Introduction
Treatment of chronic tinnitus is a challenging problem. Many different treatment modalities have been reported, but so far none has significantly improved tinnitus. In recent years, low power laser therapy has been widely used in the treatment of tinnitus. This treatment has previously been reported to be useful for wound healing, musculoskeletal diseases and pain control.Reference Basford1–Reference Walker, Akhanjee, Cooney, Goldstein, Tamyoshi and Sgal-Gidan4 Published studies give conflicting success rates, from 80 per cent to no significant improvement in the relief of tinnitus.Reference Wilden and Dindinger5, Reference Mirz, Zachariae, Andersen, Nielsen, Johansen and Bjerring6
In this study, we tested the efficacy of a new, low power (5 mW) laser device, used on a short treatment schedule, in the treatment of chronic tinnitus. Results were compared with those of previous studies.
Subjects and methods
The study was commenced after obtaining the approval of the institutional review board. All patients consented to participate in the study after being informed of the potential benefits and risks of the procedure.
The study included 66 ears of 45 patients (18 women and 27 men) between the ages of 25 and 77 years (mean 55.8 years) with chronic unilateral or bilateral tinnitus. The average duration of tinnitus was eight years (range six months to 25 years). Subjects were randomised to either the active or the placebo treatment group. Assignment to either group was made by staff operating the laser. Patients who were judged to be suitable for the study were assigned to either group alternately, up to the 30th patient. The following 15 patients were included in the active laser group. Patient assignment was not known by the staff responsible for evaluating the outcome. Similarly, the patients were unaware of which group they were in. Both active and placebo laser was administered in the same sessions in a similar manner.
Laser device and procedure
The Tinnimed® laser device (HT International, Pforzheim, Germany) was used to irradiate the cochlea via the external auditory meatus. This device has three parts: a laser source, an optical fibre for transporting the laser beam from its source to the external auditory canal, and an ear piece (Figure 1). The ear piece is positioned in the external auditory canal and aligned towards the tympanic membrane and the promontory, in order to direct the laser beam to the cochlea. An adjustable ear clip firmly holds the ear piece on the left or right ear. The device's laser safety class is 1 M and the tissue penetration length is 1.6 cm.
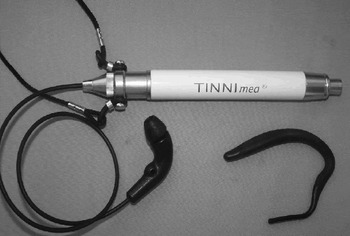
Fig. 1 The Tinnimed® laser device.
The active laser was used to irradiate 45 ears in 30 patients. In this group, the laser output was 5 mW and the wavelength was 650 nm. The cochlea was irradiated via the external auditory meatus for 15 minutes once daily for a week.
In the placebo group, dummy laser irradiation was performed using the same technique as for the active laser treatment, except for the activation of the laser beam. The placebo treatment was performed on 21 ears in 15 patients.
All patients were questioned about chronic aspirin and ototoxic drug consumption, acoustic trauma, chronic ear disease and vertigo. A detailed physical examination was performed, including a comprehensive otological examination. A complete blood count, biochemical profile and urinalysis were performed before treatment.
A questionnaire adapted from a previous study by Shiomi et al.8 (Table I) was used to assess subjective improvement in patients' tinnitus symptoms, i.e. loudness, duration and degree of annoyance of tinnitus. The patients were asked to use the questionnaire to indicate the severity of their tinnitus prior to the procedure and two weeks after the final laser treatment, using a five-point symptom scale for loudness, duration and degree of annoyance of tinnitus.
Table I Questionnaire Rating Scale for Loudness, Duration and Degree of Annoyance of Tinnitus

Adapted with permission
Audiological assessment, including pure tone audiometry, speech audiometry, tympanometry and acoustic reflexes, was performed using a clinical audiometer (AC40, Interacoustics, Assens, Denmark) prior to and two weeks after completion of treatment.
All patients were asked to observe and describe any side effects experienced during and after laser treatment.
Exclusion criteria comprised the presence of objective tinnitus, acute acoustic trauma, otosclerosis, chronic suppurative ear disease and perforated tympanic membrane. Patients with tinnitus of less than six months' duration were also excluded from the study. Patients taking medication for tinnitus were accepted into the study one month after they had ceased their medication, if they still had tinnitus.
A decrease of one scale point, on the questionnaire scales for loudness, duration and degree of annoyance of tinnitus, was accepted as an improvement. The results of the questionnaire and the audiological tests were evaluated by the chi-square test.
Results
Biochemical analysis revealed elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rates in three patients and raised total cholesterol and triglyceride levels in four patients. Two patients who had been receiving low dose acetylsalicylic acid had ceased this medication one month before the study; both these patients had suffered from tinnitus before taking the drug. None of the biochemical findings seemed to be related to tinnitus.
The new laser unit was used without any technical problems. The procedures were performed in all patients, without major complications or side effects. No pathological changes were seen at the external ear canal and the tympanic membrane of the irradiated ear. The transmeatal low power laser was tolerated well by all patients. Patients did not report any sound or sensation during or after treatment, as the device emitted no sound or heat during active or inactive periods.
Questionnaire results
The reported improvements in tinnitus rating after treatment with active laser are shown in Table II. Patients' loudness, duration and degree of annoyance of tinnitus were respectively improved in up to 48.8, 57.7 and 55.5 per cent. One patient in this group reported that his tinnitus had disappeared following treatment.
Table II Effect of Laser on Tinnitus*

* In active laser group, n = 45.
In the placebo group, patients' loudness, duration and degree of annoyance of tinnitus were respectively improved by only 19, 14.3 and 19 per cent. One subject in this group experienced worsening of his tinnitus.
The differences between the two groups' ratings were statistically significant (p < 0.05) (Tables III to V).
Table III Improvement in Tinnitus Loudness by Group

*Percentage of row data; †percentage of column data. n = patients
Table IV Improvement in Tinnitus Duration by Group

*Percentage of row data; †percentage of column data. n = patients
Table V Improvement in Degree of Annoyance of Tinnitus by Group

*Percentage of row data; †percentage of column data. n = patients
Audiology results
Before treatment, of the 66 ears, 36 had both tinnitus and hearing loss (23 sensorineural and 13 mixed) whereas 30 had only tinnitus (with normal hearing levels of between 0–25 dB). No serious audiological complications were encountered, except for two patients whose hearing levels decreased post-treatment by 10 dB. One of these patients was in the active group whereas the other was in the placebo group. Three other patients in the active laser group had increased hearing thresholds post-treatment (less than 6 dB) (hearing threshold increases of less than 10 dB were not accepted as a complication). Despite impaired hearing, the duration and degree of annoyance of tinnitus improved in all these patients. There was a tendency for tinnitus loudness scores to be greater in patients with worse hearing thresholds in both groups. There was no statistically significant difference between the hearing levels of the two groups (p > 0.05).
Discussion
The mechanism of action of low power laser on the inner ear and on tinnitus is not well understood. With regard to the metabolism of cells, non-invasive, low power laser acts very positively by enhancing oxidative activity and protein synthesis.Reference Chomete, Auriol and Zeitoun7, Reference Shiomi, Takahashi, Honjo, Kojima, Naito and Fujiki8 Various authors have reported laser-induced effects on cell proliferationReference Abergel, Lyons, Castel, Dwyer and Uitto9–Reference Hans, Breugel and Bar11 and on adenosine triphosphateReference Passarella, Casamassima, Molinari, Pastore, Quagliariello and Catalano12 and collagen synthesis,Reference Lam, Abergel, Castel, Meker, Dwyer and Uitto10 as well as a decrease in hypoxic injury and reductive stressReference Zhu, Wei, Jang, Hichks, Lanzafame and Wang13 and a release of growth factors.Reference Yu, Naim and Lanzafame14 The effects of low power laser are reported to be biophysiological rather than thermal.Reference Nakashima, Ueda, Misawa, Suzuki, Tominaga and Ito15 In animal experiments, the amplitude of the compound action potential was reduced after low power laser irradiation of the cochlea directly through the round window.Reference Shiomi, Takahashi, Honjo, Kojima, Naito and Fujiki8 Another proposed mechanism is blood flow increase associated with suppression of the sympathetic nerve action potential.Reference Schaffer, Bonel, Sroka, Schaffer, Busch and Reiser16 Low power laser has been suspected to improve local microcirculation and to increase oxygen supply to hypoxic cells.Reference Nakashima, Ueda, Misawa, Suzuki, Tominaga and Ito15, Reference Simunovic17 Despite an abundance of data, there seems to be a lack of animal studies investigating the effects of low power laser on the cochleovestibular system, for example regarding cochlear microphonics, auditory brainstem responses or histological alterations. Further studies could be performed using an animal model of tinnitus to test how low power laser affects the inner ear and improves tinnitus.
Previous studies evaluating low power laser for the treatment of tinnitus have been equivocal, with both positiveReference Wilden and Dindinger5, Reference Shiomi, Takahashi, Honjo, Kojima, Naito and Fujiki8, Reference Hahn, Sejna, Stolbova and Cocek18 and negativeReference Mirz, Zachariae, Andersen, Nielsen, Johansen and Bjerring6, Reference Nakashima, Ueda, Misawa, Suzuki, Tominaga and Ito15 effects reported. Shiomi et al. treated tinnitus using low power laser irradiation (40 mW with a wavelength of 830 nm) via the external auditory meatus; 60 per cent of their patients improved, without any reported complications.Reference Shiomi, Takahashi, Honjo, Kojima, Naito and Fujiki8 One uncontrolled laser study reported beneficial effects of low power laser irradiation on tinnitus in over 75 per cent of 139 patients.Reference Wilden and Dindinger5 Hahn et al. studied 120 patients suffering from chronic tinnitus and showed a relatively high rate of positive change in tinnitus status (50.8 per cent).Reference Hahn, Sejna, Stolbova and Cocek18
However, other studies of low power laser treatment have reported more controversial findings. Mirz et al. reported no statistically significant differences between laser (50 mW) and placebo groups in their double-blind, placebo-controlled study.Reference Mirz, Zachariae, Andersen, Nielsen, Johansen and Bjerring6 Nakashima et al. studied 45 patients, comparing low power laser and placebo laser, and found no statistically significant difference.Reference Nakashima, Ueda, Misawa, Suzuki, Tominaga and Ito15
In the present study, there was wide variation in patient parameters (i.e. age, duration of tinnitus and associated hearing loss). This was because we did not limit patient inclusion, other than by the exclusion criteria described above, as the tinnitus itself was of unknown but presumably multifactorial aetiology.
The therapeutic success rates for low power laser are controversial and subject to ongoing discussion. Differences in technical parameters, irradiation targets, treatment schedules and study designs make it difficult to compare the outcome rates for different studies. The biological effect of low power laser depends strongly on its wavelength and on proper positioning of the radiator, rather than on the power output.Reference Tauber, Baumgartner, Schorn and Beyer19 In the present study, a new device emitting very low power laser (5 mW) with a wavelength of 650 nm was used over a relatively short treatment schedule. Our results were similar to those of studies with higher success rates. The Tinnimed device used was portable, with no head set parts or desk units. We believe that easy to use devices and shorter treatment schedules make laser treatment more feasible for patients suffering from tinnitus.
• In recent years, low power laser therapy has become widely used in the treatment of tinnitus; reported success rates have ranged from 0 to 80 per cent
• This study investigated the efficacy of a new, low power (5 mW) laser device, in a short treatment schedule, in the treatment of chronic tinnitus
• This low power laser appeared useful for the relief of chronic tinnitus. However, further studies are required to optimise the laser treatment regimen and to exclude side effects
Sudden deafness and dizziness have been previously reported as side effects of laser treatment for tinnitus.Reference Nakashima, Ueda, Misawa, Suzuki, Tominaga and Ito15 We encountered mild hearing losses in two patients in the present study. However, it was not obvious whether this was caused by laser treatment, since one patient belonged to the active group and the other to the placebo group. The reason for these side effects is unclear and should be further examined using larger treatment groups.
Another question is whether low power laser confers any long term benefit. Patients were not followed up, on a methodological basis, after the present study. However, at the time of writing, those patients who had benefited from low power laser repeatedly reported that their tinnitus was improved compared with the pre-treatment period.
Conclusion
We performed a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind study to investigate the effectiveness of laser therapy for tinnitus, using a new device permitting very low power laser output, on a short term treatment schedule. This treatment method resulted in effective attenuation of the reported loudness (in 48.8 per cent), duration (in 57.7 per cent) and degree of annoyance (in 55.5 per cent) of patients' tinnitus. However, the potential therapeutic effects of low power laser on tinnitus are still obscure. Although our results are encouraging, further studies are required in order to optimise the laser treatment regimen and to exclude side effects.








