Introduction
Unipolar depressive disorders are the leading cause of disease burden in middle- to high-income countries, and have been predicted to become the worldwide leading cause of disease burden by 2030 (World Health Organization, 2008). Depression is associated not only with suffering, disability and impaired health (Moussavi et al., Reference Moussavi, Chatterji, Verdes, Tandon, Patel and Üstün2007; Ormel et al., Reference Ormel, Petukhova, Chatterji, Aguilar-Gaxiola, Alonso, Angermeyer, Bromet, Burger, Demyttenaere, de Girolamo, Haro, Hwang, Karam, Kawakami, Lepine, Medina-Mora, Posada-Villa, Sampson, Scott, Ustun, Von Korff, Williams, Zhang and Kessler2008), but also considerable societal costs (Cuijpers et al., Reference Cuijpers, Smit, Oostenbrink, de Graaf, Ten Have and Beekman2007). Nevertheless, most people who suffer from depression never receive adequate treatment (e.g. Thornicroft et al., Reference Thornicroft, Chatterji, Evans-Lacko, Gruber, Sampson, Aguilar-Gaxiola, Al-Hamzawi, Alonso, Andrade, Borges, Bruffaerts, Bunting, de Almeida, Florescu, de Girolamo, Gureje, Haro, He, Hinkov, Karam, Kawakami, Lee, Navarro-Mateu, Piazza, Posada-Villa, de Galvis and Kessler2017). The majority of patients with mood disorders are found in primary care (e.g. ESEMeD⁄MHEDEA 2000 investigators, 2004). In the treatment of depression, the primary care context offers both advantages – for example, in terms of a low threshold for health care seeking, and the tradition of a lifetime perspective on health – and challenges, for example, with regard to the gap in mental health competency, and the integration with specialist care services. Most patients with depression prefer psychological treatment over pharmacotherapy (McHugh et al., Reference McHugh, Whitton, Peckham, Welge and Otto2013), and the psychological treatment that has been most studied in the treatment of depression is cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) (National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health, 2010). Individual one-to-one CBT constitutes the gold standard format, but the treatment can also be delivered as group therapy or guided self-help, for example, via the Internet (Hedman et al., Reference Hedman, Ljótsson and Lindefors2012) or as bibliotherapy (Cuijpers, Reference Cuijpers1997). Meta-analyses have provided preliminary evidence that CBT for depression may be effective in the primary care context, but there is a rapid development of this research field and several key questions for implementation in routine care remain unanswered (Cuijpers et al., Reference Cuijpers, van Straten, van Schaik and Andersson2009; Linde et al., Reference Linde, Sigterman, Kriston, Rucker, Jamil, Meissner and Schneider2015; Twomey et al., Reference Twomey, O'Reilly and Byrne2015). For example, long-term effects have not been investigated, the relative efficacy of delivery formats is largely unknown (Linde et al., Reference Linde, Sigterman, Kriston, Rucker, Jamil, Meissner and Schneider2015), potential moderators of treatment effect like the number of sessions and therapist qualifications have not been investigated for CBT specifically, and it is unclear whether CBT is suitable for primary care patients who have depressive symptoms but do not meet full diagnostic criteria for depression. Increased knowledge in these areas is likely to facilitate the implementation of treatment in primary care, and the integration with psychiatric care for this large patient group. We therefore conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of CBT for adult primary care patients with depression.
Method
Search strategy
A systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines (Moher et al., Reference Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff and Altman2009). We searched PubMed and PsycINFO for randomised controlled trials where CBT was compared with a control condition in the treatment of adults with depression in primary care. Our strategy was to conduct a relatively broad search and combine terms for adult patients, depression, CBT and primary care (see the online Supplementary material for complete search terms). We began work on study selection in October 2014, and last searched databases on 6 November 2018. In order to identify both early works and recent articles not yet categorised in the databases, no filters or restrictions (e.g. with regard to study time of publication) were applied. We also read the reference lists of all included studies, and considered studies found in the process of data extraction and in previous meta-analyses. We did not search for unpublished studies. Because all data were collected at the study level, we did not deem it necessary to obtain ethics approval for this review.
Selection of studies
The eligibility of all unique search hits was assessed by one of the authors (FS or EA) in three stages. First, publications were excluded based on titles, then on abstracts and finally on full texts. Reason for exclusion was defined as the first exclusion criterion identified. In order to validate the selection process, all studies that reached the stage of full-text evaluation were also read by a second assessor (EA, MHL or JF). Whenever there was disagreement on whether to include a study, a third author (EHL or FS) was consulted and a decision made in consensus after discussion. If vital information to assess study eligibility was missing, corresponding authors were contacted and asked to provide that information. This occurred in 33 cases, of which 24 replied.
Eligibility criteria
(a) We required studies to have investigated the effect of CBT for depression. CBT was defined as either cognitive therapy (i.e. where the treatment is designed to work through cognitive restructuring), behaviour therapy (i.e. behavioural activation focusing on increasing positive reinforcement), or a combination of the two. Treatments were required to have as their principal aim to reduce symptoms of depression, and to last more than 1 week. Third-wave approaches to CBT such as acceptance and commitment therapy, dialectical behaviour therapy and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy were not included. CBT could be delivered in any format (e.g. as face-to-face therapy, online treatment or bibliotherapy), as long as there was support from a clinician. The amount of support could, however, be minimal, for example, consisting of one phone call only.
(b) We required all patients to either (I) meet diagnostic criteria for a unipolar depressive disorder such as DSM-IV major depressive disorder, (II) score above a recognised cut-off for depression or (III) have depressive symptoms. Our experience from working in primary care is that patients with elevated depressive symptoms who do not meet full criteria for a diagnosis of depression make up a substantial portion of those offered a treatment focusing on reducing depression symptoms. This inclusion criterion was therefore deliberately vague so as to capture studies of high ecological validity, and enable moderator analysis to assess if the manner in which the eligibility criterion was formulated (diagnosis v. cut-off v. depressive symptoms) was predictive of outcome. No restrictions were made with regard to comorbidity, but we did not include studies of bipolar disorders, seasonal affective disorders or pre-/postnatal depression.
(c) Only studies where the entire sample consisted of adult patients (⩾18 years) were included.
(d) Studies were required to have a primary care focus, meaning that either (I) more than half of the sample was recruited from primary care or (II) CBT was delivered in primary care. This was arguably the criterion most difficult to assess, not least due to notable international differences in organisation of the health care system, and also because articles were not explicit about the setting where treatments were conducted. Whenever necessary, authors were contacted and asked if the majority of their sample had been recruited through primary care, and/or whether they would characterise the setting where patients received treatment as primary care. In this study, we regarded primary care as being non-specialised, i.e. concerned with most common disease states, relatively accessible and commonly serving the role of a first step or ‘gatekeeper’ in relation to secondary care.
(e) All studies had to be randomised controlled trials where CBT was compared with a control condition. The control condition could be treatment as usual (TAU), antidepressants, another psychological treatment, waiting-list or a placebo (psychological or pharmacological). We excluded studies where the patient was not the unit of randomisation, and studies which solely compared different forms of CBT against each other.
(f) Studies had to be published in an English-language journal with peer-review.
(g) Studies were only included if the effect of CBT on its own could be estimated. In other words, if the experimental condition involved substantial structured interventions in addition to CBT (e.g. the addition of antidepressant medication), the study was excluded. If the CBT condition included access to TAU, the study was included because this did not constitute a structured parallel treatment.
Data extraction
Most of the data extraction was done in parallel by two independent assessors (FS and EA). For most studies, the primary outcome was included in the meta-analysis. If a primary outcome was not specified, or if the primary outcome was not a measure of depression, the first measure of depression reported in the article was chosen. For studies that used both self-reported and independently assessed measures of depression, we followed the procedure of previous meta-analyses (Cuijpers et al., Reference Cuijpers, Berking, Andersson, Quigley, Kleiboer and Dobson2013) and based our estimates on the mean effect size from these two measures. We also assembled data on responder and remission rates, where the former was operationalised as the proportion of patients who achieved a clinically significant symptom reduction and the latter was operationalised as the proportion of patients who did not meet criteria for depression or who scored below an adequate cut-off score for depression. We did not include estimates which conflated symptom reduction (i.e. response) with endpoint score (i.e. remission). Remission rates were based only on those studies where it was clear that no patient met the criterion for remission at baseline. In order to enable moderator analyses, data were also collected about study design and patient characteristics (e.g. country, mean age, type of control), as well as the characteristics of CBT (e.g. delivery format, number of sessions, therapist qualifications). CBT protocols were classified as being in individual format if the majority of the treatment content was delivered through extensive one-to-one contact with a therapist (face-to-face, via telephone or online), in group format if the majority of the treatment content was delivered through sessions with more than one patient, and as guided self-help if most of the content was intended to be conveyed by the means of a text or didactic material, with little (typically <3 h) therapist support.
Risk of bias assessment
We assessed study risk of bias based on the Cochrane collaboration's tool (Higgins et al., Reference Higgins, Altman, Gotzsche, Juni, Moher, Oxman, Savovic, Schulz, Weeks and Sterne2011), and rated the following dimensions: (I) random sequence generation, (II) allocation concealment, (III) blinding of outcome assessment, (IV) incomplete outcome data and (V) selective reporting. Studies were rated in terms of high risk of bias, low risk of bias or insufficient information (when a criterion could not be assessed). Criterion III (‘blinding of outcome assessment’) was rated as ‘not applicable’ for studies where all depression measures were self-reported. We did not rate criterion ‘blinding of participants and personnel’ because it is not possible for those who administer psychological treatments to be blinded with regard to the treatment that they are delivering. Ratings for criteria III, IV and V focused on those continuous outcomes which were used for the meta-analysis.
Statistical analysis
Analyses were done in R 3.4.4 (R Core Team, 2016) with metafor 2.0-0 (Viechtbauer, Reference Viechtbauer2010). Controlled effect sizes on continuous measures were quantified as Hedges’ g; g > 0 favouring CBT (Hedges, Reference Hedges1981). In cases where studies did not report means and standard deviations to allow for conventional computation of effect sizes, approximations were used (Lipsey and Wilson, Reference Lipsey and Wilson2001). Absolute values for g of 0.2 are usually regarded as small, 0.5 as moderate and 0.8 as large (Cohen, Reference Cohen1988).
Controlled effect sizes for responder and remission rates were instead reported as odds ratios (OR), i.e. the ratio of the odds of a beneficial outcome in CBT and the corresponding odds in the control condition, where OR>1 is in favour of CBT. We also reported the number needed to treat (NNT), which is the inverse of the absolute risk difference. The NNT stands for the average number of patients necessary to assign to CBT in order to achieve one beneficial case (i.e. one case of response or remission) that would not have been achieved had the patients instead been assigned to the control group.
We based all aggregation of effect sizes on random-effects models fitted with the restricted maximum likelihood estimator (linear regression for g and NNT, logistic regression for OR). For continuous outcome measures, we first did a primary comparison of CBT (any form) and control conditions (any form). Second, we explored possible moderators of this between-group effect based on Q-tests and meta-regression (most pre-specified, except: therapist adherence reported, expert-level therapists, use of cognitive interventions, session length). Our ambition was to only analyse putative moderators where at least 75% of the studies reported data. Two exceptions from this rule were however made because we found these tests important. One was a comparison of studies with high and low ratings on the allocation concealment risk-of-bias criterion, and the other was a comparison based on the setting where CBT was delivered (primary care v. specialist setting with patients from primary care). Because p values for the Q statistic were often of limited value due to low power, and also in order to quantify the pooled effects in subgroups of studies (e.g. differentiate between CBT formats), we also conducted a series of secondary subgroup analyses. These corresponded to the levels of putative moderators, so that we, for example, could present separate effect sizes for individual CBT, group CBT and guided self-help CBT. Key estimates based only on the subsample of studies where CBT was not delivered outside of primary care are provided as online Supplementary material.
Heterogeneity was estimated based on the Q- and I 2 statistics, where the latter stands for the proportion of the total variance between studies that can be attributed to true study differences in effects, rather than random (sampling) error. I 2 is measured in percentage, where values of 25, 50 and 75% represent low, moderate and high heterogeneity, respectively (Higgins et al., Reference Higgins, Thompson, Deeks and Altman2003). Publication bias was assessed based on visual inspection of funnel plots in combination with Egger's intercept test (Egger et al., Reference Egger, Davey Smith, Schneider and Minder1997), and the Duval and Tweedie trim and fill procedure with the R 0 estimator (Duval and Tweedie, Reference Duval and Tweedie2000).
Results
After reading 372 articles in full text, assessors agreed to include 29 studies (κ = 0.81), and disagreed on 12 studies, of which three were included after discussion with a third author. These three studies were discussed due to the most common reason for disagreement, which was different views on whether studies had a primary care focus (6/12). The second most common topic of discussion was whether CBT protocols targeted depression specifically (3/12). The remaining three differences concerned whether the patients had elevated symptoms of depression, whether the sample was mixed with other disorders and whether the treatment was to be regarded as CBT. Two additional studies were found through reference lists and during data extraction, which resulted in 34 randomised controlled trials included in meta-analysis (Fig. 1) (Teasdale et al., Reference Teasdale, Fennell, Hibbert and Amies1984; Ross and Scott, Reference Ross and Scott1985; Scott and Freeman, Reference Scott and Freeman1992; Scott et al., Reference Scott, Tacchi, Jones and Scott1997; Ward et al., Reference Ward, King, Lloyd, Bower, Sibbald, Farrelly, Gabbay, Tarrier and Addington-Hall2000; Watson et al., Reference Watson, Gordon, Stermac, Kalogerakos and Steckley2003; Willemse et al., Reference Willemse, Smit, Cuijpers and Tiemens2004; Dalgard, Reference Dalgard2006; Smit et al., Reference Smit, Kluiter, Conradi, van der Meer, Tiemens, Jenner, van Os and Ormel2006; González González et al., Reference González González, Fernández Rodríguez, Pérez Rodríguez and Amigo2007; Spek et al., Reference Spek, Nyklicek, Smits, Cuijpers, Riper, Keyzer and Pop2007; Laidlaw et al., Reference Laidlaw, Davidson, Toner, Jackson, Clark, Law, Howley, Bowie, Connery and Cross2008; Lovell et al., Reference Lovell, Bower, Richards, Barkham, Sibbald, Roberts, Davies, Rogers, Gellatly and Hennessy2008; Wiles et al., Reference Wiles, Hollinghurst, Mason, Musa, Burt, Hyde, Jerrom, Lewis and Kessler2008; Kessler et al., Reference Kessler, Lewis, Kaur, Wiles, King, Weich, Sharp, Araya, Hollinghurst and Peters2009; Serfaty et al., Reference Serfaty, Haworth, Blanchard, Buszewicz, Murad and King2009; Hegerl et al., Reference Hegerl, Hautzinger, Mergl, Kohnen, Schutze, Scheunemann, Allgaier, Coyne and Henkel2010; Naylor et al., Reference Naylor, Antonuccio, Litt, Johnson, Spogen, Williams, McCarthy, Lu, Fiore and Higgins2010; Cramer et al., Reference Cramer, Salisbury, Conrad, Eldred and Araya2011; Dwight-Johnson et al., Reference Dwight-Johnson, Aisenberg, Golinelli, Hong, O'Brien and Ludman2011; Ekers et al., Reference Ekers, Richards, McMillan, Bland and Gilbody2011; Joling et al., Reference Joling, van Hout, van't Veer-Tazelaar, van der Horst, Cuijpers, van de Ven and van Marwijk2011; Levin et al., Reference Levin, Campbell, McGovern, Gau, Kosty, Seeley and Lewinsohn2011; Casañas et al., Reference Casañas, Catalán, del Val, Real, Valero and Casas2012; Power and Freeman, Reference Power and Freeman2012; Sørensen Høifødt et al., Reference Sørensen Høifødt, Lillevoll, Griffiths, Wilsgaard, Eisemann, Waterloo and Kolstrup2013; Wiles et al., Reference Wiles, Thomas, Abel, Ridgway, Turner, Campbell, Garland, Hollinghurst, Jerrom, Kessler, Kuyken, Morrison, Turner, Williams, Peters and Lewis2013; Williams et al., Reference Williams, Wilson, Morrison, McMahon, Walker, Allan, McConnachie, McNeill and Tansey2013; Husain et al., Reference Husain, Chaudhry, Fatima, Husain, Amin, Chaudhry, Ur Rahman, Tomenson, Jafri, Naeem and Creed2014; Kivi et al., Reference Kivi, Eriksson, Hange, Petersson, Vernmark, Johansson and Björkelund2014; Gilbody et al., Reference Gilbody, Littlewood, Hewitt, Brierley, Tharmanathan, Araya, Barkham, Bower, Cooper, Gask, Kessler, Lester, Lovell, Parry, Richards, Andersen, Brabyn, Knowles, Shepherd, Tallon and White2015; Kanter et al., Reference Kanter, Santiago-Rivera, Santos, Nagy, Lopez, Hurtado and West2015; Chowdhary et al., Reference Chowdhary, Anand, Dimidjian, Shinde, Weobong, Balaji, Hollon, Rahman, Wilson, Verdeli, Araya, King, Jordans, Fairburn, Kirkwood and Patel2016; Gilbody et al., Reference Gilbody, Lewis, Adamson, Atherton, Bailey, Birtwistle, Bosanquet, Clare, Delgadillo, Ekers, Foster, Gabe, Gascoyne, Haley, Hamilton, Hargate, Hewitt, Holmes, Keding, Lilley-Kelly, Meer, Mitchell, Overend, Pasterfield, Pervin, Richards, Spilsbury, Traviss-Turner, Trepel, Woodhouse, Ziegler and McMillan2017).

Fig. 1. Flowchart of study selection process. CBT, cognitive behaviour therapy; RCTs, randomised controlled trials.
Study characteristics
From the 34 randomised controlled trials of CBT for depression in primary care, we analysed post-treatment data from 5358 patients; 2543 in CBT (35 conditions) and 2815 controls (45 conditions). In terms of CBT formats, 17 conditions were individual CBT with extensive support either face-to-face or remotely, seven were group therapies, 10 were guided self-help CBT with little therapist support and one was a mixed individual and group therapy sample. As to therapists, 31% (11/35) of CBT conditions employed psychologists or psychotherapists, 14% (5/35) unqualified personnel, 11% (4/35) nurses and 43% (15/35) mixed professions or other/unspecified. The mean number of sessions was 9.8 (s.d. = 3.8), and the mean session length was 58.1 min (s.d = 21.6). The most common control condition was TAU, which consisted of a wide range of treatments usually offered in primary care such as visits with a general practitioner, antidepressant medication, counselling or referral for psychological treatment. As to country of origin, 50% (17/34) of the trials were based in the UK, 12% (4/34) in the Netherlands, 12% (4/34) in the USA, 6% (2/34) in Norway, 6% (2/34) in Spain and the remaining 15% (5/34) in other countries. Additional study and condition characteristics are presented in the online Supplementary material.
Study risk of bias
The risk of bias varied considerably between studies (Fig. 2, online Supplementary Table DS3). While random sequence generation and allocation concealment were adequate in the majority of cases, the most common reason for risk of bias was incomplete outcome data. Three studies were given a low risk of bias rating on all applicable criteria (Wiles et al., Reference Wiles, Thomas, Abel, Ridgway, Turner, Campbell, Garland, Hollinghurst, Jerrom, Kessler, Kuyken, Morrison, Turner, Williams, Peters and Lewis2013; Husain et al., Reference Husain, Chaudhry, Fatima, Husain, Amin, Chaudhry, Ur Rahman, Tomenson, Jafri, Naeem and Creed2014; Gilbody et al., Reference Gilbody, Lewis, Adamson, Atherton, Bailey, Birtwistle, Bosanquet, Clare, Delgadillo, Ekers, Foster, Gabe, Gascoyne, Haley, Hamilton, Hargate, Hewitt, Holmes, Keding, Lilley-Kelly, Meer, Mitchell, Overend, Pasterfield, Pervin, Richards, Spilsbury, Traviss-Turner, Trepel, Woodhouse, Ziegler and McMillan2017). Two additional studies (Smit et al., Reference Smit, Kluiter, Conradi, van der Meer, Tiemens, Jenner, van Os and Ormel2006; Joling et al., Reference Joling, van Hout, van't Veer-Tazelaar, van der Horst, Cuijpers, van de Ven and van Marwijk2011) fell just short of this mark because no pre-registered study protocol could be found (selective reporting unclear).

Fig. 2. Study risk of bias based on the Cochrane collaboration's tool. Please note that these ratings apply to the outcome aggregated in the primary meta-analysis.
Post-treatment effects on depressive symptoms
Based on 46 randomised comparisons of CBT to control conditions in the treatment of depression in primary care, the pooled effect size was g = 0.22 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.15–0.30] in favour of CBT. Heterogeneity was significant and in the low-to-moderate range (I 2 = 40%; Q 45 = 78, p = 0.002). The pooled effect size of those five studies with lowest risk of bias (see above) was g = 0.19 (95% CI 0.06–0.32). Effect sizes based on the subsample of comparisons (40/46) where CBT was not delivered outside of primary care were also similar (online Supplementary material). Figure 3 displays a forest plot of study effect sizes with CI.

Fig. 3. Forest plot of all comparisons (k = 46) of CBT and control conditions. ADM, antidepressant medication; CBT, cognitive behaviour therapy; GSH, guided self-help; TAU, treatment as usual.
Moderators and subgroups
Moderator and subgroup analyses are presented in Table 1 and online Supplementary Tables DS4 and DS5. As to study design, CBT had a significant controlled effect regardless of whether patients were included based on a diagnosis of depression, a cut-off score or depressive symptoms only (p = 0.347). The choice of control condition was associated with outcome (p = 0.041). For example, the three studies which compared CBT against a waiting list reported a moderate pooled effect size (g = 0.48), whereas the pooled difference between CBT and other psychological treatments was close to zero (g = −0.02). There was no significant difference in effect between studies from Europe and studies from other parts of the world (p = 0.896). The following variables also did not moderate the controlled effect of CBT: mean baseline depression severity, mean patient age, proportion female, publication year, weeks to the primary endpoint and the Cochrane risk of bias criteria.
Table 1. Moderator analyses of cognitive behaviour therapy and control groups in the treatment of depression and subclinical depression in primary care: categorical variables
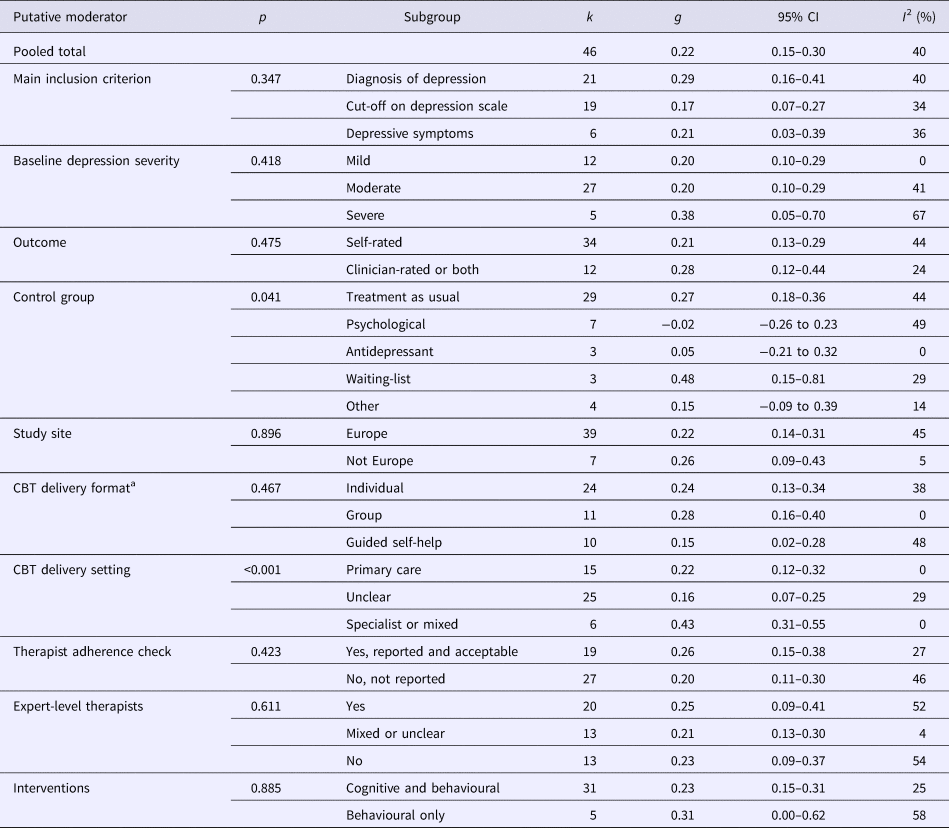
CBT, cognitive behaviour therapy.
a One comparison excluded from this analysis due to mixed CBT format. The ‘individual’ category included one-to-one treatment via the Internet or telephone.
As to the characteristics of CBT, there was no significant difference in effect between delivery formats (ps = 0.234–0.765). Individual CBT (g = 0.24), group CBT (g = 0.28) and guided self-help CBT (g = 0.15) were all more effective than the control condition. Studies where CBT was conducted with primary care patients in a research or specialist setting were associated with a larger effect than studies where CBT was delivered in a primary care setting (g = 0.43 v. 0.22; p = 0.009). The following variables did not moderate the effect of CBT: number of sessions, session length, if an adherence check was reported, if expert-level therapists (i.e. psychologists/psychotherapists or equivalent) delivered the treatment and if the treatment was based on both cognitive techniques and behavioural activation or the latter only.
Follow-up effects on depressive symptoms
Controlled follow-up effects of CBT were reported for 27 comparisons from 21 studies. The pooled last follow-up assessment (M = 10.2 months, s.d. = 9.4; Mdn = 8) effect size was g = 0.17 (95% CI 0.10–0.24) in favour of CBT. Heterogeneity was low (I 2 = 18%; Q 26 = 30, p = 0.269). Approximately 70% (19/27) of these comparisons were against a TAU control condition, and had a pooled controlled effect size of g = 0.19 (95% CI 0.10–0.28; I 2 = 30%; Q 18 = 22, p = 0.216).
Responder and remission rates
Responder rates were reported for nine comparisons from nine studies, and the most common criterion for response was a symptom reduction of at least 50%. The aggregate responder rate was 49% (95% CI 42–56) in CBT and 26% (95% CI 15–37) in the control groups, which corresponded to OR = 2.47 (95% CI 1.60–3.80) and NNT = 4.60 (95% CI 3.25–7.84). Heterogeneity of the OR was moderate (I 2 = 54%; Q 8 = 18, p = 0.024). Remission rates were reported for 20 comparisons from 17 studies, and cut-off scores clustered around θ = 55–66 on the latent depression metric published by Wahl et al. (Reference Wahl, Löwe, Bjorner, Fischer, Langs, Voderholzer, Aita, Bergemann, Brähler and Rose2014). The aggregate remission rate was 45% (95% CI 39–51) in CBT and 35% (95% CI 27–42) in the control conditions, which corresponded to OR = 1.56 (95% CI 1.15–2.14) and NNT = 10.08 (95% CI 5.83–36.90). Again, heterogeneity of the OR was moderate (I 2 = 65%; Q 19 = 54, p < 0.001).
Publication bias
As judged from visual inspection of the funnel plot there appeared to be no asymmetry of effect sizes in relation to the standard error (online Supplementary Fig. DS1). Egger's test was not significant (p = 0.323). Based on Duval and Tweedie's procedure, no study was missing on the left side of the graph (P = .500), and no imputation was indicated.
Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis based on 34 randomised controlled trials found that CBT has a significant though small controlled effect on depression for adult primary care patients (g = 0.22), and that the effect is sustained at follow-up (g = 0.17). The body of studies was moderately heterogeneous, with most CBT conditions being individual therapy (24/46 = 52%), and most comparisons against TAU (29/46 = 63%). CBT was more effective than the control also for patients who had depressive symptoms without meeting full criteria for depression. All CBT formats, i.e. individual therapy, group therapy and guided self-help, were significantly more effective than the control conditions. Based on the NNT statistic, it appears that it is typically necessary to treat approximately five patients with CBT rather than the control condition to achieve one additional responder, and to treat approximately 10 patients with CBT instead of the control condition to achieve one additional case in remission.
The validity of our findings is indicated by our use of broad search criteria in combination with a reliable inclusion procedure with independent assessors. This is to date, and to our knowledge, the largest meta-analysis of CBT for depression in primary care, and the first meta-analysis to investigate follow-up effects in this context.
Comparison with prior research
The remission rates of the present study were similar to those reported in studies of CBT for depression outside of primary care (Cuijpers et al., Reference Cuijpers, Karyotaki, Weitz, Andersson, Hollon and van Straten2014). Our findings are also in line with previous meta-analyses which have demonstrated the efficacy of CBT as compared with TAU for depression in the primary care context (Cuijpers et al., Reference Cuijpers, van Straten, van Schaik and Andersson2009; Linde et al., Reference Linde, Sigterman, Kriston, Rucker, Jamil, Meissner and Schneider2015; Twomey et al., Reference Twomey, O'Reilly and Byrne2015). Controlled effect sizes were however smaller than in previous meta-analyses, possibly because two previous meta-analyses of CBT in primary care had a higher proportion of comparisons with average severe depressive symptoms at baseline (29%/56% v. 11% in this sample) (Cuijpers et al., Reference Cuijpers, van Straten, van Schaik and Andersson2009; Linde et al., Reference Linde, Sigterman, Kriston, Rucker, Jamil, Meissner and Schneider2015).
Our finding that CBT has a similar effect on depression as other psychological interventions in primary care (g = −0.02) is tentative given the small subsample (k = 7), though also consistent with a previous meta-analysis of CBT in both primary care and other settings (Cuijpers et al., Reference Cuijpers, Berking, Andersson, Quigley, Kleiboer and Dobson2013). However, it is probably important to differentiate between psychological treatments, which could not be done here due to the small number of comparisons against psychological interventions.
Based on the present study, most aspects of the treatment format, such as treatment length, do not appear to be important for the controlled effect of CBT in primary care. It must be noted, however, that the present study had insufficient power to detect small to moderate effects, or to explore the inter-relationships between putative moderators based on multivariate analyses.
Another noteworthy finding was that if the treatment was delivered in primary care, this was associated with a smaller controlled effect (g = 0.22) than if the patients were from primary care but the treatment took place elsewhere (g = 0.43). A possible explanation for this is that clinicians working in other contexts than primary care were more likely to be highly qualified. Non-expert therapists were employed by 60% (9/15) of CBT conditions in primary care v. 0% (0/6) of CBT conditions delivered elsewhere.
Limitations
The primary limitation of this meta-analysis was that only 9% (3/34) of the included studies had low risk of bias on all eligible bias criteria. Approximately half of the studies reported outcomes susceptible to bias due to missing outcome data or inadequate handling of missing data (e.g. large proportion of missing data, high risk of data missing not at random or extensive imputation based on last-observation-carried-forward). It is conceivable that the high rate of missing data distorted the outcome.
Another limitation is that the inclusion of multiple comparisons from one randomised controlled trial may be argued to lead to biased estimates and artificially reduced heterogeneity, given that conditions are ‘counted twice’. Although there is some truth to this, we also regard it as important not to arbitrarily disregard comparisons from trials which incorporated more than two conditions of interest.
Because there was a significant heterogeneity in most analyses, it is probably important to differentiate between studies and conditions in order to generalise our findings and make valid inferences about real-world situations. It has, for example, been demonstrated that the components of TAU, which was the most common comparator, tend to vary considerably from study to study (Watts et al., Reference Watts, Turnell, Kladnitski, Newby and Andrews2015).
We also wish to point out two caveats related to our reporting of responder and remission rates. First, the OR presented here do not approximate risk ratios because response and remission were common outcomes (Cummings, Reference Cummings2009). Use of the OR is nevertheless commonplace, and facilitates comparisons with previous meta-analyses (e.g. Linde et al., Reference Linde, Sigterman, Kriston, Rucker, Jamil, Meissner and Schneider2015). Second, use of the NNT in meta-analyses rests on the strong assumption that the difference between the response rate in the CBT condition and the response rate in the control condition are approximately equal over studies. An advantage of the NNT is, however, that it is relatively easy to understand.
Clinical implications and recommendations for future research
Despite notable uncertainty about exact effects, this meta-analysis indicates that CBT for depression is effective in the primary care context. Considering the high prevalence of the disorder and high strain on psychiatric care, we regard this as an important finding because it suggests that it is feasible, as a first step, to offer patients with mild to moderate depression treatment in primary care. In contrast, treatment for severe depression could be argued to fall outside of the generalist tradition of primary health care, and has rarely been studied in this context.
As for future research on CBT for depression in primary care, we advise investigators to adhere to common guidelines for the conduct and publication of clinical trials (Schulz et al., Reference Schulz, Altman, Moher and Group2010; Higgins et al., Reference Higgins, Altman, Gotzsche, Juni, Moher, Oxman, Savovic, Schulz, Weeks and Sterne2011). Of particular importance, we urge that missing data be properly addressed, and that future publications be more explicit about the setting of treatment delivery. For the field to move forward, we also encourage more direct comparisons between active structured treatments.
Conclusion
CBT is an effective treatment for adult depressed primary care patients, and effects are sustained over time. Effect sizes in comparison to TAU are typically small, but may be clinically important given the high prevalence of depression in the primary care setting, patient demand for psychological treatment and high strain on specialist psychiatry.
Author ORCIDs
Fredrik Santoft 0000-0003-0673-6521, Erland Axelsson 0000-0003-2562-2925, Lars-Göran Öst 0000-0002-4351-2810, Maria Hedman-Lagerlöf 0000-0002-3581-099X, Jens Fust 0000-0002-4706-092X, Erik Hedman-Lagerlöf 0000-0002-7939-9848.
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291718004208
Author contributions
FS and EA contributed equally to this study. FS, EA, LGÖ and EHL designed the study. All authors took part in the data collection. EA conducted the statistical analysis. All authors contributed to the publication. EA had full access to all data, and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the presented analysis.
Financial support
This research was funded by Karolinska Institutet and Stockholm County Council, none of which had any role in the design, execution or publication of the study.
Conflict of interest
None.






