Introduction
Tortuosity of the internal carotid artery is a rare condition. It is important that head and neck surgeons recognise this anomaly because an abnormal carotid artery is a risk factor during pharyngeal procedures, both major (e.g. oropharyngeal tumour resection) and less extensive (e.g. tonsillectomy, adenoidectomy and peritonsillar abscess drainage by blade incision). This condition is often diagnosed on the basis of radiological examinations such as contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance angiography, and digital subtraction angiography. Several cases of a tortuous internal carotid artery presenting as a pharyngeal mass have been reported in the English language literature over the past 30 years.Reference Ricciardelli, Hillel and Schwartz1–Reference Prokopakis, Bourolias, Bizaki, Karampekios, Velegrakis and Bizakis8 In almost all the cases, the anomaly was on the right side. This right-sided predominance may be attributed to anatomical influences and factors affecting blood pressure. Furthermore, the typical causes of peripheral vascular disease (i.e. hypertension, hyperlipidaemia and smoking) are probably also contributory factors.
We report two cases of tortuous right internal carotid arteries presenting as tumourous pharyngeal masses.
Case report
Case one
An 86-year-old woman was referred to our hospital complaining of a slight throat pain and a foreign body sensation of several months' duration. She had a history of cerebral infarction and was being treated with Ifenprodil Tartrate.
On physical examination, the patient had a pulsatile mass on the right posterior wall of the oropharynx. Indirect laryngoscopy revealed a pulsatile, tumourous mass extending from the nasopharynx to the hypopharynx on the right side (Figure 1). The pharyngeal mucosa appeared normal. The results of other head and neck examinations (including cranial nerves) were unremarkable.

Fig. 1 Indirect laryngoscopic views showing (a) a pulsating mass extending from the nasopharynx to the hypopharynx on the right side, and (b) a pulsatile mass on the right posterior wall of the oropharynx.
A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the neck was performed, revealing an anomaly of the right internal carotid artery. The artery projected globally toward the right pharynx. The CT scan clearly showed the tortuous internal carotid artery at the tonsil level, with impingement on the posterior oropharyngeal wall (Figure 2).

Fig. 2 (a) Axial, contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) neck scan showing the internal carotid artery projecting globally toward the right pharynx. (b) Coronal, contrast- enhanced CT neck scan clearly showing the tortuous internal carotid artery at the tonsillar level, with impingement on the posterior oropharyngeal wall.
The patient was informed of the diagnosis, and no treatment was provided.
Case two
A 76-year-old woman presented to our hospital with a sensation of throat obstruction lasting several weeks. She had a medical history of arteriosclerosis obliterans of the legs and was being treated with Aspirin.
During ENT examination, endoscopy showed a pulsating, tumourous mass on the right posterolateral nasopharyngeal wall. There were no bruits over the nasopharyngeal or neck masses.
An MRI of the neck showed marked elongation and looping of the right internal carotid artery (Figure 3). No aneurysm or tumour was detected in the head and neck. The patient had no symptoms suggesting cranial nerve involvement (e.g. visual disturbance or transient ischaemic attacks) or cerebrovascular accident.

Fig. 3 Axial (a) and coronal (b) magnetic resonance imaging scans of the neck, showing marked elongation and looping of the right internal carotid artery. No aneurysm or tumour was detected in the head and neck.
The patient was informed of the diagnosis in detail. It was decided to manage her condition with observation only.
Discussion
Tortuosity of the internal carotid artery has long been recognised as an uncommon anomaly encountered during head and neck examinations. Otolaryngologists were the first clinicians to focus attention on this condition.Reference Johnson, Stambaugh, Richmond, Richmond and Balbuena3 Such internal carotid deformities are significant, especially to otolaryngologists and head and neck surgeons, as they may lead to haemorrhagic emergencies during tonsillectomy, adenoidectomy, major oropharyngeal tumour resection and peritonsillar abscess drainage by blade incision.
Internal carotid tortuosity, kinking and coiling can be either congenital or acquired.Reference Leipzig and Dohrmann9 The internal carotid arteries are formed in the embryo from the remnants of the third aortic arch and dorsal aortas, by the fifth week of development. When the fetus matures and elongates, the great vessels and the heart descend in the thorax. An aberration in this process results in redundancy of the internal carotid artery, and hence an anomaly of congenital origin.Reference Ricciardelli, Hillel and Schwartz1–Reference Johnson, Stambaugh, Richmond, Richmond and Balbuena3 However, the incidence of internal carotid artery tortuosity is higher in the elderly, which indicates that an acquired factor may be responsible.Reference Weibel and Fields10 The typical causes of peripheral vascular disease (i.e. hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, atherosclerosis and smoking) may contribute to the development of this anomaly. In addition, internal carotid artery tortuosity may then become more pronounced with age due to loss of vessel wall elasticity. In the elderly, such a deformity is commonly noted as elongation of the aorta and internal carotid artery.
We reviewed the literature on tortuous internal carotid artery presenting as a pharyngeal mass, and identified a total of 14 cases, including the above two cases, reported over the past 30 years (Table I).Reference Ricciardelli, Hillel and Schwartz1–Reference Prokopakis, Bourolias, Bizaki, Karampekios, Velegrakis and Bizakis8 The mean age of reported patients at diagnosis was 71.1 years (range, 56–86 years). There were six men and eight women (male to female ratio, 3:4). Complications of hypertension and atherosclerosis were present in four (28.6 per cent) and three (21.4 per cent) cases, respectively. Intravascular complications or complications of heart disease were present in nine cases (64.3 per cent); however, in three of these cases these complications were not described in detail.
Table I Reported cases of tortuous internal carotid artery presenting as pharyngeal mass

Pt = patient; y = years; F = female; M = male; R = right; L = left; Ca = carcinoma; IHD = ischaemic heart disease; CHD = coronary heart disease; HT = hypertension
• Tortuosity of the internal carotid artery is a rare condition, which appears to almost always affect the right side
• Head and neck surgeons should recognise this anomaly, as an abnormal carotid artery is a risk factor during both major (e.g. oropharyngeal tumour resection) and less extensive procedures (e.g. tonsillectomy, adenoidectomy and peritonsillar abscess drainage)
• This condition is often diagnosed from radiological examinations such as contrast-enhanced computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance angiography and digital subtraction angiography
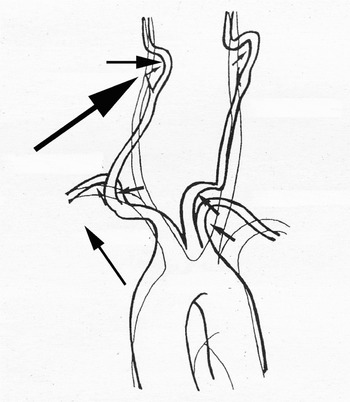
In 13 of the 14 reported cases (92.9 per cent), the anomaly was on the right side. At the point where the right common carotid artery arises from the brachiocephalic trunk, the artery is located close to the aorta and has higher blood pressure. Hypertension and atherosclerosis induce hypertrophy of the heart, which causes the aorta to be lifted up at right angles toward the head. Because the common carotid artery is fixed around the thyroid cartilage at the point of bifurcation, a force vector is created toward the midline. Thus, atherosclerosis of the internal carotid artery leads to formation of global projections of the vessel into the right retropharyngeal space, which has loose soft tissues (Figure 4). This may explain the right-sided predominance of this anomaly.

Fig. 4 Diagram explaining the right-sided predominance of tortuous internal carotid artery. Large arrow indicates a force vector created toward the midline, while small arrows indicates force vectors at each points of the arteries.
When tortuosity of the internal carotid artery is an isolated and asymptomatic finding, no treatment is necessary. However, head and neck surgeons should be aware of the possibility of this condition when providing clinical treatment. Patients should be informed of their condition, and this finding must be clearly documented in their health records for reference.