to assign some percentage of the remaining variation to the additional axes, of which there will be one for each item seriated. Accordingly, even in a perfectly seriated sequence, PCo1 cannot account for 100% variation nor even can the sum of PCo1 and PCo2.
Results
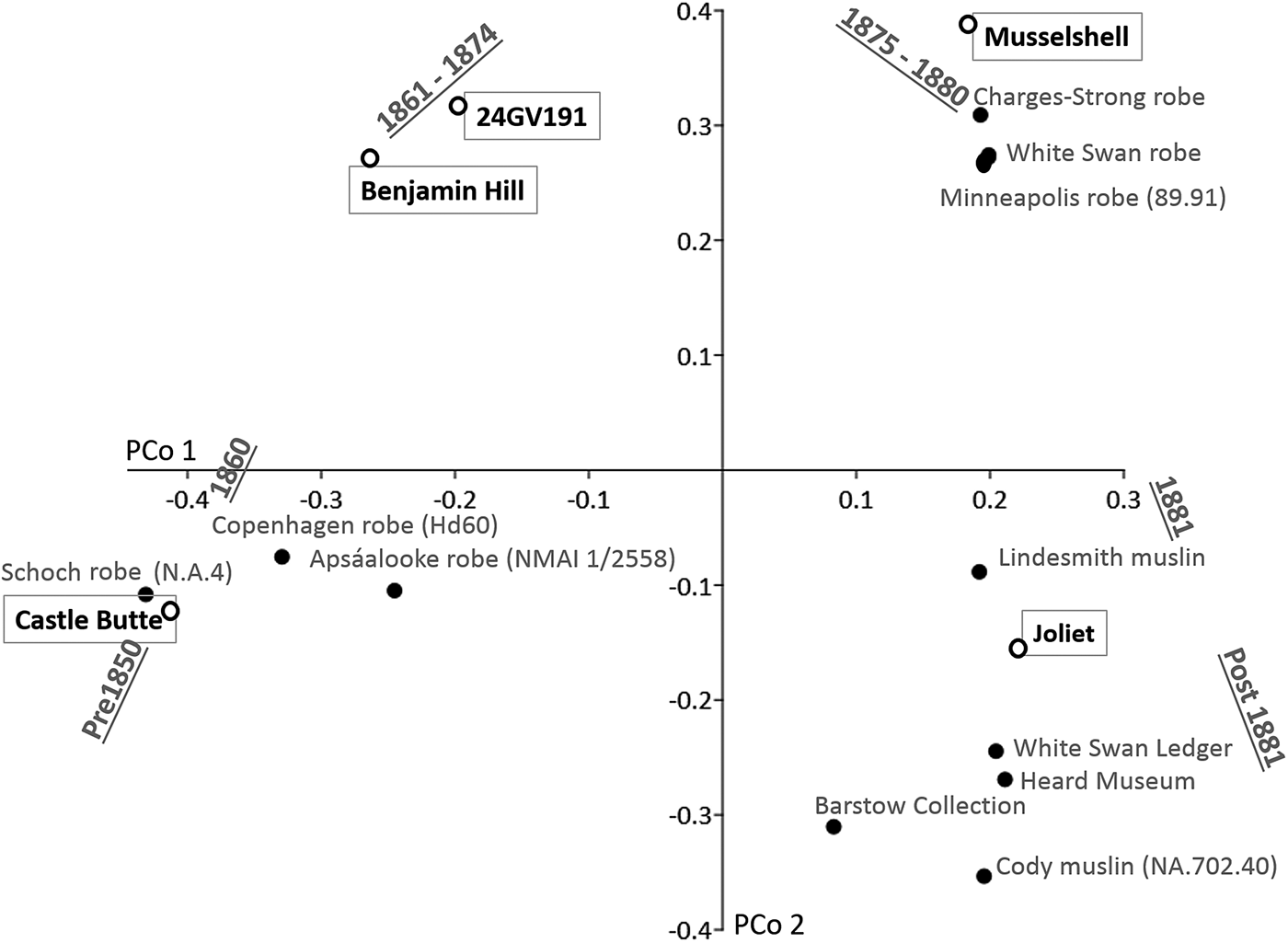
Figure 8 shows the results of the PCo analysis. The portable biographic artworks of different dates are clearly placed in different sections of the graph in a broadly arch-shaped manner. For instance, the oldest robes are placed in the lower-left quadrant, with the Schoch robe (c. 1837) at the very left edge. The slightly later Copenhagen and Apsáalooke robes, dating before 1861, are also in this quadrant. The robes of circa 1875–1880 (i.e., the Minneapolis, Charges-Strong, and White Swan robes) are placed in the upper-right quadrant of the plot, whereas the Lindesmith muslin of about 1881 is placed below these and closer to a group that represents works of post-1881.
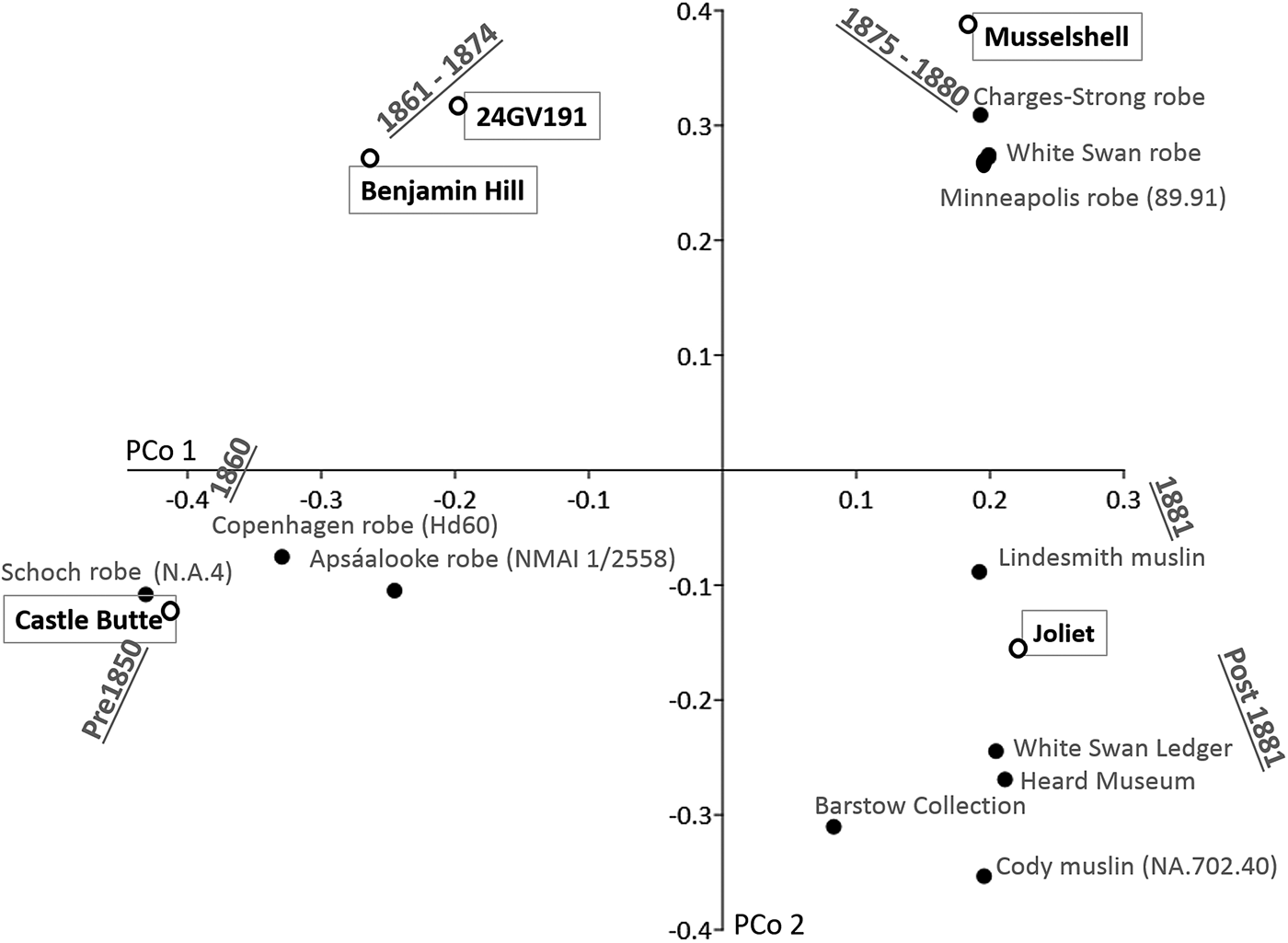
Figure 8. Principal coordinates (PCo) plot showing relationships between rock art sites and dated biographic artworks based on the inputted stylistic data. Rock art sites are indicated by open circles, portable artworks by closed circles (dots). PCo 1 explains 63% of the variation among items, whereas PCo 2 explains 10.4% of the variation. All remaining coordinates explain less than 8% of the total variation.
Given this distribution, the relative position of the five rock art sites would indicate they were drawn across a span of differing decades during the nineteenth century (Figure 8). The Castle Butte imagery is placed closest to the Schoch robe, consistent with a pre-1850 date and probably close in age to that of the Schoch robe itself. Along PCo 1, which illustrates the primary axis of variation, both Benjamin Hill and 24GV191 plot closer to the Copenhagen and Apsáalooke robes, but they also pull away from these robes on the second axis (i.e., PCo 2). Based on this result, two possible interpretations might be suggested for the positioning of these two rock art sites. One possibility is they fall into a date range of around the late 1860s to the early 1870s for which there are little well-dated comparative robe/ledger data. That is, they are not “outliers” but fall exactly where they might be expected to in a broadly parabolic arch-shaped seriated sequence, if they fall into the 10–14 years or so of space (i.e., c. 1861–1874) for which there is no comparative portable art. This dating is likely because they lack the conical headgear and the V-neck and striped-bodied human forms seen on the Copenhagen or Apsáalooke robes. A second possibility is that these sites may be closer in date to the Copenhagen and Apsáalooke robes (i.e., c. 1850–1861) than they appear, but as rock art sites they tend to “pull” away from the main group in the PCo if differences in media conspire to alter stylistic features. That is, V-neck forms and striped-bodied humans might hypothetically be more difficult to draw on rock art than their robe counterparts and thus less likely to be included. However, this seems unlikely given that well-formed V-neck humans and striped-bodied humans are represented at Castle Butte. Either way, the analysis conservatively narrows their chronology to a 25-year period of about 1850–1875 and, given their position on the PCo and the considerations outlined, in all likelihood to a 15-year period of about 1860–1875. The inferred age of the Musselshell scene would be about 1875–1880. Joliet is placed in the quadrant containing robes dating after 1881, suggesting it is the youngest of the five sites we examine here. Notably, it is placed away from the robes of about 1875–80 and plots closest to the Lindesmith muslin of 1881. Accordingly, this result would be most consistent with a date after 1881 but most likely early within the 1880s.
Given the PCo results, we constructed a hypothetical chronological sequence for all the biographic artworks and tested its statistical significance using occurrence seriation analysis. The results of this analysis shown in Figure 9 produced a high seriation index (0.79), which is highly statistically significant (p < 0.0001). Figure 9 also illustrates the proposed sequence of stylistic changes in different features of the Crow artworks during the course of the nineteenth century.

Figure 9. Occurrence seriation of items based on the proposed temporal sequence for both portable artworks and rock art sites. Portable artworks are positioned according to their known dates, and rock art scenes are positioned based on their estimated date through their placement in the PCo analysis. Traits (columns) are arranged to maximize their fit along the diagonal (see text for discussion).The seriation index is 0.79, which is highly statistically significant (p < 0.0001). (Color online)
Discussion and Conclusions
Some 35 years ago, Conner laid down a challenge, stating that not only was there a need to provide a missing stylistic and chronological link between Crow rock art and its robe art equivalents but also that such a link would “probably never be found” (Reference Conner1984:136). Our study has empirically tackled this steep challenge head-on, using data from portable Crow artworks to provide a chronological framework that not only permits five Crow rock art sites to be better placed in temporal sequence but also helps us see some of their stylistic details within the overall context of changing patterns that occurred during the nineteenth century.
Figures 9 and 10 are important because they illustrate how the rock art sites fit within different stylistic phases that have previously been documented in Crow biographic artworks. Castle Butte is in the “early robe art” Crow style (sensu Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2019) with its simply drawn horses and faceless humans. Benjamin Hill and 24GV191 are also both part of the early robe art style, but of a later date. These forms are distinct from the “late robe art style” best typified by the Minneapolis, Charges-Strong, and White Swan robes, as well as the imagery from Musselshell. In this phase there is the more regular and more detailed occurrence of facial features in the scenes' participants, but the art lacks all of the details seen in the full ledger style (Figures 9 and 10). Joliet, meanwhile, falls squarely within the “ledger art style” of Crow biographic imagery, containing many details (e.g., stirrups, revolvers, and more realistic portraiture) not generally seen in earlier works.

Figure 10. The evolution of stylistic details in Crow biographic imagery.
Both the PCo analysis and the occurrence seriation analysis indicate that the imagery we examined at Castle Butte is pre-1850 and was most likely drawn around the 1830s. This is a time when lifeways within the Crow tribe were influenced by increased numbers of horses and firearms, the effects of which were exacerbated by the burgeoning fur trade on the Northern Plains (Hoxie Reference Hoxie1995). To the authors of the imagery at Castle Butte and to the wearer of the Schoch robe that dates to around the same time, the reservation life in place by the end of the nineteenth century would have seemed inconceivable.
A slightly later generation of Crow artists, most likely after 1860, inscribed the petroglyphs seen at 24GV191 and Benjamin Hill. New features—unknown to Crow artists before 1850—were used by the artist at 24GV191: they included exaggerated fetlocks on horses' hooves and a more natural depiction of the jawline. Notably, one of the artists at Benjamin Hill was still using the traditional Crow-style capture hand convention to illustrate the capturing of an enemy's weapon (Figure 3). As we have noted elsewhere, this convention likely had gone out of use by the 1870s, and its disappearance may well indicate shifting attitudes that were part of wider societal changes as the Crow entered the final third of the nineteenth century (Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2019). It must also be noted that another artist at Benjamin Hill incorporated simple facial features into one human figure in the form of tear-streak face paint on one of the participants in the scene (Figure 3). This may be one of the earliest occurrences of facial features drawn in Protohistoric/Historic period Crow biographic artworks, which in the earlier nineteenth century had included only faceless human forms. Biographic images like those at Benjamin Hill had, as one of their primary purposes, the illustration of the deed being done, rather than identification of a specific person, so the people are actors in a narrative and facial features are uncommon in early examples (Keyser Reference Keyser1987:48–50). Conversely, many earlier Late Prehistoric period shield bearers also attributed to Crow people (Keyser and Poetschat Reference Keyser and Poetschat2014:120–122; McCleary Reference McCleary2016:59–63) had facial features, but these warriors were drawn for iconic/ceremonial purposes, and the aim of these features was to personalize them as real people, rather than actors in a narrative (Keyser and Poetschat Reference Keyser and Poetschat2014:40).
Carocci (Reference Carocci2017) has argued that the more realistic depiction of human faces in Plains artwork may indicate changed perceptions on the part of the artists. During the turbulent nineteenth century, Crow society saw marked changes in features of their broader environment, such as the expansion (and later decline of) the fur trade, the increased encroachment of Europeans, growing hostilities with neighboring tribes, and the eventual shift to reservation life (Hoxie Reference Hoxie1995). Several of these factors inevitably underlie some of the changing features observed in biographic artworks as the nineteenth century progressed (Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2019). Although the facial features at Benjamin Hill are subtle and human forms are still largely portrayed in a more traditional manner, the incorporation of these features may allude to the wider changes going on in Crow society during the 1860s, which included their allying with the U.S. military in 1866 as part of the offensive against the Lakota (Hoxie Reference Hoxie1995). Given the occurrence of faces in earlier Crow iconic/ceremonial art, their apparent abandonment, and their reemergence in this later Crow biographic art, it is plausible that the personalization of figures in this later biographic art may have been a direct result of their developing a closer relationship with Euro-Americans.
The artists at Joliet and Musselshell were visually describing historical events in a societal context that would have seemed very different from that experienced by the artists at Castle Butte. Indeed, the Joliet imaginary may have seemed “alien” or “foreign” to these early-nineteenth-century warriors (compare Figures 2 and 6). The 50 or so years that had passed between the laying down of imagery at Castle Butte and the inscribing of tribal history at Joliet had seen the Crow cede land to the U.S. government in the 1860s, increased reliance on government agency supplies in the late 1870s, the demise of the old nomadic lifeways, and the definite commencement of the “reservation” era by the time the 1880s were underway (Hoxie Reference Hoxie1995; Voget Reference Voget and DeMallie2001). Our analysis suggests that the imagery at Joliet was drawn in the early 1880s, placing it closest to the Lindesmith muslin of 1881. This is particularly important because it highlights the capacity of our method to tie rock art to historically and ethnohistorically documented events. The Hot Dance scene at Joliet demonstrates this acutely (Figure 6a). Given that the Hot Dance has long been a subject of interest among nonindigenous chroniclers of Crow history (e.g., Lowie Reference Lowie1935:206–213; Wildschut Reference Wildschut1928), the panel at Joliet has attracted attention for its capacity to tie archaeological imagery to documented events, especially the transfer of this dance from the Hidatsa to the Crow (Keyser and Cowdrey Reference Keyser and Cowdrey2008; Keyser et al. Reference Keyser, Sundstrom and Poetschat2006; McCleary Reference McCleary2008b; Reference McCleary2016). As detailed by McCleary (Reference McCleary2016:117–119), there is strong ethnohistorical evidence that knowledge of the Hot Dance came to the Crow from the Hidatsa in 1882, probably during the fall of that year, and that the panel at Joliet documents its reception by the Crow. The results of our analysis provide archaeological confirmation of this.
As mentioned, we used the method described here in three earlier studies to provide chronological assessments for Blackfoot robe and rock art (Keyser and Lycett Reference Keyser and Lycett2019; Lycett and Keyser Reference Lycett and Keyser2017, Reference Lycett and Keyser2018). This method also offers exciting possibilities for future research not only with additional Crow rock art but also with pictographs and petroglyphs from other areas of the world. On the Northern Plains, for example, a study currently in progress is attempting to expand these methods to several other, less well-known sites with Crow rock art. Likewise, given the quantity of detailed portable art and rock art attributed to Cheyenne and Lakota artists from the Black Hills region of the Northwestern Plains, that art also seems to be a likely candidate for a similar analysis. We are also optimistic that our method can be modified for use in other areas. In principle, the method might be adapted for rock art in any region of the world where the presence of dated historical items and imagery can be compared directly with the rock art sites that yield similar images. Published information on Asian rock art sites as far afield as Oman (Fossati Reference Fossati2015), Kazakhstan (Hermann et al. Reference Hermann, Zheleznyakov and Maryashev2013), Iran (Nejad et al. Reference Nejad, Salehi and Veisi2012), and China (Demattè Reference Demattè2004), for instance, suggests they contain imagery that might be analyzed using this type of approach.
In other areas of the world, the approach might also be slightly modified for further applications. For example, the introduction of various Mesoamerican trade goods and concepts (e.g., Tlaloc, Spider Woman, Knife Wing/Morning Star, and others) and new ceramic designs into the rock art of the late Jornada and Pueblo III–IV cultures of New Mexico and surrounding regions (Schaafsma Reference Schaafsma2000) might provide features amenable to these forms of analysis. Further refinement of the dating of Southwestern rock art sites with the help of information from kiva murals, painted potsherds, and native historic documents from various Mesoamerican sources has the potential to yield new insights into the origin and expansion of the Kachina complex and of warfare among the Pueblos (Schaafsma Reference Schaafsma2000, Reference Schaafsma2013; Schaafsma and Schaafsma Reference Schaafsma and Schaafsma1974).
In sum, the methodological framework we have begun developing provides a promising means of placing Crow rock art sites more accurately within their chronological, social, and stylistic contexts (Figure 10). There are, however, ways in which this initial effort might be further developed. Most notably, as more Crow artworks—both rock art and portable examples—are examined, it may be necessary to expand the range of features analyzed, especially once pre-nineteenth-century (i.e., pre-robe art) imagery is more fully incorporated into such analyses (Figure 10). Sadly, there is a notable dearth of biographical Crow portable artworks from around the decade of about 1865–1875, which might provide valuable insights at a critical phase in Crow tribal history. Should such artworks come to light, they might provide a means of tightening the chronology for rock art sites such as 24GV191 and Benjamin Hill even more. However, there is ample evidence that this framework provides an objective means of stylistically and chronologically comparing Crow biographic rock art to Crow portable artworks, which can more fully allow the incorporation of rock art into the wider discussion of how these works provide a window into Crow tribal history during the nineteenth century.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the editor and three reviewers, including Tim McCleary, for their time and constructive comments on the text. We also thank Mavis and John Greer, George Stoll, Stu Conner, and Bonnie Smith for providing images used in this research. We thank Marisa Giorgi for the Spanish translation of the abstract.
Data Availability Statement
Data are provided in the supplemental materials, Figure 9, and the sources cited in Table 1.
Supplemental Materials
For supplementary material accompanying this article, visit https://doi.org/10.1017/aaq.2019.48
Supplemental Text 1. Portable Biographic Artworks Used in the Analysis.
Supplemental Table 1. Data Matrix (Jaccard distances) Used for Analysis.