Introduction
At older ages, loneliness and social isolation are significant problems, and increasingly viewed as widespread health concerns (Hafner, Reference Hafner2016; Nutt, Reference Nutt2016). These factors are linked to depression and early mortality, especially in later life stages (Luo et al., Reference Luo, Hawkley, Waite and Cacioppo2012; Perissinotto et al., Reference Perissinotto, Stijacic Cenzer and Covinsky2012; Holt-Lunstad et al., Reference Holt-Lunstad, Smith, Baker, Harris and Stephenson2015; Pantell et al., Reference Pantell, Rehkopf, Jutte, Syme, Balmes and Adler2013). Alternatively, social connection and social support are strong predictors of wellbeing: individuals with larger and stronger networks are healthier and experience greater social support and reduced levels of cognitive decline than those with lower levels of social connection (KP Smith and Christakis, Reference Smith and Christakis2008; Seeman et al., Reference Seeman, Miller-Martinez, Stein Merkin, Lachman, Tun and Karlamangla2011; Cherry et al., Reference Cherry, Walker, Brown, Volaufova, Lamotte, Welsh, Su, Jazwinski, Ellis, Wood and Frisard2013).
Newer communication technologies, including social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter, have rapidly gained prominence because they enhance social connection and support weaker forms of relationships (Vitak, Reference Vitak2014). The use of social media is associated with higher levels of social connectivity and lower levels of loneliness among users (Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, Trenwith, Zubrinich and Corlis2010; K-T Lee et al., Reference Lee, Noh and Koo2013), perhaps because it encourages self-disclosure, which in turn leads to higher levels of social support (K-T Lee et al., Reference Lee, Noh and Koo2013). It is reasonable to anticipate that the use of social media may present an accessible and relatively low-cost mechanism to enhance social connection, and therefore life quality, at older ages.
Despite the linkage between social media and enhanced social connection, the association between social media and social wellbeing has not been widely explored for adults at older ages. Of studies that have been conducted, many focus on the benefits of social media activity in youthful populations (e.g. Grieve et al., Reference Grieve, Indian, Witteveen, Tolan and Marrington2013; Spiliotopoulos and Oakley, Reference Spiliotopoulos and Oakley2013). Other studies focus on older adults, but largely examine attitudes and perceptions toward socials media and its use (e.g. Hope et al., Reference Hope, Schwaba and Piper2014). Few studies permit causal conclusions between social media use and its effects (Nef et al., Reference Nef, Ganea, Müri and Mosimann2013), which is perhaps not surprising given the widespread adoption of these platforms. However, with only about one-third of all adults over the age of 65 years using social media (Anderson and Perrin, Reference Anderson and Perrin2017), older adults present a unique opportunity through which social media effects might be examined. With a relatively lower user base in this age group, social media use can be introduced in an experimental format such that effects of its use might be examined.
This paper reports on such a study, one which preliminarily explores the social wellbeing effects caused by social media use among older adults, aged 65 years and older. Using a ‘wait-list’ control design, novice social media users engaged in a four-week social media training workshop as an experimental intervention. Baseline assessment and multiple post-tests provided a framework to address the question, ‘Does the use of social media by older adults1 result in social benefits?’ These results are part of a larger pilot study that examines how social media technologies might be employed to offset health risk factors and improve health outcomes in an older population.
Social connection and age
Interpersonal connection provides individuals with intimacy, social integration, nurturing, reassurance of worth and assistance (Weiss, Reference Weiss1969). The relationship between one's social environment and health is quite strong (Kaplan et al., Reference Kaplan, Cassel and Gore1977; Uchino et al., Reference Uchino, Cacioppo and Kiecolt-Glaser1996), and numerous studies have explored the key dimensions of sociality that contribute to health. These include social support, or the provision of resources by an individual's social network (Wallston et al., Reference Wallston, Alagna, DeVellis and DeVellis1983); social integration, or participation in a broad range of social relationships (Seeman, Reference Seeman1996); and social connectedness, or the ways in which individuals interact (Cohen, Reference Cohen2004).
Maintaining social connection becomes more difficult in later life due to decreased physical mobility and the incidence of chronic disease, factors which occur at higher rates in the older adult population (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2013). Retirement and the death of spouses and friends reduce the quantity and quality of social relationships. While often welcome and necessary, transition to alternative living facilities, such as assisted care or independent living communities, can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and social isolation, as ties with neighbours and friends in the community become more difficult to maintain (Cummings, Reference Cummings2002; Winningham and Pike, Reference Winningham and Pike2007; Bekhet and Zauszniewski, Reference Bekhet and Zauszniewski2012).
In addition, older adults have smaller social networks and less-frequent contacts within their networks than younger adults (Lansford et al., Reference Lansford, Sherman and Antonucci1998; Cornwell et al., Reference Cornwell, Laumann and Schumm2008). Differences in size may result from the types of connections that are present within the network: older adult social networks contain fewer peripheral relationships than those of younger persons (Fung et al., Reference Fung, Carstensen and Lang2001). Some studies have also suggested that older adults have a stronger preference for close and familiar connections, and thus denser networks, than younger persons, reflecting a motivation to preserve emotional resources (Fredrickson and Carstensen, Reference Fredrickson and Carstensen1990). However, other studies suggest that older adults experience less relational closeness within their networks than younger adults, and that factors other than age, such gender or the absence or presence of a spouse, are more relevant to network density (Cornwell et al., Reference Cornwell, Laumann and Schumm2008).
These conflicting results draw attention to the limitations of merely using age as a measure in effects research. Age has historically represented the effects of three distinct dimensions of an individual's life trajectory: (a) ageing, or physical and cognitive changes associated with maturation; (b) period, or the influences that occur through time; and (c) cohort, or the unique socio-historical time into which an individual is born (Settersten and Mayer, Reference Settersten and Mayer1997). These dimensions are intersecting, and challenging, if not impossible, to tease apart (Bynner, Reference Bynner2016); thus, alternative approaches have sought to distinguish life trajectories across adulthood.
One such perspective is the lifecourse approach (Elder, Reference Elder1998; Giele and Elder, Reference Giele, Elder, Giele and Elder1998), which recognises that cohorts, or that group of individuals born at the same point in historical time, do not age in the same way. Rather, an individual's social and historical contexts, relationships, personal agency and major life events form a conceptual framework for explaining differences in outcomes (Giele and Elder, Reference Giele, Elder, Giele and Elder1998; Giele, Reference Giele2009). Consequently, lifecourse research seeks to identify the distinctive experiences that a cohort shares, and also the differential effects that cause differences between cohorts (Settersten, Reference Settersten2003).
Lifecourse studies often partition the life trajectory into three major phases: education and training, which encompasses the stages from infancy to independence and permanence in the workplace, usually ranging in age from birth to early/mid-twenties; continuous work, which usually ranges from the mid-twenties until early/mid-sixties; and leisure, or post-employment/retirement, usually ranging from mid-sixties until death (Settersten, Reference Settersten2003). A lifecourse approach to examining communication media would therefore focus on differences in the outcomes of using them, such as different patterns of social connectedness, and would seek to examine the ways in which use of these media are differentiated among those in different life phases.
Communication media and social wellbeing
Communication media play an important role in enhancing social wellbeing and connection. At older ages, the use of communication media is associated with reducing loneliness and increasing social contact (Cotten et al., Reference Cotten, Anderson and McCullough2013). Social media are newer forms of communication technology that support social connection and facilitate access to social resources by creating digital representations of an individual's social network and enabling communication between members of the network. Typically described as platforms, which are deployed through computers, tablets and smartphones, they have the potential to generate important psychological benefits for older users, as they afford the use of multiple communication modalities, which is linked to higher levels of psychological wellbeing at older ages (Chan, Reference Chan2014).
The use of social media is associated with social wellbeing and social connection among adults, more generally, and adolescents when used to foster community (Burke et al., Reference Burke, Marlow and Lento2010; Grieve et al., Reference Grieve, Indian, Witteveen, Tolan and Marrington2013; Allen et al., Reference Allen, Ryan, Gray, McInerney and Waters2014). Social media encourage sharing and self-disclosure, which in turn may lead to higher levels of social support (K-T Lee et al., Reference Lee, Noh and Koo2013). In younger user groups, social media use has been positively linked to the creation and maintenance of social capital, or access to social resources (Ellison et al., Reference Ellison, Steinfield and Lampe2007; Burke et al., Reference Burke, Marlow and Lento2010).
Evidence of negative consequences of social media activity on wellbeing is equivocal. At least one study has found that the use of social media is associated with depression and anxiety among younger adults, aged 19–32 years (Lin et al., Reference Lin, Sidani, Shensa, Radovic, Miller, Colditz, Hoffman, Giles and Primack2016), but other studies have found no significant linkage (Jelenchick et al., Reference Jelenchick, Eickhoff and Moreno2013; Aalbers et al., Reference Aalbers, McNally, Heeren, de Wit and Fried2019). Loneliness has been associated with social media use in university students in one study, possibly due to individuals seeking to compensate for limited offline relationships (Skues et al., Reference Skues, Williams and Wise2012), but another study found no relationship between social media use and loneliness (Dienlin et al., Reference Dienlin, Masur and Trepte2017).
Social media increase the ability to create and maintain weaker relationships (Vitak, Reference Vitak2014), and allow a larger number of connections to be maintained at once (Donath, Reference Donath2007). Because social media, and social network sites in particular, facilitate communication among one's connections (Whiting and Williams, Reference Whiting and Williams2013), they provide enhanced access to social resources which are provided within these relationships (Ellison et al., Reference Ellison, Steinfield and Lampe2007). Consequently, social network site users have more acquaintances, greater levels of face-to-face interaction and higher levels of bridging social capital than non-users (Steinfield et al., Reference Steinfield, Ellison and Lampe2008; Brandtzæg, Reference Brandtzæg2012). Social media also allow individuals to monitor a larger number of weak connections with reduced effort, thereby enhancing the potential for weak relationships to become stronger and more valuable with time (Levin et al., Reference Levin, Walter and Murnighan2011). Whether these benefits extend to users in older age groups has not been widely explored.
Older adults and social media
The popular press often portrays the use of information and communication technologies (ICTs) as primarily dominated by youth and young adults, and this is especially true with social media (e.g. Castillo, Reference Castillo2017). Recent studies indicate that older adults are rapidly adopting social media applications to communicate with friends and family, albeit at significantly lower rates than younger persons (Greenwood et al., Reference Greenwood, Perrin and Duggan2016). Studies on older adult use of ICTs have noted the presence of a ‘grey divide’ (Millward, Reference Millward2003), or a particularly steep drop-off in ICT use between those in the ‘younger-old’ group (i.e. those younger than 70 years) and those that are ‘older-old’, often characterised as age 70 years and above (Duggan et al., Reference Duggan, Ellison, Lampe, Lenhart and Madden2014; Greenwood et al., Reference Greenwood, Perrin and Duggan2016). Though noted specifically within internet use (Duggan and Brenner, Reference Duggan and Brenner2013; Friemel, Reference Friemel2014), this gap is quite pronounced with social media as well, as social media adoption rates, already relatively low in adults above the age of 65 years, drop precipitously beyond the age of 80 years (A Smith, Reference Smith2014).
Lower levels of engagement can result from preference, and especially from a lack of perceived relevance to everyday life. Perceived benefit is a strong motivational factor for the use of technology use by older adults generally (Czaja et al., Reference Czaja, Charness, Fisk, Hertzog, Nair, Rogers and Sharit2006; Sayago et al., Reference Sayago, Sloan and Blat2011), and a lack of perceived benefits have been cited by older adults as reason for not using social media platforms (Lehtinen et al., Reference Lehtinen, Näsänen and Sarvas2009; Sundar and Hirsch, Reference Sundar and Hirsch2011; Braun, Reference Braun2013; Lampe et al., Reference Lampe, Vitak and Ellison2013; Luders and Brandtzæg, Reference Luders and Brandtzæg2014). Social media platforms are often perceived by older adults as a lesser form of interpersonal interaction than more traditional communication forms (Lehtinen et al., Reference Lehtinen, Näsänen and Sarvas2009; Luders and Brandtzæg, Reference Luders and Brandtzæg2014) and they sometimes regard social media as a communication modality that is appropriate only for younger persons (Hope et al., Reference Hope, Schwaba and Piper2014).
Once the benefits of social media participation are recognised, adults at older ages are more likely to engage in use (Braun, Reference Braun2013). Connection with younger and extended family can be an important motivation for older adults to consider using social media (Sundar and Hirsch, Reference Sundar and Hirsch2011; Bell et al., Reference Bell, Fausset, Farmer, Nguyen, Harley and Fain2013; Luders and Brandtzæg, Reference Luders and Brandtzæg2014). However, because the value in using a particular social media platform is often predicated on the presence of one's friends and acquaintances also using that platform (Hargittai, Reference Hargittai2008; Hendler and Golbeck, Reference Hendler and Golbeck2008), the relevance of these media to older adults, who encounter lower levels of peer engagement, may be somewhat diminished (Yu et al., Reference Yu, Ellison and Lampe2018).
For older users, the use of social network sites has been associated with reduced feelings of loneliness (Burke et al., Reference Burke, Marlow and Lento2009; Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, Trenwith, Zubrinich and Corlis2010; Sheldon, Reference Sheldon2012) and enhanced feelings of social connectedness (Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, Trenwith, Zubrinich and Corlis2010; Bell et al., Reference Bell, Fausset, Farmer, Nguyen, Harley and Fain2013); however, studies until now have largely been observational and have not permitted causal conclusions. Research on the relationship between the use of social media and life quality is thin, but some studies have found that internet and social network site use are not linked to quality of life in later life (Slegers et al., Reference Slegers, Van Boxtel and Jolles2008; PSN Lee et al., Reference Lee, Leung, Lo, Xiong and Wu2010; Leung, Reference Leung2010; Sundar and Hirsch, Reference Sundar and Hirsch2011). Key to these results may be the lower participation rates in social media at older ages. With fewer available peer connections on a platform, social capital benefits may be less easily realised. In addition, lower usage rates also limit the types of individuals that can be studied, favouring the inclusion of novice social media participants (Leist, Reference Leist2013), who may need greater longevity in their social media platform use to derive social value.
Skills are another important component to lowered usage rates, as deficiencies in this area are also attributed as barriers to internet and technology use by older individuals (Aula, Reference Aula2005; van Deursen and van Dijk, Reference van Deursen and van Dijk2009). Older adults often cite a lack of skills, or lack of confidence in their own skills, as reason to not engage in social media platforms (Lehtinen et al., Reference Lehtinen, Näsänen and Sarvas2009; B Lee et al., Reference Lee, Chen and Hewitt2011; Luders and Brandtzæg, Reference Luders and Brandtzæg2014; A Smith, Reference Smith2014). Instructional and informational support has enabled older adults to build self-efficacy and skills with respect to ICT use, reducing anxiety and improving self-confidence (Rosenthal, Reference Rosenthal2008). The provision of instructional support similarly stimulates social media participation by older adults as well, reducing perceptual barriers and addressing skills deficiencies (Gibson et al., Reference Gibson, Moncur, Forbes, Arnott, Martin and Bhachu2010; Xie et al., Reference Xie, Watkins, Golbeck and Huang2012; Luders and Brandtzæg, Reference Luders and Brandtzæg2014).
In summary, significant benefits to health and wellbeing can arise through social engagement; yet at older ages, individuals may find social connection more difficult to sustain. The use of communication media is related to reduced levels of loneliness and enhanced social connection; social media, specifically, appear to function in this fashion with younger adult populations. Lifecourse theory establishes that outcomes related to social media use for older adults may be different from those experienced at earlier points in the life trajectory, so inquiry into whether similar benefits extend to adults at more advanced lifestages is justified. Older adults often face barriers to the use of newer communication media due to deficiencies in digital skills and knowledge; however, instructional support has been demonstrated to assist older adults to overcome these challenges and utilise social media.
Instructional support has an additional advantage from a research perspective, as such training can be used as an experimental manipulation to investigate the causal relationship between social media use and social wellbeing. This study attempts to explore the benefits of social media use by examining social media activity among a group of novice older adult users, employing a training workshop as an intervention. Specifically, three significant dimensions of social wellbeing are assessed: access to social resources, which is closely tied to the availability of social support; loneliness; and social connection.
Social media use has been tied to perceptions of access to social resources among younger adults, and often is examined as the construct social capital (Ellison et al., Reference Ellison, Steinfield and Lampe2007, 2014; Vitak et al., Reference Vitak, Ellison and Steinfield2011). Thus, the first research question addresses whether similar perceptions arise as a result of social media engagement with older adult users:
• RQ1: Does social media use result in perceptions of increased access to social resources for older adults?
Research on the use of social media and loneliness has had mixed results, with studies demonstrating that social media users have increased levels of loneliness (Brandtzæg, Reference Brandtzæg2012), reduced loneliness (Sheldon, Reference Sheldon2012), and no effect on loneliness in younger populations (Burke et al., Reference Burke, Marlow and Lento2010; Dienlin et al., Reference Dienlin, Masur and Trepte2017). The use of technology more generally (a combined measure of the use of social media, email, online chat, etc.) has been linked to reductions in loneliness among older adults (Chopik, Reference Chopik2016). Thus, further investigation of the effects of social media use specifically with an older population is meaningful. The second research question is therefore:
• RQ2: Does social media use result in reduced loneliness for adults at older ages?
Finally, studies have linked social media use to social connection in younger (Grieve et al., Reference Grieve, Indian, Witteveen, Tolan and Marrington2013) and older populations (Sinclair and Grieve, Reference Sinclair and Grieve2017), though causal relationships have not been established. Thus, the final research question probes the causal relationship between social media use and social connection:
• RQ3: Does social media use result in enhanced social connection for adults at older ages?
Method
To examine the potential social effects of social media use among older adults, a four-week social media training workshop was conducted as an exploratory experimental intervention. Six training workshops were administered in a randomised, wait list control design with novice social media users as participants (N = 47). The instructional workshops were devoted to helping participants learn how to use the social media platforms of Facebook and Twitter, with approximately 75 per cent (three sessions) devoted to Facebook use and 25 per cent (one session) devoted to Twitter use. In addition, the sessions addressed potential obstacles to social media adoption, and included training on digital literacy skills and education on perceptual barriers, such as concern about potential privacy violations. Approximately two months after completion of the final workshop, two debriefing focus groups (N = 14) were held to gather feedback on the workshop learning experiences and ongoing use of social media on an everyday basis. In addition, one-on-one interviews (N = 9) were held with individual participants to probe more fully the benefits and challenges of using social media associated with social media use. In addition to the linkage between social media use and social wellbeing, the study also explored the relationship between social media use and certain cognitive behaviours. This paper reports on findings with respect to the social outcomes.
Sample
Forty-seven participants were recruited through two sponsor independent living facilities (ILCs) in the Midwestern United States of America (USA) and included both residents of the ILCs and older adults living in nearby communities. The sponsoring facilities each provided meeting space for the workshop sessions and assisted in publicising the study to potential participants through newsletters and announcements in general programming in nearby communities. Inclusion criteria were: minimum age of 65 years; cognitively intact, as determined by the Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire; less than ten hours of Facebook use in the previous six months; and no visual impairment that would prevent viewing a computer screen. Eligible participants were randomised into either an intervention workshop group or ‘wait-list’ control group, which completed the workshop intervention after the study period concluded. Over the course of the study, six participants withdrew due to health considerations or family suggestion. In addition, five participants were unable to complete all three assessment visits; due to the nature of this analysis, data from these individuals were excluded from analysis.
The final participant group was comprised of 36 individuals, of whom 25 (69.4%) were female. Participant ages ranged from 67 to 86 years, with a mean of 76.8 years. Approximately 92.3 per cent of the participants identified as Caucasian, with 5.1 per cent African American and 2.6 per cent Hispanic. Participants were diligent social media learners, with more than 85 per cent of the sample attending all four workshop sessions. Table 1 summarises sample descriptives at baseline, broken down by control and intervention groups.
Table 1. Sample descriptives at baseline

Notes: SD: standard deviation. MMSE: Mini Mental State Examination. 1. Seven-point scale: 0 = never, 7 = multiple times per day.
Intervention
The social media training workshops were designed to improve participant social media skills and reduce perceptual barriers to social media use. Sessions were held in a classroom setting, using equipment supplied by the research team. Six workshop groups met once per week for four weeks, two hours per session (a total of eight classroom hours of instruction). Participants used individual laptop computers and visual support was provided via a screen and projector, which was connected to the instructor's laptop. Each session was led by the researcher, whose research activity is concentrated in social media and social networks; a research assistant was available for one-on-one support throughout the session for participants who requested additional assistance. Workshop sessions were scripted, to ensure comparability of the material between groups. Instructional topics included setting up an account and use of Facebook and Twitter, privacy and online security, social media etiquette, and the use of social media for messaging, photo sharing, status updates and information gathering. Approximately nine participants were enrolled in each workshop group. Participants were encouraged to use the Facebook and Twitter platforms outside the workshop sessions and throughout the study period.
Measures
Participants were assessed at three time intervals: at baseline (just prior to the start of the workshop), at four weeks (completion of the social media intervention workshop for the intervention group) and at four months (three months after workshop completion for the intervention group). In addition to demographic information, participants reported on their internet and social media use and overall health.
Access to social resources was measured in two ways: the resource generator (RG), as adapted for US populations (Vandergaag and Snijders, Reference Vandergaag and Snijders2005; Foster and Maas, Reference Foster and Maas2016), which includes sub-scales for expert access (RG-Expert), problem solving (RG-ProbSol) and personal support (RG-PerSup); and the internet social capital scale, which includes sub-scales for bridging (ISCS-Bridge) and bonding (ISCS-Bond) social capital (Williams, Reference Williams2006). RG was measured using a five-point Likert scale, with overall scores ranging from 21 to 105, with higher scores indicating greater access to resources; the RG-Expert (range 10–50), RG-ProbSol (range 7–35) and RG-PerSup (range 4–20) sub-scales similarly suggest greater access to resources at higher values. ISCS-Bridge and ISCS-Bond were also scored on five-point Likert scales, with scores ranging from 10 to 50 and higher scores indicating greater access to social resources. Loneliness was measured using the UCLA loneliness scale, Version 3 (Russell, Reference Russell1996), with scores ranging from 20 to 80 and higher scores revealing higher levels of loneliness. Finally, two dimensions of social connection were assessed: the social connectedness scale (RM Lee and Robbins, Reference Lee and Robbins1995); and perceptions of social integration, using the social integration sub-scale of the social provisions scale (Cutrona and Russell, Reference Cutrona, Russell, Jones and Perlman1987). Scores on social connectedness ranged from 8 to 48, with lower scores indicating greater levels of social connectedness. Social integration was scored from 4 to 16, with higher scores indicative of higher levels of social integration. Examples of items for all of these scales can be found in the online supplementary material.
Results
Data were analysed using a repeated-measure, between-groups analysis of variance (mixed ANOVA) in SPSS v25.0.0.1 to determine effects of the social media workshop. Baseline measurements were used as the initial measure for the analysis.
Internet and social media use
Participants in both the control and intervention groups reported no significant difference in their internet use over the study period at either the four-week or four-month assessment points. As anticipated, the workshop intervention was successful at increasing social media use among the intervention participants. Intervention participants reported a statistically significant increase in social media use from the baseline average of 6.0 minutes per week to an average of 25.5 minutes per week (t = 2.89, p = 0.016, d = 0.87). Reported social media activity declined after the intervention workshops ended, however, as participants reported an average of 17.5 minutes per week at the four-month assessment. Over the entire four-month study period, however, those participating in the intervention reported a significant overall increase in their social media use over the baseline (within group analysis: t = 2.45, p = 0.034, d = 0.74). While social media use increased over the study period for intervention participants, we noted that overall internet use did not increase significantly. This may have occurred because social media usage may substitute for other forms of general internet use, such as email or visiting news sites.
Access to social resources
To explore RQ1, or the effects of the social media intervention on perceived access to social resources, Table 2 provides a summary the means and standard deviations for each of RG, including sub-scales for RG-Exp, RG-ProbSol and RG-PerSup, and ISCS-Bridge and ISCS-Bond broken down by the control and intervention groups across the three measurement periods.
Table 2. Perceived access to social resources
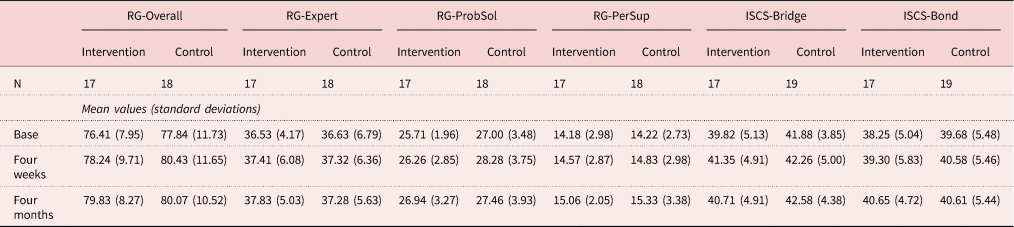
Notes: RG: resource generator, which includes sub-scales for expert access (RG-Expert), problem solving (RG-ProbSol) and personal support (RG-PerSup). ISCS: internet social capital scale, which includes sub-scales for bridging (ISCS-Bridge) and bonding (ISCS-Bond) social capital.
In response to RQ1, results did not demonstrate that social media use resulted in increased perceived access to social resources. As shown in Table 3, after adjusting for baseline scores, there was no significant interaction between the intervention and time for any of the measures of perceived access to social resources and no significant main effects for the intervention. Both groups evidenced a statistically significant improvement on perceived access to overall resources (RG-Overall F 2,66 = 3.19, p = 0.048, ηp2 = 0.09) and bonding social capital (ISCS-Bond F 2,68 = 3.29, p = 0.04, ηp2 = 0.09) over the study period, and we explain this increase as an effect of participating in the study. Comparative results provide no support for a conclusion that social media use provides increased perceived access to social resources for adults at older ages. It should be noted that RG data for one participant in the control condition was not collected during the second visit, so the RG analysis was conducted with N = 35 cases of data.
Table 3. Effects of intervention on perceived access to social resources

Notes: RG: resource generator, which includes sub-scales for expert access (RG-Expert), problem solving (RG-ProbSol) and personal support (RG-PerSup). ISCS: internet social capital scale, which includes sub-scales for bridging (ISCS-Bridge) and bonding (ISCS-Bond) social capital. 1. Greenhouse-Geisser correction was used.
Significance level: * p < 0.05.
Loneliness
RQ2 examines whether social media use by older adults reduces feelings of loneliness. After adjusting for baseline measures, there was no significant interaction between the intervention and time (F 2,68 = 0.75, p = 0.48, ηp2 = 0.02) and no significant main effects for the intervention (F 1,34 = 1.00, p = 0.32, ηp2 = 0.03) in reported feelings of loneliness. Both groups experienced significant improvements (decreases) in perceived loneliness over the study period (F 2,68 = 61.58, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.64), again potentially explained by participation in the study. Summarised in Table 4, these results provide no support for the conclusion that social media use reduces feelings of loneliness among this group of older adults.
Table 4. Effects of intervention on perceptions of loneliness

Significance level: *** p < 0.001.
Social connection
RQ3 interrogated whether the use of social media by older adults results in greater levels of social connection, as measured by the social connectedness and the social integration scales. The results of these analyses, along with the means and standard deviations for both the control and intervention group across the three measurement periods are summarised in Table 5.
Table 5. Effects of intervention on social connectedness and social integration

Significance level: ** p < 0.01.
Unlike the other measures of social wellbeing, analysis of the social connection measures provided conflicting results. Measures of social connectedness demonstrated no main effects for time (F 2,68 = 1.12, p = 0.33, ηp2 = 0.03) or the intervention (F 1,34 = 1.13, p = 0.30, ηp2 = 0.03), and no interaction effects (F 2,68 = 1.09, p = 0.34, ηp2 = 0.03) across the study period. Likewise, the social provisions/social integration measure demonstrated no main effects for the intervention (F 1,34 = 1.80, p = 0.19, ηp2 = 0.05) and a very weak main effect for time (F 2,68 = 2.68, p = 0.08, ηp2 = 0.07). A statistically significant effect was noted for the interaction of the social media workshop and time (F 2,68 = 5.75, p = 0.005, ηp2 = 0.15), however. This suggests that enhanced feelings of social connection when using social media depends on time, which logically makes sense. Figure 1 provides a plot of the means for social integration over the three measurement periods. Further analysis of the interaction's component parts reveals that a significant difference in feelings of social integration occurred during the workshop phase of the study, that is between the baseline and workshop completion measurement stages (F 1,34 = 0.29, p = 0.59, ηp2 = 0.14), and not in the post-workshop phase (F 1,34 = 5.35, p = 0.027, ηp2 = 0.01). It is possible that this improvement may stem from participation in the workshop group itself, and not from social media use. Notably, the intervention group started with a somewhat lower baseline measure of social integration, which increased during the workshop period to levels close to the control group.

Figure 1. Estimated marginal means of social integration.
Despite the measures of social connection appearing somewhat contradictory, the interaction effect between the social media workshop and time in the social integration measure lends some support to the idea that novice users may need longer experience using social media to derive social benefits.
Discussion
These findings are somewhat surprising, given prior research which suggests that social media use results in higher levels of social connection and reduced levels of loneliness among younger users. Yet, taken in the context of ageing and the lifecourse, these results may not be so surprising after all. Older adults can be viewed as distinct from other user groups in a myriad of ways; this study presents support for the idea that the benefits of social media use, like the benefits related to other forms of digital interaction, may not be distributed uniformly among varying groups of users (Helsper and van Deursen, Reference Helsper and van Deursen2016). In addition, this study provokes questions regarding causality between social media use and social benefits, especially in relatively short time horizons and within an older user base.
The lack of social benefits may somewhat explain the lower social media adoption rates among older adults overall, but may also provide evidence that factors other than merely ‘laggard’ behaviour, or slow adoption of technology, should be considered. With older adults, three specific influences intersect with their lifecourse position in ways that may explain differences in benefits between older and younger users: gaps in network coverage on technological platforms, perceptions of the value of weak connections in the social network and a reduced digital skills base. These factors are relevant to understanding the use of social media at older ages, and emphasise that social media may fulfil different needs at varying lifestages.
Gaps in network coverage
In younger age groups, use of social network sites is associated with greater access to social resources, especially bridging social capital (Ellison et al., Reference Ellison, Steinfield and Lampe2007; Kwon et al., Reference Kwon, D'Angelo and McLeod2013), reduced levels of loneliness (Ryan and Xenos, Reference Ryan and Xenos2011; K-T Lee et al., Reference Lee, Noh and Koo2013) and enhanced feelings of social connectedness (Grieve et al., Reference Grieve, Indian, Witteveen, Tolan and Marrington2013) because younger users use sites to regenerate and maintain relationships (Joinson, Reference Joinson2008; Spiliotopoulos and Oakley, Reference Spiliotopoulos and Oakley2013). But making and maintaining social connection via social media may not be as easily accomplished at older ages, due to lower adoption rates among older users. Lower adoption rates translate into a reduced availability of similarly aged connections, resulting in gaps in the social fabric of many older adults’ online networks. This, in turn, provides reduced opportunity to derive social benefits from one's peer network, despite peers being an important source of social support in later life (Cantor, Reference Cantor1979; Peters et al., Reference Peters, Hoyt, Babchuk, Kaiser and Iijima1987; De Vries et al., Reference De Vries, Utz, Caserta and Lund2014). In debriefing interviews with participants, these gaps became evident as participants acknowledged that their friends were ‘not all on Facebook and, if they are on Facebook, they're like me. Do we check it every day? No’ (female, age 70). In other words, individual social networks were not reliably present in digital social media platforms, which reduced incentives to participate. This effectively diminishes the opportunity for potential social benefits to be derived through social media activity.
The gaps in network representation in digital platforms are analogous to the concept of structural holes, or spaces within a social network between disconnected individuals (Burt, Reference Burt1997). The notion of ‘structural holes’ is applied when describing organisational networks. It describes latent relationships, or those which have the potential to exist within an organisational network, but do not. The positionality of an individual within the network relative to a structural hole is pertinent. Typically, proximity to a structural hole represents a positive opportunity for the individual to benefit as a broker of information by bridging the missing relationship. Under this theory, these structural holes should present opportunities for older adults to gain through their social media use, resulting in some form of social benefit as they would be ‘brokers’ of the resources that travel through the network. More recently, however, the positive effects of structural hole proximity have been questioned, especially in contexts like those experienced by older persons, where co-operation or identity are relevant. Recent work has suggested that the presence of structural holes constrains the social capital benefits accruing to the individual (Xiao and Tsui, Reference Xiao and Tsui2007; Bizzi, Reference Bizzi2013). The findings of this study are consistent with this latter conceptualisation. The presence of network gaps/structural holes limits the potential of peer network support that can be derived through social media use for older adults.
Perceptions of weak connections
A second factor relevant to older adult use of social media may lie in how individuals perceive their digitalised social network, and especially weak ties. Weak connections hold considerable value for individuals, providing distinct functions for social support: extending access to information; facilitating low-risk discussions of high-risk topics; providing benchmarks for comparison; and fostering a sense of community (Adelman et al., Reference Adelman, Parks, Albrecht, Albrecht and Adelman1987; Fingerman, Reference Fingerman, Lang, Fingerman and Fitzpatrick2003). An advantage of social media use is the ability to maintain a larger number of weak connections (Donath, Reference Donath2007) at a much lower ‘cost’ in terms of time and effort. In addition, these media provide efficient mechanisms of broadcast communication which enable individuals to ascertain sources of support (Vitak, Reference Vitak2014), and they make relevant connections between contacts (such as friends of friends) more visible, which fosters social connectivity (O'Riordan et al., Reference O'Riordan, Feller and Nagle2012).
Major motivations to use social network sites lie in the ability to maintain peripheral social relationships, share photos and videos with individuals seen less frequently, and reconnect with those one has lost contact with (Spiliotopoulos and Oakley, Reference Spiliotopoulos and Oakley2013). As individuals age, however, their social networks contract and they become more selective in the relationships they maintain (Carstensen, Reference Carstensen and Jacobs1992a). Knowledge-gathering goals diminish and connections with weaker relationships contract (Carstensen, Reference Carstensen1992b; Lockenhoff and Carstensen, Reference Lockenhoff and Carstensen2004). At later lifestages, individuals look to spend more time with familiar and rewarding relationships and contraction of an individual's social network is often deliberate (Carstensen and Mikels, Reference Carstensen and Mikels2005). These naturally occurring processes hold considerable weight in regarding social network sites as useful in later life. In addition, prior studies have also highlighted that older adults do not perceive that computer-mediated relationships are less costly to maintain than non-computer-mediated relationships (Wright, Reference Wright2000), and this may hold true for social media as well.
In debriefing interviews, participants acknowledged their connection selectivity and spoke of strong preferences for creating online ties with stronger relationships, such as younger family members, over weak relationships. They suggested that they held little value for maintaining weak relationships via social media, characterising such relationships as ‘not interesting’ (male A, age 79) and their related content as not ‘meaningful’ (male B, age 79). In explaining this reaction, one participant noted that the banal content that is often created on social media platforms, such as religious views or reminiscing, frequently contains ‘things that people really don't want to hear or know anything about’ (female, age 73). Attributing low value to weak relationships, thus, devalues a key benefit of social media and may provide additional context for the lack of social benefits found in this study.
Reduced digital skills base
Finally, as many older adults are novice social media users, these results may demonstrate that they also need more experience in using these platforms to derive social benefits. Social benefits do not arise from social media use spontaneously; studies have demonstrated that certain activities, such as comments on postings and messages sent to connections, result in higher social benefits (Burke et al., Reference Burke, Marlow and Lento2010; Ellison et al., Reference Ellison, Vitak, Gray and Lampe2014), and others, such as passive consumption of social media content, may have negative effects (Burke et al., Reference Burke, Marlow and Lento2010). Moreover, those with low literacy skills in using social media may experience more negative outcomes or may not use it in ways that promote social benefits (Ellison et al., Reference Ellison, Vitak, Steinfield, Gray, Lampe, Trepte and Reinecke2011). As the participants in this study were true social media learners, their activities and proficiency levels may not have progressed sufficiently during the study period to realise measurable social benefits.
Limitations and future work
Because of the small sample size, this study was exploratory in nature and leaves open the possibility of Type II error, or the possibility that we found no associations with social benefits when such benefits may actually be present. Likewise, this study is limited by the voluntary nature of experimental research. As all the participants in this study indicated a desire and willingness to learn how to use social media, generalisability to the wider older adult population may be limited. In addition, participants self-reported data on the social outcome variables, leaving the possibility of some slight reporting error.
As previously noted, the study period was a relatively short duration to study media effects; future work might explore the impacts of a more extensive workshop with a larger number of participants and a prolonged study period. It might also investigate whether the cost of maintaining weak connections through social media is as efficient in later life as it appears to be at younger ages.
Conclusion
This study examined the social benefits of social media use by employing a four-week social media workshop as a pilot intervention. Despite indications that social media use results in improved social wellbeing among younger persons, this study did not find that such benefits extended to adults at older ages. Possible reasons for these discrepancies may be attributable to lifestage as well as technological proficiency, as gaps in the technological representations of older adult social networks and preferences for strong relationships over weak ones may diminish the social benefits that can be derived from social media use. It is clear from these results, however, that additional investigation is needed to understand what role, if any, social media can positively play in the everyday lives of older persons.
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/S0144686X19001570.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to express appreciation to Melissa Martinez, Renee Smith-Ray and Kristin Boulter for their assistance in carrying out this research project.
Financial support
This work was supported by the Midwest Roybal Center for Health Promotion and Translation at the University of Illinois at Chicago and the National Institute on Aging (NIA) (grant number P30AG022849). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIA or the National Institutes of Health.
Ethical standards
Human subjects review was conducted by the Institutional Review Board at the University of Illinois at Chicago under protocol #2015-0463.








