Introduction
The number of Americans aged 65 years and older is expected to double from 43.1 million to 83.7 million by 2050, Reference Ortman, Velkoff and Hogan1 and over this time, the number of seriously injured older adults will continue to increase. Geriatric trauma patients have higher mortality, increased hospital length of stay, and consume more hospital resources at similar injury severity scores compared to younger trauma patients. Reference Werman, Erskine and Caterino2–Reference Spaite, Criss and Valenzuela5 These discrepancies are partially explained by increased co-morbidities, lower physiological reserve, and under-triage. Reference Spaite, Criss and Valenzuela5–Reference Hashmi, Ibrahim-Zada and Rhee8 Many injuries in older adults can be managed in a community hospital. However, some injuries are sufficiently severe to require trauma center care, and a system must be in place for Emergency Medical Services (EMS) to correctly identify and transport these patients to a trauma center. Reference Sharma9,Reference Meldon, Reilly and Drew10
Making the right triage decision can be daunting as EMS providers weigh the differing injury characteristics of trauma patients and the estimated transit times to the nearest trauma center. Unfortunately, under-triage of geriatric trauma patients has been described in several trauma systems and appears to be a common problem. Reference Chang, Bass and Cornwell11–Reference Cox, Morrison, Cameron and Smith13 In response, geriatric-specific criteria have been developed and added to the existing Field Triage Guidelines. Reference Sasser, Hunt and Faul14 Despite evidence that these criteria can effectively identify older patients likely to benefit from trauma center care, to date, efforts to implement geriatric-specific criteria for trauma triage of older adults have failed to solve the under-triage problem. Reference Ichwan, Darbha and Shah15 Available evidence suggests that improving the triage of older adults will require enhanced education of EMS providers and characterization of the extent of the problem both regionally and nationally. Geriatric trauma under-triage in the presence of specific physiologic criteria indicating a serious injury remains incompletely understood. Reference Caterino, Brown and Hamilton16,Reference MacKenzie, Rivara and Jurkovich17
In part as a response to these challenges, North Carolina (NC) USA implemented state-wide Trauma Triage Destination Plans (TTDPs) on January 1, 2010 in all 100 of NC’s EMS systems to guide destination decision making 18 (Figure 1). The EMS systems in NC are generally divided by county (n = 100) and are comprised of full-time, part-time, and volunteer EMS providers. Moss, et al confirmed that all EMS systems in NC have developed system-specific guidelines from the original TTDP template that were distributed to all EMS personnel. Specifically, these authors confirmed that each EMS county in NC had adopted and revised its own version of the TTDP and that almost every EMS county (98%) had conducted face-to-face training with its EMS personnel to distribute the plan. They also reported various systems of quality assurance to confirm EMS personnel use in the field. Reference Moss, Cowden and Atterton19 However, neither compliance with these plans for older adults nor the effect of the plans on the triage of injured older adults have been studied. Another study recently examined the implementation of the NC TTDP for all patients and did not observe changes in trauma center transportation for those meeting TTDP criteria. Reference Brice, Shofer and Cowden20 Within this context, the purpose of this study is to examine the impact of the NC TTDP’s implementation on the prehospital triage of geriatric patients by specific TTDP physiologic criteria.
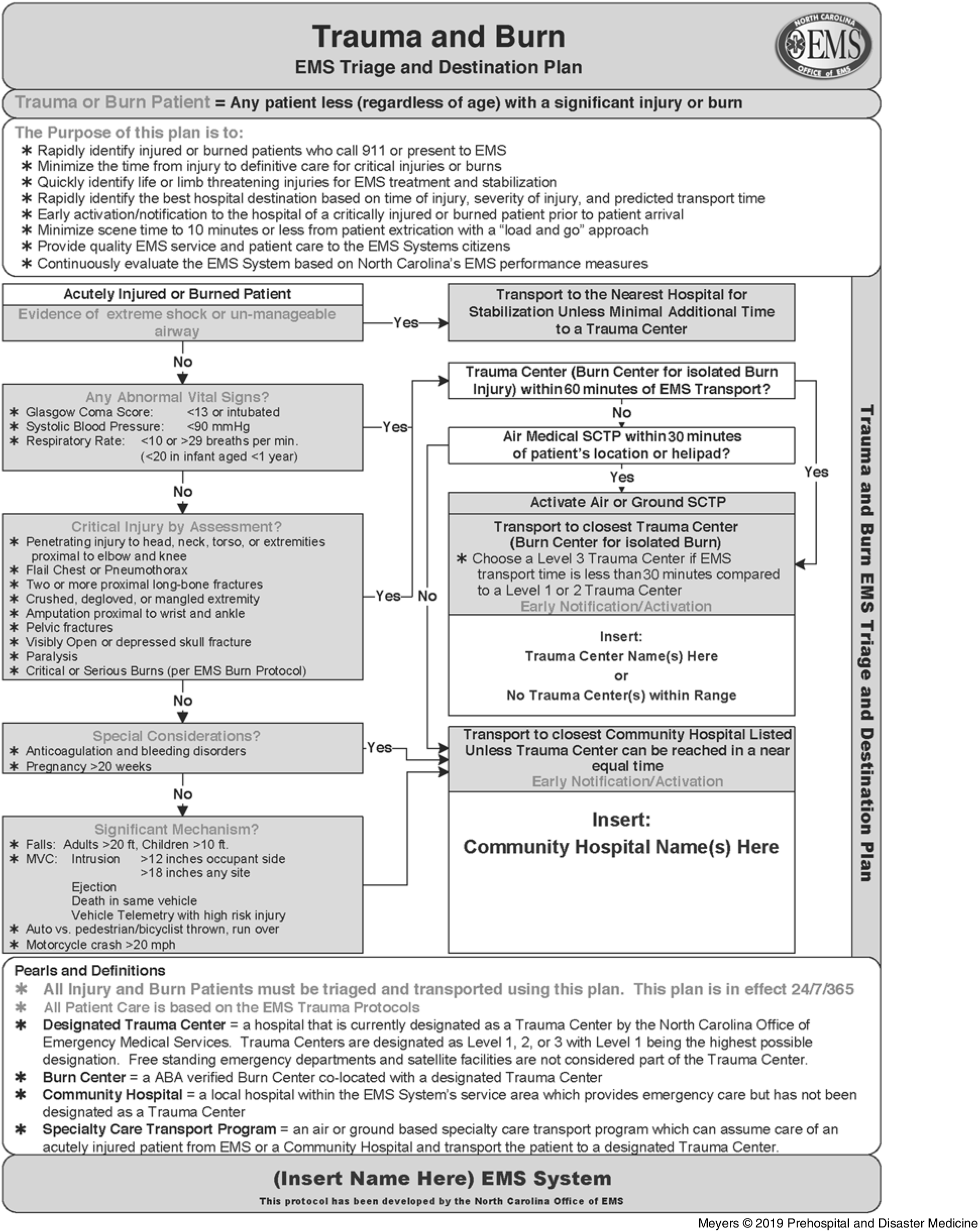
Figure 1. The North Carolina Trauma Triage Destination Plan.
Methods
Study Design
The research group conducted a retrospective cohort study of geriatric trauma patients evaluated and transported by NC EMS between March 1, 2009 through September 30, 2009 and March 1, 2010 through September 30, 2010. Because the NC TTDP was implemented state-wide on January 1, 2010, the group selected time intervals flanking the implementation date to allow for analyses of patient populations before and after its implementation. The group allowed a three-month gap period between pre- and post-TTDP implementation to allow for a “ramp up” time for EMS to become accustomed to utilizing the TTDP protocol. This study was reviewed and approved by the University of North Carolina Institutional Review Board (IRB; Chapel Hill, North Carolina USA). Written informed consent from patients was waived by the IRB. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (Washington, DC USA) had no role in the in the design, methods, subject recruitment, data collections, analysis, or preparation of this paper, but they did provide funding to this project.
Study Setting and Population
North Carolina has a population of approximately 10 million with over 15% of those individuals aged 65 years or older, making NC an ideal place to evaluate the effectiveness of a TTDP for the older adult population. Ethnically, the population consists of 71.0% Caucasian, 22.2% African American, 1.6% Native American, 2.9% Asian, and 9.2% Hispanic. The median household income is $48, 256. 21
The EMS agencies in NC are organized into 100 county-based EMS systems, each of which has a single Medical Director. The EMS providers operate under standing state-wide protocols developed and maintained by the NC Chapter of the American College of Emergency Physicians (Irving, Texas USA). On-line medical control is available for EMS providers, but is not required to access and complete a protocol or transport decision.
All NC EMS patients evaluated and transported during the study time period were eligible for inclusion if they met the following criteria: (1) age 50 years or older; (2) transported to a NC hospital by NC EMS; (3) experienced an injury; and (4) met NC TTDP physiologic criteria for trauma. An injury was defined as follows:
1. Dispatch Complaint of an animal bite, assault, burns, electrocution, fall victim, industrial accident/inaccessible, incident/other entrapments, mass-casualty incident, stab/gunshot wound, traffic accident, traumatic injury (NEMSIS E03_01);
2. Injury = yes (NEMSIS E09_04);
3. Any Injury Cause (NEMSIS E10_01);
4. Provider Impression of traumatic injury, sexual assault/rape, inhalation injury/toxic gas, smoke inhalation, or electrocution (NEMSIS E09_15 and/or NEMSIS E09_16); or
5. Procedure of extrication, rescue, spinal immobilization, splinting-basic, splinting-traction, chest decompression, wound care, wound care-hemostatic agent, wound care-taser barb removal, wound care-irrigation, wound care-tourniquet (NEMSIS E19_03).
Physiological TTDP criteria included: (1) Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score <13 or intubated (NEMSIS E14_19); (2) systolic blood pressure <90 mmHg (NEMSIS E14_04); or (3) respiratory rate <10 or >29 breaths per minute (NEMSIS E14_11). 22 Exclusion criteria included: (1) missing patient name, date of birth, or receiving facility; (2) dead on scene; (3) not transported by EMS to a hospital from the scene; and (4) interfacility transports.
Study Protocol
The Prehospital Medical Information System (PreMIS) warehouses prehospital patient care records for NC EMS systems. The PreMIS is a National EMS Information System-compliant administrative data system implemented in 2002 and owned by the NC Department of Health and Human Services Office of Emergency Medical Services (Raleigh, North Carolina USA). The PreMIS is maintained by the EMS Performance Improvement Center (Chapel Hill, North Carolina USA), which supports the daily operations and provides technical assistance for end users. At the time of the study, NEMSIS Version 2 was in use.
Each of NC’s licensed EMS agencies is required by state rule to collect and submit data into PreMIS for every EMS encounter. Data submitted by individual agencies undergo an initial data validation process prior to the agency being granted permission to submit into the database. Periodic re-validation is conducted to ensure accuracy. The PreMIS contained 1.35 million records for 2009 and 1.45 million records for 2010 representing 100 % of the EMS agencies and events within NC. Reference Mears, Pratt and Glickman23
Patient demographics, incident characteristics, patient physiologic data and injury characteristics, and patient transport characteristics were collected from PreMIS.
Geocoding
The incident address, defined as the location at which EMS met the patient for assessment and treatment, for each patient encounter was geocoded using ArcGIS (Esri StreetMap North America, Data and Maps 10.1; Esri; Redlands, North Carolina USA). Any address not automatically geocoded when entered into ArcGIS was manually searched using Google Maps (Google Inc.; Mountain View, California USA). After data cleaning using Google Maps, addresses were re-geocoded in ArcGIS. Travel time and distance in road miles from incident address to nearest hospital, nearest trauma center, and actual hospital to which the patient was transported were calculated.
Key Outcome Measures
The key outcome measure was transport of geriatric patients to a trauma center in compliance with the NC TTDP as compared to trauma triage patterns prior to implementation of the TTDP. Under-triage rates were also examined. The NC TTDP states that any trauma patient meeting physiologic criteria without need for immediate hospital care (eg, evidence of extreme shock or un-manageable airway) who is within 60 minutes of a trauma center by ambulance should be transported to that trauma center. If the patient is ≥60 minutes from a trauma center, the patient should be transported to a trauma center by an air medical provider if available within 30 minutes. Otherwise, the patient should go to the closest hospital. 18 Patients who met these criteria and who were not transported to a Level 1 or Level 2 trauma center were considered under-triaged.
All cases were classified based on their transport destination and whether they occurred pre-implementation or post-implementation of the NC TTDP. Patients were further classified based on whether they were closest to a trauma center or non-trauma center; distance to the nearest trauma center (ie, <60 or ≥60 minutes); mode of transport; blood pressure (ie, <90 versus ≥90 mm Hg); respiratory rate (ie, <10 or >29 versus 10–29 breaths per minute); GCS score (ie, <13 versus 13–15); whether or not they were ventilated in the field; sex; age (ie, 50–59, 60–69, 70–79, or ≥80); race; and urbanicity status. Urbanicity for each record was categorized according to the 2013 Urban Influence Codes developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (Washington, DC USA).
Data Analysis
Analyses consisted of descriptive statistics on demographic and transport data. Chi-square analysis was performed to assess differences in patient demographics, patient vitals, and transport characteristics by trauma center and non-trauma center. In addition, sub-analyses using chi-square test and Z-score analyses were performed on patients who were nearest a non-trauma center; this sub-group of patients represents an area of particular interest for EMS decision making where EMS must consciously take measures to follow the protocol and safely transport patients to trauma centers. Changes in EMS destination decision making were assessed before and after TTDP implementation via Z-scores. Additionally, sex and age groups 50–59 and ≥80 years old were analyzed separately using the chi-square test in the pre- and post-TTDP periods. The youngest and oldest age groups were compared in further sub-analysis as it was hypothesized that triage decisions would vary most in these age groups.
All analyses were performed using SAS statistical software (Version 9.4; SAS Institute; Cary, North Carolina USA). Statistical significance was determined using an alpha of 0.05.
Results
Sample Characteristics
During the study timeframe, 5,345 geriatric trauma patients meeting at least one NC TTDP physiologic criteria were transported by EMS to hospitals and met all the study criteria (Table 1). The dataset suffered a 4.2% (n = 223) loss of data at the outset due to missing data, including age, date of birth, and destination facility. Patients ≥80 years made up the single greatest age percentage (32.5%; n = 1,738). Cases were evenly distributed among urban, suburban, and rural areas. For most trauma patients, the closest hospital was not a trauma center (81.5%; n = 4,354). However, most trauma patients were injured within 60 minutes of a trauma center (69.3%; n = 3,704). Less than 3.0% (n = 133) of trauma patients were transported by air medical resources.
Table 1. Patient Characteristics Overall and by Site of Care

Overall Transport Decision Making
There were no significant differences between pre- and post-TTDP trauma center populations (Table 2). In general, the same proportion of geriatric trauma patients meeting physiologic criteria were transported to trauma centers pre-TTDP and post-TTDP (pre 24.4%; post 24.4; Table 2). Few patients bypassed a closer hospital in favor of a trauma center (pre 12.6% [n = 250; 95% CI 11.1–14.1]; post 11.9% [n = 282; 95% CI 10.6–13.2]; Table 3). Even when the trauma was within 60 minutes of a trauma center, few patients bypassed closer hospitals for a trauma center (pre 17.9% [n = 220; 95% CI 15.8–20.1]; post 16.7% [n = 248; 95% CI 14.8–18.6]). While no difference was found between the pre- and post-time interval when the trauma occurred more than 60 minutes from a trauma center (pre 4.0% [n = 30; 95% CI 2.6–5.3]; post 3.9% [n = 34; 95% CI 2.6–5.1]), it is important to note the dramatic decline in patients transported to a trauma center when the 60-minute threshold was crossed during both time intervals (pre 13.9% decrease; post 12.8% decrease).
Table 2. Percentage of Study Patients Transported to a Trauma Center Pre- and Post-Implementation of the North Carolina Trauma Triage Destination Plans (n = 1,304)

Abbreviations: GCS, Glasgow Coma Scale; TTDP, Trauma Triage Destination Plan.
Table 3. Percentage of Study Patients Transported to a Trauma Center Pre- and Post-Implementation of the North Carolina TTDPs, Among Patients Who Were Closer to a Non-Trauma Center (n = 532)

Abbreviations: GCS, Glasgow Coma Scale; TTDP, Trauma Triage Destination Plan.
Transport Based on Age
Within a population of seriously injured trauma patients aged 50 years and older, increasing age was associated with lower rates of trauma center transportation (P <.05; Table 1). Rates of trauma center transport for patients aged 50–59 years pre- and post-TTDP were 30.5% (n = 185; 95% CI, 26.9–34.2) and 30.7% (n = 213; 95% CI, 24.5–36.9), compared to patients >80 years pre- and post-TTDP 19.9% (n = 157; 17.09–22.65) and 19.5% (n = 185; 17.0–22.0; P <.05). This difference in age groups was also observed for the subset of patients in whom the closest hospital was or was not a trauma center (Table 4 and Table 5). Fewer patients in each age group bypassed a closer hospital for a trauma center after implementation of the TTDP (Table 3).
Table 4. Transport Destination by Age and Sex, Pre- and Post-Implementation of the North Carolina Trauma Triage Destination Plans

Abbreviation: TTDP, Trauma Triage Destination Plan.
a Indicates P value <.05.
Table 5. Transport Destination by Age and Sex, Pre- and Post-Implementation of the North Carolina TTDPs, Among Patients Who Were Closer to a Non-Trauma Center

Abbreviation: TTDP, Trauma Triage Destination Plan.
a Indicates P value <.05.
Transport Based on Specific Abnormal Physiologic Criteria
Nearly one-fourth of geriatric trauma patients meeting each of the three physiologic criteria categories were transported to trauma centers in both pre- and post-TTDP periods (Table 2). No significant differences were found in community hospital bypass decision making for hypotensive patients comparing pre- and post-TTDP populations (Table 3).
Discussion
In this study of injured adults aged 50 years and older with physiologic markers of serious injury, the implementation of the NC TTDP did not result in a change in transport patterns to a trauma center. Under-triage was common. For the entire study sample, high under-triage rates pre-implementation (75.6%) were found that did not change post-implementation (75.6%). Under-triage rates were even higher for patients whose closest hospital was not a trauma center and for patients whose injury occurred ≥60 minutes from a trauma center. Neither of these distance from trauma center sub-populations benefitted from improved EMS destination decision making post-TTDP. High rates of under-triage were observed among the subset of patients who were hypotensive, had a low GCS, or had an abnormal respiratory rate. Over the entire study time frame, only 2.5% (n = 133) of the current study population was transported by air, yet approximately 30.7% (n = 1,641) of this population was eligible according to the current NC TTDP (≥60 minutes from the nearest trauma center). Further, there was no evidence of increased use of air medical transport after implementation of the TTDP. Observed rates of under-triage were substantially higher than the acceptable rate of under-triage of five to ten percent identified by the American College of Surgeons (Chicago, Illinois USA). Reference Rotondo, Cribari and Smith24
This study adds to this literature in several ways. First, the problem of under-triage is confirmed for older adults even with specific physiologic markers of injury severity that almost all EMS providers would agree are highly concerning in the setting of trauma (hypotension, bradypnea, tachypnea, or a GCS <13). Second, this study demonstrates that under-triage occurs among patients for whom the injury occurs less than 60 minutes from a trauma center and is a much greater problem among those living more than 60 minutes from a trauma center. The latter is an important concern for the state of NC and other states with substantial rural populations. Regarding the lack of air transport for rural patients, this is a complex issue likely related to cost, availability of aircraft, weather conditions, terrain, and patient preference, among others. A future study could focus on factors mitigating use of air medical transport. Third, under-triage rates are highest for the eldest patients. Fourth, this under-triage persists even after comprehensive adoption of a revised trauma destination plan by all 100 of the states EMS systems. Given past research and this current study, compliance with Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC; Atlanta, Georgia USA) field triage guidelines for the older adult population is likely a national problem with serious consequences for quality of care and outcomes for geriatric trauma patients.
In this study, increasing under-triage with increasing age was observed both before and after implementation of the NC TTDP. A prior study found the chance of being treated at a Level 1 trauma center to be 89% less likely for a person aged 80 or older compared to a person aged <65 when both meet trauma triage criteria. Reference Nakamura, Daya and Bulger12 Many hypotheses could be generated for this finding such as patient preference, under-resourced EMS systems, or ageism. Further research is needed to clarify the causes of under-triage in the oldest trauma patients.
These results do not elucidate a single explanation for the observed under-triage of geriatric trauma patients. Possible explanations include an inadequate number or poor distribution of trauma centers, the high-cost of air medical transport, resistance to change, or lack of use of the TTDP among EMS providers. Studies in other regions of the US have illustrated significant noncompliance related to trauma triage guidelines for the geriatric population, and even more specifically in relation to physiological criteria. Reference Gage, Traven and Rivara25–Reference Ma, MacKenzie and Alcorta27 This finding is especially problematic given other studies have found physiologic criteria to be the most accurate in predicting severe traumatic injury. Reference Ma, MacKenzie and Alcorta27–Reference Henry, Hollander and Alicandro29 A recent study suggests that reflexive thinking by EMS providers based on the general appearance of the patient and the scene, rather than careful consideration of the presenting case and local guidelines, may be an important cause of under-triage. Reference Jones, Cushman and Lerner30 This is problematic as previous research has shown limitations in the ability of EMS providers to accurately predict clinical outcomes, necessity of transport, and hospital admission. Reference Brown, Hubble and Cone31 The study authors decided the likely cause to be a disconnection between guidelines and their actual real-world application. For instance, EMS providers argued that the use of the GCS score was not practical in the prehospital setting. Reference Jones, Cushman and Lerner30 The current study’s results support the growing body of evidence that EMS providers often under-triage older trauma patients to local hospitals rather than trauma centers. Future revisions to the TTDP may be necessary to alleviate the divergence between protocol and practice, but any such changes will likely need to be coupled with an educational program and feedback system for EMS providers making these decisions. The introduction of more standardized approaches such as trauma triage checklists to encourage thoughtful consideration over intuition from EMS providers may also be helpful. Reference Platts-Mills, Evans and Brice32
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
Strengths of this study include the use of data from the entirety of a geographically large and heavily populated state with a mix of urban and rural populations, comparison of results before and after a comprehensive update to the triage destination plans, and a focus on patients with physiologic criteria indicative of serious injury. This study also has several limitations. In NC, older adults tend to reside in more rural areas, a result of the younger population moving to urban areas for education and employment opportunities. This has the effect of increasing the number of older adults experiencing injuries far from trauma centers. This fact matters because other studies have already demonstrated that traumatic injuries occurring farther from Level 1 or Level 2 trauma centers are associated with greater risk of death. Reference Brown, Rosengart, Billiar and Peitzman33,Reference Jarman, Curriero and Haut34 However, when looking at patients within the data set located within 60 minutes of a trauma center, under-triage was still found to be greater amongst the older geriatric adults compared to the younger geriatric adults (74.2% versus 55.1% under-triage, respectively) suggesting that regardless of location, older patients are more likely to be under-triaged. Other factors such as patient preference, extreme patient acuity (extreme shock, unmanageable airway), or adverse weather conditions may in individual cases contribute to the under-triage of geriatric trauma patients. However, these factors are unlikely to explain the extremely high observed rates of under-triage among the geriatric population. Finally, outcome data are lacking. The most impactful outcome of interest is, of course, survival and disability. Lacking an integrated health data exchange, authors were not able to link EMS patient data to the many hospitals in NC. Future work providing data exchanges between EMS, hospitals, and rehabilitation facilities will allow for a more robust and complete evaluation of the effect of trauma triage.
Conclusion
Among older trauma patients in NC meeting trauma triage physiologic criteria for trauma center transportation, very high rates of transportation to non-trauma centers were found. The implementation of the NC TTDP did not result in a change in transportation of trauma patients 50 years and older meeting triage guidelines to a trauma center. Increased EMS education and feedback is recommended regarding field triage guidelines and the importance of trauma center care for geriatric trauma patients. Further research into the effectiveness of the current trauma triage protocols, the need for more standardized approaches in EMS decision making, and analysis of external influences that affect EMS personnel choice of hospital will further enable directed interventions.
Conflicts of interest/funding
Funding was provided from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA; Washington, DC USA). The NHTSA had no role in the in the design, methods, subject recruitment, data collections, analysis, or preparation of this paper. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.








