Introduction
One of the major goals of parasitological research is to clarify the life cycles of parasites. Most of these parasites have complex life cycles, being trophically transmitted between intermediate and definitive hosts (Thomas et al., Reference Thomas, Guégan and Renaud2009; Thieltges et al., Reference Thieltges, Amundsen, Hechinger, Johnson, Lafferty, Mouritsen, Preston, Reise, Zander and Poulin2013). Although the evolution of parasites and that of hosts are not independent of each other, parasites can evolve far more rapidly than hosts (Kochin et al., Reference Kochin, Bull and Antia2010). As a consequence, parasites can switch hosts in a given environment (Kochin et al., Reference Kochin, Bull and Antia2010), and a single parasite species can have multiple intermediate and definitive host species (Near, Reference Near2002; Mayer et al., Reference Mayer, Dailey and Miller2003; Royal et al., Reference Royal, Dailey, Demaree and Sakanari2004; La Sala & Martorelli, Reference La Sala and Martorelli2007; Steinauer et al., Reference Steinauer, Nickol and Ortí2007; Kochin et al., Reference Kochin, Bull and Antia2010; La Sala et al., Reference La Sala, Perez, Smits and Martorelli2013).
Parasites of the genus Profilicollis (Polymorphidae: Acanthocephala) infect marine mammals, shorebirds and waterfowl as definitive hosts, and amphipods, decapods and euphausiids as intermediate hosts (Balboa et al., Reference Balboa, Hinojosa, Riquelme, Rodríguez, Bustos and George-Nascimento2009; García-Varela et al., Reference García-Varela, Pérez-Ponce de León, Aznar and Nadler2013). In the definitive predator host, the adult female worm develops and produces eggs (acanthors) that are released into the environment through the host faeces. Upon its intake by an arthropod host, the acanthor develops in the haemocoele into an acanthellae and then into a cystacanth. Finally, the cystacanth infects the definitive host when the latter predates upon an infected intermediate prey host (Zdzitowiecki, Reference Zdzitowiecki1985).
Two Profilicollis species have been described from the shores of the south-east (SE) Pacific (Amin, Reference Amin2013) – P. altmani (Perry, 1942; = P. bullocki Mateo, 1982) and P. antarcticus Zdzitowiecki, 1985 – which infect intermediate hosts from segregated habitats with little or no spatial overlap. While P. altmani infects the sandy-shore molecrab Emerita analoga (Stimpson, 1857) (Goulding & Cohen, Reference Goulding and Cohen2014; Rodríguez & D'Elía, Reference Rodríguez and D'Elía2016), P. antarcticus infects the estuarine crab Hemigrapsus crenulatus (Varunidae; Milne-Edward, 1837) (Haye & Ojeda, Reference Haye and Ojeda1998; Latham & Poulin, Reference Latham and Poulin2002a). However, recent work challenges the identification of the Profilicollis species that infects H. crenulatus, which has been ascribed either to P. antarcticus or another species, namely P. chasmagnathi (Balboa et al., Reference Balboa, Hinojosa, Riquelme, Rodríguez, Bustos and George-Nascimento2009). Therefore, it is still unclear which species actually infects the estuarine crab H. crenulatus.
In addition to the unclear parasite–intermediate host link described above, the identity of the species of Profilicollis infecting the definitive hosts is also unclear. While P. antarcticus has been registered only as a parasite of the kelp gull Larus dominicanus (Lichtenstein, 1823) (Torres et al., Reference Torres, Ruiz, Gesche and Montefusco1991, Latham & Poulin, Reference Latham and Poulin2002b), P. altmani has been described in that seabird in addition to Chroicocephalus maculipennis Lichtenstein, 1823, Leucopheus pipixcan (Wagler, 1831), Podiceps sp. and Numenius phaeopus (Linnaeus, 1758). However, significant morphological differences between P. altmani individuals collected from different seabird species have been found (Riquelme et al., Reference Riquelme, George-Nascimento and Balboa2006), suggesting that these individuals might belong to more than one species.
In order to answer the question of which parasite species (co-)occur in this parasitic system, we can suggest that, due to the differences in the prey item consumption and high mobility of seagulls (Smith, Reference Smith2007; Yorio et al., Reference Yorio, Marinao, Retana and Suárez2013), both Profilicollis species could be found co-occurring in any of the definite hosts. On the other hand, intermediate host species occur in specific habitats and with little spatial overlap (i.e. molecrabs inhabiting full marine habitats and crabs inhabiting estuaries), which can stimulate specific and strict parasite–intermediate host relationships (Near, Reference Near2002; Steinauer et al., Reference Steinauer, Nickol and Ortí2007). Thus, we might expect parasite co-occurrence in definitive, but not in intermediate, hosts. Testing this hypothesis requires the accurate identification of parasite species. Up to now, the identification of these species has been almost exclusively based on morphological characters. The analysis of this type of evidence has provided valuable contributions to our understanding of parasite–host interactions, but its reliability can be severely compromised by the high morphological similarity among acanthocephalan species (Near et al., Reference Near, Garey and Nadler1998, Balboa et al., Reference Balboa, Hinojosa, Riquelme, Rodríguez, Bustos and George-Nascimento2009) and the scarce knowledge of their geographic variation. Therefore, the assessment of molecular data provides an opportunity to identify cryptic species accurately (e.g. Goulding & Cohen, Reference Goulding and Cohen2014; Rodríguez & D'Elía, Reference Rodríguez and D'Elía2016), and can well be used to shed light on the potentially complex Profilicollis interaction network in SE Pacific shores.
Here, we test whether multiple Profilicollis species are able to co-occur in definitive (seagulls) and intermediate (marine and estuarine crabs) hosts in SE Pacific shores. We analysed molecular data in order to identify accurately acanthocephalan specimens collected from intermediate and definitive hosts along 1200 km of the Chilean SE Pacific coast.
Materials and methods
Collection and examination of crab and avian hosts
The study area corresponded to marine and estuarine systems along the SE Pacific coast of Chile. Sandy-shore molecrabs, estuarine crabs and seagulls were captured at six sites located between 29.9 and 39.5°S, spanning 1200 km of the shore. The sandy beaches surveyed were ‘Coquimbo’ (29.9°S–71.2°W), ‘Dichato’ (36.4°S–72.9°W), ‘Colcura’ (37.1°S–73.1°W), ‘Calfuco’ (39.7°S–73.3°W) and ‘Chaihuín’ (39.9°S−73.5°W). The estuarine site corresponded to the mouth of the Valdivia River, ‘Niebla’ (39.8°S–73.4°W).
In the sandy-shore sites, 239 individuals of the molecrab E. analoga were captured during 2014 and 2015 in winter and summer seasons. At each site and sampling time, four transects were randomly deployed perpendicularly to the shoreline. Along each transect we placed six sampling stations located c. 2 m apart from each other, from the effluent line to the swash line. Plastic corers (0.03 m2) were buried to a depth of 20 cm and the sand was sieved through a 1-mm-mesh sieve. Crabs were transferred to the laboratory for parasite identification and sorting. In the estuarine site, 30 individuals of H. crenulatus were sampled by hand between October 2015 and March 2016 along a 300-m transect on promontory rocks.
A total of 16 seagulls were captured around 40°S on the SE Pacific coast. Specimens were captured in resting areas by means of a 3 × 5 m Whosh net trap installed in the morning and activated after 2 h. After capture, the specimens were sedated with 40 mg kg−1 of ketamine plus 7 mg kg−1 of xylazine and transferred to the laboratory. In addition, we analysed nine seagulls found dead during March–April 2015 and summer of 2016 in the sampling region around 40°S. In summary, the analysed seagull sample was as follows: C. maculipennis (n = 8), L. dominicanus (n = 8), L. modestus (n = 8) and L. pipixcan (n = 1).
Each sampled crustacean was dissected, and the abundance of Profilicollis spp. in the haemocoele was determined under a stereomicroscope. Seagulls were euthanized using an overdose of 0.2–1 ml kg−1 intracardiac thiopental. Afterwards, the birds were necropsied and each gastrointestinal tract was removed and opened in order to sort, identify and count the Profilicollis parasite specimens. Parasites were identified on the basis of published morphological characters (e.g. Riquelme et al., Reference Riquelme, George-Nascimento and Balboa2006; Balboa et al., Reference Balboa, Hinojosa, Riquelme, Rodríguez, Bustos and George-Nascimento2009). A total of 749 Profilicollis specimens were extracted from the different hosts (see table 1) and were stored in 95% ethanol for subsequent DNA extraction. Prevalence and intensity of infection in each host species were calculated according to Bush et al. (Reference Bush, Lafferty, Lotz and Shostak1997).
Table 1. The prevalence (%), mean intensity (MI), range and number of sequences analysed (NS) of two species of Profilicollis in intermediate and definitive hosts from eight sites along the SE Pacific coast of Chile; N = number of hosts examined.

Molecular and phylogenetic analyses
Genetic analyses were based on a fragment of 578 bp of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I (COI) gene. Sequences were gathered from 64 individuals of Profilicollis collected from both crustacean (E. analoga: 32; H. crenulatus: 1) and the four seagull species (C. maculipennis: 10; L. dominicanus: 11; L. modestus: 9; L. pipixcan: 1). Total DNA was isolated using a commercial extraction kit and the COI gene was amplified using the protocol and primers detailed by Folmer et al. (Reference Folmer, Black, Hoeh, Lutz and Vrijenhoek1994); amplicons were sequenced using an external sequencing service (Macrogen Inc., Seoul, South Korea). DNA sequences were edited using Codon-Code (Codon-Code, Dedham, Massachusetts, USA) and deposited in GenBank (KX646746–KX646796 and KX702242–KX702254). These sequences were integrated in a matrix, with one sequence for each haplotypic class of Profilicollis found by Goulding & Cohen (Reference Goulding and Cohen2014) and Rodríguez & D'Elía (Reference Rodríguez and D'Elía2016); these sequences (P. altmani: 74; P. antarcticus: 3; P. botulus: 1) were downloaded from GenBank. Therefore, a total of 142 sequences of Profilicollis were analysed. Sequences of Polymorphus minutus and Arhythmorhynchus brevis, which are closely related to Profilicollis (García-Varela et al., Reference Garcés-Vargas, Ruiz, Pardo, Nuñez and Pérez-Santos2013), were used to form the outgroups.
Sequences were aligned in Clustal as implemented in MEGA 7 (Tamura et al., Reference Tamura, Stecher, Peterson, Filipski and Kumar2013) using default parameter values. Observed genetic distances (p) between haplotype and sample pairs were calculated in MEGA 7. Phylogenetic relationships were inferred via Bayesian analysis (BA) implemented in MrBayes 3.1 (Ronquist & Huelsenbeck, Reference Ronquist and Huelsenbeck2003). BA consisted of two independent runs, each with five heated and one cooled Markov chains and the HKY + G model, selected by means of the jModel Test (Darriba et al., Reference Darriba, Taboada, Doallo and Posada2012). All model parameters were estimated in MrBayes. Uniform-interval priors were assumed for all parameters except for base composition and substitution model parameters, for which we assumed a Dirichlet prior. Runs were allowed to proceed for 20 million generations, with trees sampled every 1000 generations per chain. To check for convergence on a stable log-likelihood value, we plotted the log-likelihood values against generation time for each run. The first 25% of the trees were discarded as burn-in and the remaining trees were used to compute a 50% majority rule consensus tree and to obtain posterior probability (PP) estimates for each clade.
Results
The phylogenetic analysis indicated that haplotypes of Profilicollis fell into two main, highly supported clades (fig. 1) that, according to Goulding & Cohen (Reference Goulding and Cohen2014) and Rodríguez & D'Elía (Reference Rodríguez and D'Elía2016), correspond to P. altmani (PP = 1) and P. antarcticus (PP = 1), respectively. As in Rodríguez & D'Elía (Reference Rodríguez and D'Elía2016), the genus Profilicollis is not a monophyletic clade with the current taxonomic assignment of these outgroups. All sequences of cystacanths found in the marine molecrab E. analoga and all-but-one haplotypes of adult worms found in specimens of the four surveyed seagulls fell into the clade of P. altmani. On the other hand, all haplotypes of Profilicollis specimens from the estuarine crab H. crenulatus and one haplotype of an adult Profilicollis from a L. dominicanus seagull fell in the clade of P. antarcticus. The two sequences of cystacanths from H. crenulatus that were too short to be included in the phylogenetic analysis were indistinguishable from those of the P. antarcticus clade. Finally, the individuals of both species of Profilicollis found in L. dominicanus were extracted from two distinct gull individuals.

Fig. 1. Genealogical relationships of haplotypes of the COI gene of Profilicollis altmani (green) and P. antarcticus (red), as a result of Bayesian analysis. Support values correspond to posterior probability (only those for species and relationships among species are shown). GenBank accession numbers and host species are given at terminal labels. Sampling sites are indicated as CA = Calfuco, CH = Chaihuin, CO = Colcura, CQ = Coquimbo and DI = Dichato. Specimen numbers are also provided.
The sample of P. altmani showed a low level of genetic variation. On average, the analysed haplotypes of this species differed by 1% (range 0–2.5%). The haplotypes of P. altmani (of cystacanths and worms) from a given host species did not form a monophyletic group. In addition, the sample of P. altmani did not show a discernible geographic structure (see also Goulding & Cohen, Reference Goulding and Cohen2014). For instance, a haplotype was found in worms extracted from three seagulls, namely C. maculipennis (02 in fig. 1), L. modestus (17) and L. dominicanus (06, 12), as well as from cystacanths found in E. analoga from Dichato (04) and Calfuco (14; SE Pacific coast; this study) and Bodega beach (KF835313; NE Pacific coast; Goulding & Cohen, Reference Goulding and Cohen2014). Similarly, another haplotype was found in worms from C. maculipennis (04), L. modestus (05) and L. dominicanus (07). This haplotype was also found in cystacanths of E. analoga from Coquimbo (08), Colcura (01–03), Chaihuín (08) and Calfuco (15–17; SE Pacific coast; this study), in addition to San Francisco (KF835297; NE Pacific; Goulding & Cohen, Reference Goulding and Cohen2014). In contrast, the most divergent haplotypes of P. altmani were found in individuals of E. talpoidea from North Carolina (KF835307; Goulding & Cohen, Reference Goulding and Cohen2014) and a worm of L. dominicanus (01) from the SE Pacific (this study).
The clade of P. antarcticus was strongly supported (PP = 1) and showed low genetic variation (average = 0.3%, range 0–0.7%). Haplotypes from cystacanths found in the estuarine crab H. crenulatus and from mature worms found in L. dominicanus fell into this clade. Profilicollis antarcticus did not show geographic structure; a haplotype was obtained from a cystacanth found in H. crenulatus from Niebla (05; this study) and Lenga (JX442197; García-Varela et al., Reference García-Varela, Pérez-Ponce de León, Aznar and Nadler2013). The observed genetic p-distance between the clades of P. altmani and P. antarcticus was 25%.
Prevalence and intensity of infection of P. altmani and P. antarcticus in their different hosts varied among sites (table 1). Prevalence of P. altmani in E. analoga fluctuated between 52 and 83.3% across sites. The intensity of the infection was similar between sites (between c. 1 and 3 parasites per host). Dichato did not conform to this pattern of low intensity of infection, showing c. 5 parasites per host. Profilicollis antarcticus had low prevalence in the H. crenulatus population, but it had an intensity of infection that was similar to that of P. altmani in molecrabs. Regarding the definitive hosts, prevalence and intensity of infection of both parasites were high in all seagull species (table 1). Infected seagulls showed a high degree of intestinal damage, with intestinal perforations mainly in the last two-thirds of the intestine.
Discussion
The results of this study suggest that cystacanths and adult worms sampled from crustaceans and seagulls along SE Pacific shores belong to two species of Profilicollis, P. altmani and P. antarcticus. Also, our results indicate that these two parasite species can both infect the same definitive host species from different intermediate host species. However, as these two species were found in different individual hosts, it is undetermined whether both species can co-occur in the same individual host or if competitive exclusion occurs, as has been described for some acanthocephalan species (Cezilly et al., Reference Cezilly, Gregoire and Bertin2000; Dezfuli et al., Reference Dezfuli, Giari and Poulin2001; Sures, Reference Sures2002). Juvenile P. altmani infected the sandy-shore molecrab E. analoga and the adult infected the seagulls L. dominicanus, C. maculipennis, L. modestus and L. pipixcan. Juvenile P. antarcticus, on the other hand, infected the estuarine crab H. crenulatus and the adult infected only the seagull L. dominicanus. Therefore, both species of Profilicollis co-occurred in only one of the four definitive host species (fig. 2). Despite these differences in occurrence, both parasite species shared low levels of within-species haplotype variability. The present discussion therefore considers the influence of environmental variables on a specific host–parasite relationship. The role of host traits, such as foraging behaviour, diet selectivity and mobility, as determinants of predator–prey relationship and parasitosis, is also emphasized.
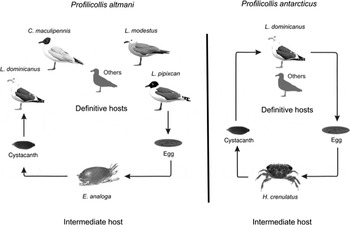
Fig. 2. Life cycle of Profilicollis altmani and P. antarcticus off the Chilean Pacific coasts. ‘Others’ are unknown definitive hosts.
We observed that P. altmani infected only E. analoga, while P. antarcticus infected only H. crenulatus as intermediate hosts. These results are well in line with previous work showing a high fidelity of P. altmani to molecrabs on the SE Pacific shore (García-Varela et al., Reference García-Varela, Pérez-Ponce de León, Aznar and Nadler2013) and elsewhere (Hennessy & Morejohn, Reference Hennessy and Morejohn1977; Goulding & Cohen, Reference Goulding and Cohen2014; Rodríguez & D'Elía, Reference Rodríguez and D'Elía2016). Similarly, P. antarcticus has only been found in one intermediate host species (H. crenulatus) and has not been found in other grapsids along the SE Pacific shore. For instance, Leiva et al. (Reference Leiva, George-Nascimento and Muñoz2015) described the parasite species composition of 15 decapod species from the central coast of Chile, and no species of Profilicollis were recorded. Therefore, alternative intermediate hosts in addition to those described here for P. altmani and P. antarcticus have not been reported.
Strict parasite–intermediate host relationships are often attributed to specific environmental conditions that vary among host types (Steinauer et al., Reference Steinauer, Nickol and Ortí2007). The coelomic cavity of invertebrates is exposed to ‘external’ environmental conditions, suggesting that the conditions in the coelom correlate with those in the environment (Near, Reference Near2002). If this holds for our model species, then we could speculate that coelomic environmental conditions of sandy-shore molecrabs and estuarine crabs differ significantly, as both environments differ in terms of water temperature, salinity and wave exposure, among other factors (Garcés-Vargas et al., Reference Garcés-Vargas, Ruiz, Pardo, Nuñez and Pérez-Santos2013). Therefore, environmental conditions may limit acanthocephalan species to particular arthropod hosts that are exposed to distinct environmental conditions.
Both parasite species analysed co-occurred in the kelp gull L. dominicanus, albeit in different individuals. This result can be a consequence of the generalist foraging behaviour of kelp gulls, which take advantage of the multiple trophic resources available along the coast from both marine and estuarine habitats (Bahamondes & Castilla, Reference Bahamondes and Castilla1986; Yorio et al., Reference Yorio, Marinao, Retana and Suárez2013). Accordingly, kelp gulls present a high diversity of endoparasites, including cestodes, nematodes, trematodes and acanthocephalans (Torres et al., Reference Torres, Ruiz, Gesche and Montefusco1991; Riquelme et al., Reference Riquelme, George-Nascimento and Balboa2006; González-Acuña et al., Reference González-Acuña, Cerda, López, Ortega, Mathieu and Kinsella2009; Diaz et al., Reference Diaz, Cremonte and Navone2011). In contrast, the degree of diet and habitat generalism of the other three seagulls analysed here – L. modestus, L. pipixcan and C. maculipennis – seems to be less clear. For instance, while L. modestus tends to specialize on molecrabs as its main foot item (Blokpoel et al., Reference Blokpoel, Boersma, Hughes and Tessier1992), L. pipixcan is a kleptoparasitic species that steals different kinds of food from other seabird species (Khatchikian et al., Reference Khatchikian, Favero and Vassallo2002; pers. obs.). Chroicocephalus maculipennis can be found in freshwater marshes and intertidal sandy shores (Khatchikian et al., Reference Khatchikian, Favero and Vassallo2002; Ghys & Favero, Reference Ghys and Favero2004; pers. obs.). During migratory periods, the diet of C. maculipennis is based mainly on crustaceans, including E. analoga, and other sandy-shore invertebrates (Khatchikian et al., Reference Khatchikian, Favero and Vassallo2002; Bruschetti et al., Reference Bruschetti, Bazterrica, Luppi and Iribarne2009). No P. antarcticus has been recorded infecting this species (Torres et al., Reference Torres, Schlatter, Montefusco, Gesche, Ruiz and Contreras1993). However, the low number of studies that analyse this host–parasite interaction biases the odds of finding P. antarcticus in C. maculipennis. Further field observations are needed to clarify the degree of diet specificity of these seagulls, in order to explain the occurrence patterns of their parasites.
We analysed and corroborated four definitive hosts of P. altmani and one of P. antarcticus, which raises the question of potential additional definitive hosts for these parasites in the study region. For example, along the Californian coast the surf scoter Melanitta perspicillata (Anatidae) was identified as a definitive host of P. altmani (Hennessy & Marejohn, Reference Hennessy and Morejohn1977; Lafferty et al., Reference Lafferty, McLaughlin and Dugan2013). In contrast, in ducks of the SE Pacific coast no species of Profilicollis have been recorded (Muñoz & Olmos, Reference Muñoz and Olmos2008; Hinojosa-Sáez et al., Reference Hinojosa-Sáez, González-Acuña and George-Nascimento2009). Other studies have mentioned that Calidris waders and the sea otter Enhydra lutris harbour P. altmani parasites (Hennessy & Marejohn, Reference Hennessy and Morejohn1977; Margolis et al., Reference Margolis, Groff, Johnson, McDonald, Kent and Blaylock1997; Mayer et al., Reference Mayer, Dailey and Miller2003; Riquelme et al., Reference Riquelme, George-Nascimento and Balboa2006; Buehler et al., Reference Buehler, Bugoni, Dorrestein, González, Pereira, Proença, De Lima Serrano, Baker and Piersma2010). However, these studies do not report the presence in these hosts of sexually mature Profilicollis parasites, which suggests that Calidris spp. and sea otters are not involved in the parasite life cycle (Mayer et al., Reference Mayer, Dailey and Miller2003; Buehler et al., Reference Buehler, Bugoni, Dorrestein, González, Pereira, Proença, De Lima Serrano, Baker and Piersma2010). However, and since the SE Pacific coastal vertebrate fauna has been less explored than that of the northern Pacific, we cannot rule out that other bird species can serve as a definitive host of P. altmani. Likewise, it is worth noting that there is evidence that humans and domestic animals can be infected by P. altmani when eating molecrabs and accidently ingesting cystacanths (Tantaleán et al., Reference Tantaleán, Cárdenas and Güere2002). Regarding P. antarcticus, morphology-based work suggests that Phalacrocorax atriceps is an additional definitive host in Chile (Torres et al., Reference Torres, Contreras, Cubillos, Gesche, Montefusco, Rebolledo, Mira, Arenas, Miranda, Asenjo and Schlatter1992). Since we did not analyse P. atriceps in the present study, we cannot confirm whether it is the same species infecting this host. Therefore, further research on other bird species is needed to determine whether Profilicollis spp. (co-)occur in other definitive hosts.
In summary, our molecular analysis of parasites collected from both intermediate and definite hosts along 1200 km of the SE Pacific shore allowed us to shed light on a complex interaction web in which two species of parasite, each infecting one particular intermediate host, co-occurred in the same species of definitive host. Nevertheless, it is still unknown if both species of Profilicollis can reside in the same individual or not. Also, both species of Profilicollis had low genetic variation and lacked geographical and host-related population structures. In agreement with previous evidence (Goulding & Cohen, Reference Goulding and Cohen2014), and the fact that they share the same intermediate hosts, haplotypes of both Profilicollis spp. found in a given host species did not form a monophyletic group. In addition, the topology found in the phylogenetic analysis indicates that the limits of the genera of Polymorphidae need to be further evaluated. We suggest that environmental filtering results in strict parasite–intermediate host links, while trophic generalism leads to more free-to-vary parasite–definite host links. To test this novel hypothesis and to contrast it to alternative causes related to sampling bias and alternative host species, further field-based observations of diet and habitat specificity are needed. Overall, the results presented here contribute to improving our understanding of ecological and evolutionary mechanisms that allow the co-existence of parasites belonging to complex interaction webs.
Acknowledgements
We thank the national PhD CONICYT scholarship and the Servicio Agrícola y Ganadero de Chile (SAG) for providing capture permits. Daniela López, Fernando Cerda, César Campos, Jorge Reyes and Andrés Silva provided valuable assistance during fieldwork. Claudio Verdugo kindly provided some specimens of Larus dominicanus. Eduardo Menschel kindly helped in figure design. Kennia Morales assisted us in the laboratory work.
Financial support
This work was supported by Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico (FONDECYT grants 1141037 and 1141055). While writing, N.V. was financially supported by FONDAP grant #15150003.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standards
The Chilean authority Servicio Agrícola y Ganadero allowed the capture of seagulls; permit numbers 1412/2015 and 7916/2015.





