Introduction
Endoparasitoid wasps are parasites of other insect species which deposit their eggs in the body cavity of the host and thus possess a variety of strategies to ensure the survival of their progeny. In order to provide a suitable environment for their immature stages, parasitoid wasps modify or regulate the physiological, endocrinological, and nutritional processes of their hosts (Beckage, Reference Beckage, Beckage and Thompson1993). Endoparasitoids also display passive and active strategies to avoid being recognized as non-self by the immune system of the host (Teng et al., Reference Teng, Xu, Gan, Chen, Fang and Ye2016). Passive protection can be achieved by parasitoid eggs covered with some protective surface components which are not recognized as foreign objects (Schmidt et al., Reference Schmidt, Theopold and Strand2001; Hu et al., Reference Hu, Xu, Hu, Yu, Liang and Zhang2014; Teng et al., Reference Teng, Xu, Gan, Chen, Fang and Ye2016). However, active protection involves direct modulation of the host immunity by complex mechanisms (Meng et al., Reference Meng, Qiao, Tang, Hou, Yu and Chen2018). The most common feature shared in the action of endoparasitoids in families Ichneumonidae and Braconidae is the suppression of host immune physiology by maternal factors injected with the eggs upon oviposition (Thompson, Reference Thompson1999; Schmidt et al., Reference Schmidt, Theopold and Strand2001). These factors include, depending on the species, venoms, ovarian fluids, teratocytes (embryo-derived factors) polydnaviruses (PDVs), and virus-like particles (Webb and Luckhart, Reference Webb and Luckhart1994; Luckhart and Webb, Reference Luckhart and Webb1996). Among these, PDVs and venoms appear to be the most studied maternally derived factors. In many endoparasitoid species, venom is necessary to synergize the effects of PDVs (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Schmidt and Asgari2004; Asgari, Reference Asgari, Beckage and Drezen2012). However, in endoparasitic wasps that are devoid of PDVs, venom appears to be the most important component for host manipulation (Richards and Parkinson, Reference Richards and Parkinson2000; Cai et al., Reference Cai, Ye and Hu2004; Rivers et al., Reference Rivers, Uçkan, Ergin and Keefer2010). Examples of such parasitoids include Pteromalus puparum L. (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) (Cai et al., Reference Cai, Ye and Hu2004; Wu et al., Reference Wu, Ye, Zhu, Chen and Hu2008), Pimpla turionellae L. (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) (Ergin et al., Reference Ergin, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2006), Pimpla hypochondriaca Retzius (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) (Richards and Parkinson, Reference Richards and Parkinson2000), Nasonia vitripennis Walker (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) (Rivers et al., Reference Rivers, Ruggiero and Hayes2002, Reference Rivers, Uçkan, Ergin and Keefer2010), Asobara tabida (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) (Eslin and Prevost, Reference Eslin and Prevost1996), Asobara citri (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) (Moreau et al., Reference Moreau, Eslin, Giordanengo and Doury2003), Asobara japonica (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) (Mabiala-Moundoungou et al., Reference Mabiala-Moundoungou, Doury, Eslin, Cherqui and Prevost2010), and Macrocentrus cingulum (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) (Li et al., Reference Li, Lu, Feng, Ke and Fu2007). A limited number of studies demonstrate that venom from the abovementioned ecto and endoparasitoids non-transmitting symbiotic viruses may suppress host immune reactions. Insects resist foreign materials with their highly effective immune defense mechanisms that rely on humoral and cellular components. Various types of hemocytes are the primer mediators of cell-mediated immune responses in many host–parasitoid systems including phagocytosis, nodulation, encapsulation, and melanization (Lavine and Strand, Reference Lavine and Strand2002; Marmaras and Lampropoulou, Reference Marmaras and Lampropoulou2009). In certain parasitoid–host systems, the main part of our knowledge about the immune manipulating effects including cytolitic and cytotoxic activity of parasitoids not transmitting PDVs comes from venom (Parkinson and Weaver, Reference Parkinson and Weaver1999; Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers, Ergin and Sak2010, Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011; Mabiala-Moundoungou et al., Reference Mabiala-Moundoungou, Doury, Eslin, Cherqui and Prevost2010). However, the role of calyx fluid that lacks PDVs is less well understood. In the M. cingulum–Ostrinia furnacalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) system, the ovarian proteins from M. cingulum have been shown to suppress the encapsulation ability of host hemocytes (Li et al., Reference Li, Lu, Feng, Ke and Fu2007). Mabiala-Moundoungu et al. demonstrated that A. japonica secretions from both venom gland and ovary were required to regulate synergistically the immune system of the host Drosophila melanogaster for successful parasitization (Mabiala-Moundoungou et al., Reference Mabiala-Moundoungou, Doury, Eslin, Cherqui and Prevost2010).
Previous studies in the literature demonstrated that, electron microscopic analyses of tissues associated with the female reproductive tract of P. turionella has provided no additional information of PDVs or virus-like particles in this wasp (Osman, Reference Osman1978; Osman and Führer, Reference Osman and Führer1979; Blass and Ruthmann, Reference Blass and Ruthmann1989; Ergin et al., Reference Ergin, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2006). In a recent review, the solitary pupal endoparasitoid P. turionellae has also been presented among parasitoids without PDVs or virus-like particles (Quicke and Butcher, Reference Quicke and Butcher2021). Biochemical properties (Ergin et al., Reference Ergin, Uçkan, Rivers, Rivers and Yoder2007), paralitic, cytolitic, and cytotoxic activities toward cultured cells established from Trichoplusia ni (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) of this wasp's venom (Ergin et al., Reference Ergin, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2006) were previously demonstrated. The role of parasitism and venom on total and differential hemocyte counts (Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers, Ergin and Sak2010), encapsulation and melanization ability (Uçkan et al., Reference Uçkan, Er and Ergin2010), and apoptosis of circulating hemocytes (Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011) were also examined in P. turionellae–Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) parasitoid–host system. The major part of our knowledge concerning the effects of P. turionellae on the host immunity comes from venom. To further clarify the general patterns of host immune regulation by P. turionellae, we proposed that the calyx fluid of parasitoid devoid of PDVs would also interfere with immune processes in a host–parasitoid system. For this purpose, the current study was undertaken to investigate the effects of P. turionellae calyx fluid on in vivo and in vitro hemocyte counts, hemocyte viability, extend of encapsulation and melanization response as indicators of immune functions of its lepidopteran host G. mellonella.
Material and methods
Experimental insects
Laboratory colonies of the host G. mellonella and its parasitoid P. turionellae were reared at 25 ± 1°C, 60 ± 5% relative humidity, and 12:12 (L:D) photoperiod conditions at the laboratory. Host larvae were fed with an artificial Bronskill diet (Bronskill, Reference Bronskill1961). The adult parasitoids were kept at cage (25 cm × 25 cm × 25 cm), fed with a 30% honey solution with water and provided with host pupae for hemolymph feeding. The host pupae were offered two times a week to P. turionellae females and removed after the oviposition was observed. The parasitized pupae were then stored at the same laboratory conditions mentioned above until adult emergence.
Preparation of calyx fluid and injection into G. mellonella larvae
According to our previous observation (unpublished data), P. turionellae lays eggs in up to four different G. mellonella pupae at a certain time. One female equivalent calyx (FEC) was defined as the supernatant from one pair of the divided ovary in 1 μl phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4, Sigma, Germany) according to Yu et al. (Reference Yu, Chen, Chen, Huang, Lou and Liu2007). In the light of both behavioral observation (laying eggs in four pupae at a certain time) and the literature (Yu et al., Reference Yu, Chen, Chen, Huang, Lou and Liu2007), the 0.25 FEC we used in our study seemed to be the amount required for successful parasitism. So we chose doses under and below 0.25 FEC. About 10–20-day-old adult female parasitoids were individually sterilized with ethanol (%96) and dried, then the ovaries (fig. 1) were carefully removed from the abdomen under binocular stereo microscope (Olympus SZ7, Japan). To obtain one FEC, 20 individual ovaries were punctured by a needle and placed into 100 μl sterile PBS in a 0.5 ml microcentrifuge tube on ice and then centrifuged three times at 800 g for 15 min at 4°C. After centrifugation, the obtained supernatant containing calyx fluid was transferred to a new sterile microcentrifuge tube and stored at −80°C until use (modified from Yu et al., Reference Yu, Chen, Chen, Huang, Lou and Liu2007; Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011). The FEC supernatant was diluted with appropriate concentrations of PBS before injections to host larvae.
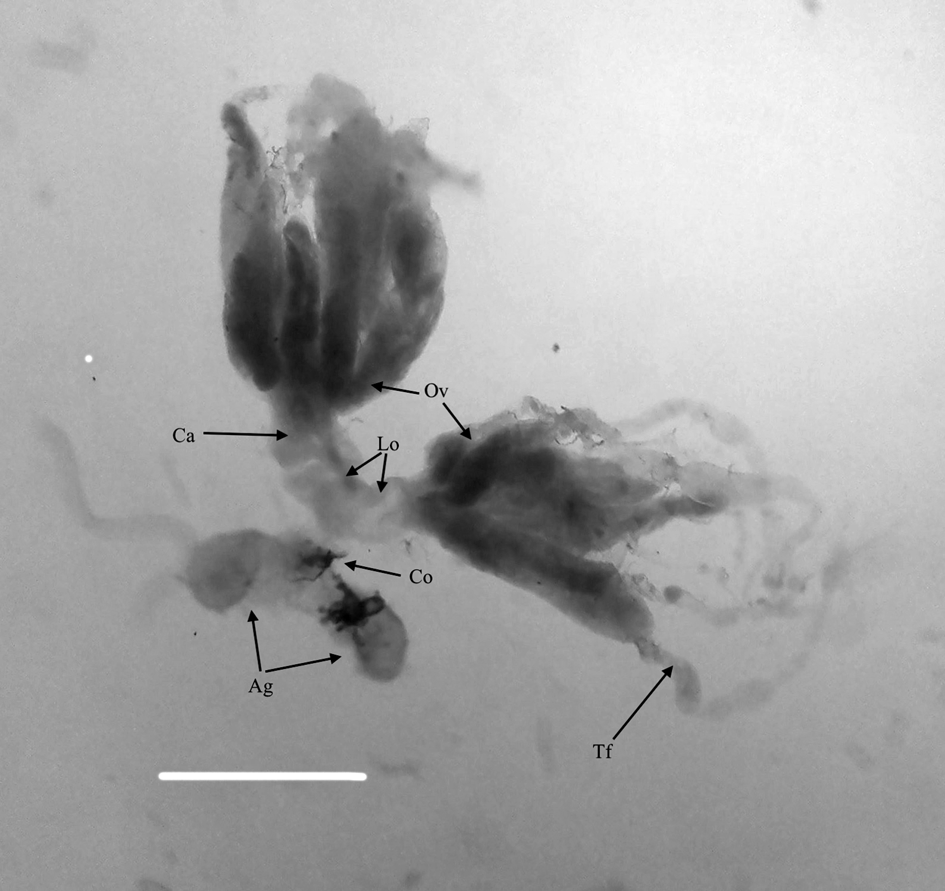
Figure 1. Ovary of P. turionellae. The bar represents 100 mm. (Ca) calyx region, (Ov) ovariole, (Lo) lateral oviduct, (Co) common oviduct, (Ag) accessory gland, (Tf) terminal filaments.
The calyx fluid was adjusted to 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, and 1 FEC with PBS that were previously injected and detected to be non-lethal for G. mellonella larvae (Unpublished data). The controls consisted of untreated, null injected (larvae were air injected), and PBS injected groups. A 5 μl solution of the calyx fluid preparation was injected to larvae from the front segment of the abdominal proleg using a Hamilton microsyringe (Hamilton Co., Reno, NV, USA). For each control and experimental group, five larvae were used and all the experiments were repeated three times.
In vivo and in vitro hemocyte count
To find out the effects of calyx fluid on total hemocyte counts (THCs), the last instar larvae of G. mellonella (0.18 ± 0.02 g) were injected by different concentrations of calyx fluid. The experimental and control larvae were bled from the front segment of the abdominal proleg with a sterile needle 1 h after injection. To determine THC in larval circulation, the in vivo and in vitro procedure of Kaya et al. (Reference Kaya, Uçkan and Er2021) were used. Briefly, 4 μl of hemolymph from each individual treated larva was obtained with a glass microcapillary tube (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) immediately mixed with 36 μl of ice-cold anticoagulant buffer (0.098 M NaOH, 0.186 M NaCl, 0.017 M Na2EDTA, and 0.041 M Citric acid, pH: 4,5) to avoid hemocyte aggregation. Ten microliters of this suspension were loaded to a Neubauer hemocytometer (Superior, Bad Mergentheim, Germany) and hemocytes were counted by Olympus BX51 phase-contrast light microscope (Olympus Corp., Tokyo, Japan).
Calyx fluid-induced changes in THCs were also examined using an in vitro assay with isolated hemocytes from G. mellonella. Hemocyte in vitro assays was performed in sterile 96-well tissue culture plates (Corning, NY, USA). Obtaining hemocytes from G. mellonella and adding them to plates were carried out in a biological safety cabinet (Esco Class II BSC, Singapore). Untreated, null, and PBS-injected G. mellonella larvae and experimental larvae that were injected with different concentrations of calyx fluid 1 h before were sterilized with 70% alcohol and washed in distilled water. After drying, 10 μl of hemolymph from individual larvae were collected with glass capillaries and added to the wells of the 96-well plates containing growth medium which consists of 81 μl of Grace Insect Medium (GIM, Gibco, Fisher Scientific, Sweden) and 9 μl of Fetal Bovine Serum (Sigma, Germany) (Tojo et al., Reference Tojo, Naganuma, Arakawa and Yoko2000). The plates were incubated for up to 24 h at 27°C in a cooling incubator and hemocyte counts were detected using an inverted microscope with phase-contrast optics (Nikon Ti-U, Japan). The in vitro hemocyte counts were estimated according to Prescott ve Breed (Reference Prescott and Breed1910) with some modifications. In order to determine THC, the microscope counting area was determined as 0.212 mm2 with the microscope software (Nis-Elements, Nikon, Japan). The imaging area was proportioned to the well area (35 mm2, provided by the manufacturer) and then the final calculation was made by multiplying it by the dilution coefficient. Five larvae were evaluated for each experimental and control assay in three replicates for in vitro hemocyte counts.
Hemocyte viability, mitotic indices
To determine the effects of calyx fluid on hemocyte viability and mitotic indices of G. mellonella larvae both in vivo and in vitro, acridine orange (AO) and ethidium bromide (EB) double staining method (Kaya et al., Reference Kaya, Uçkan and Er2021) was used. For in vivo studies, 5 μl of hemolymph obtained from calyx fluid-injected and control larvae were poured on a microscope slide. Stock solutions of AO (100 μg ml−1; Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO) and EB (100 μg ml−1; Sigma Chemical Co.) were prepared in PBS. Ten microliters of a dye mixture including equal volumes of AO and EB dyes was spread on the glass slide and immediately examined using a fluorescence microscope at blue filter (Olympus BX51, Olympus Corp.). Cells were classified as viable, early apoptotic, late apoptotic, and necrotic cells in accordance with Kosmider et al. (Reference Kosmider, Zyner, Osiecka and Ochocki2004) and Er et al. (Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011). The frequency of cells in the mitotic phase was also observed at all the treated calyx fluid concentrations and control groups by using AO and EB double staining method (Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011).
The effects of different doses of calyx fluid on hemocyte viability of G. mellonella were also examined using an in vitro assay. Ten microliters of hemolymph obtained with glass capillaries were added to the wells of the 96-well plates containing 90 μl growth medium and allowed to incubate at 27°C for 24 h. After incubation period, the growth medium was removed and 10 μl volume of AO-EB dye mixture was added to the hemocyte monolayer for 5 min. After washing the monolayers with PBS (pH 7.4), hemocyte counts were detected using an inverted fluorescence microscope with blue filter. In total, 1000 cells from individual larvae were analyzed from three randomly selected fields.
Encapsulation and melanization
To evaluate the encapsulation and melanization response parameters of G. mellonella hemocytes, Kaya et al.'s (Reference Kaya, Uçkan and Er2021) method was used. In order to evoke an encapsulation and melanization response, DEAE Sephadex A-25 Beads (40–120 μm in diameter; Sigma) were used. These beads were stained with 0.1% Coomassie Brilliant Blue G (Sigma) before injection. The beads were finally resuspended in sterile PBS at a concentration of 15–20 beads/10 μl and injected into the larval hemocoel from the front segment of the first abdominal proleg. For injection, 50 μl Hamilton microsyringe with 22 gauge (Hamilton Co.) was used. Before each injection, the stained beads in the glass Hamilton microsyringe were counted under the stereo microscope to ensure a comparable amount of beads. The larvae were left to rearing conditions for 4 and 24 h after chromatography beads injection. At the end of that time, these larvae were dissected and the beads were collected under stereo microscope (Olympus SZ7) on a glass microscope slide, as described before Kaya et al. (Reference Kaya, Uçkan and Er2021), and overlaid with a cover slip. The beads were classified according to Richards and Dani (Reference Richards and Dani2008) (fig. 2) at phase-contrast microscope (Olympus BX51). For the evaluation of melanization response, the beads are classified under four groups as reported by Kaya et al. (Reference Kaya, Uçkan and Er2021) (non-melanized; no melanization, weak; 20% melanization on bead surface, middle; 20–70% melanization on bead surface, strong; melanization more than 70% on bead surface). Each replicate contained five larvae, and experiments were replicated three times.
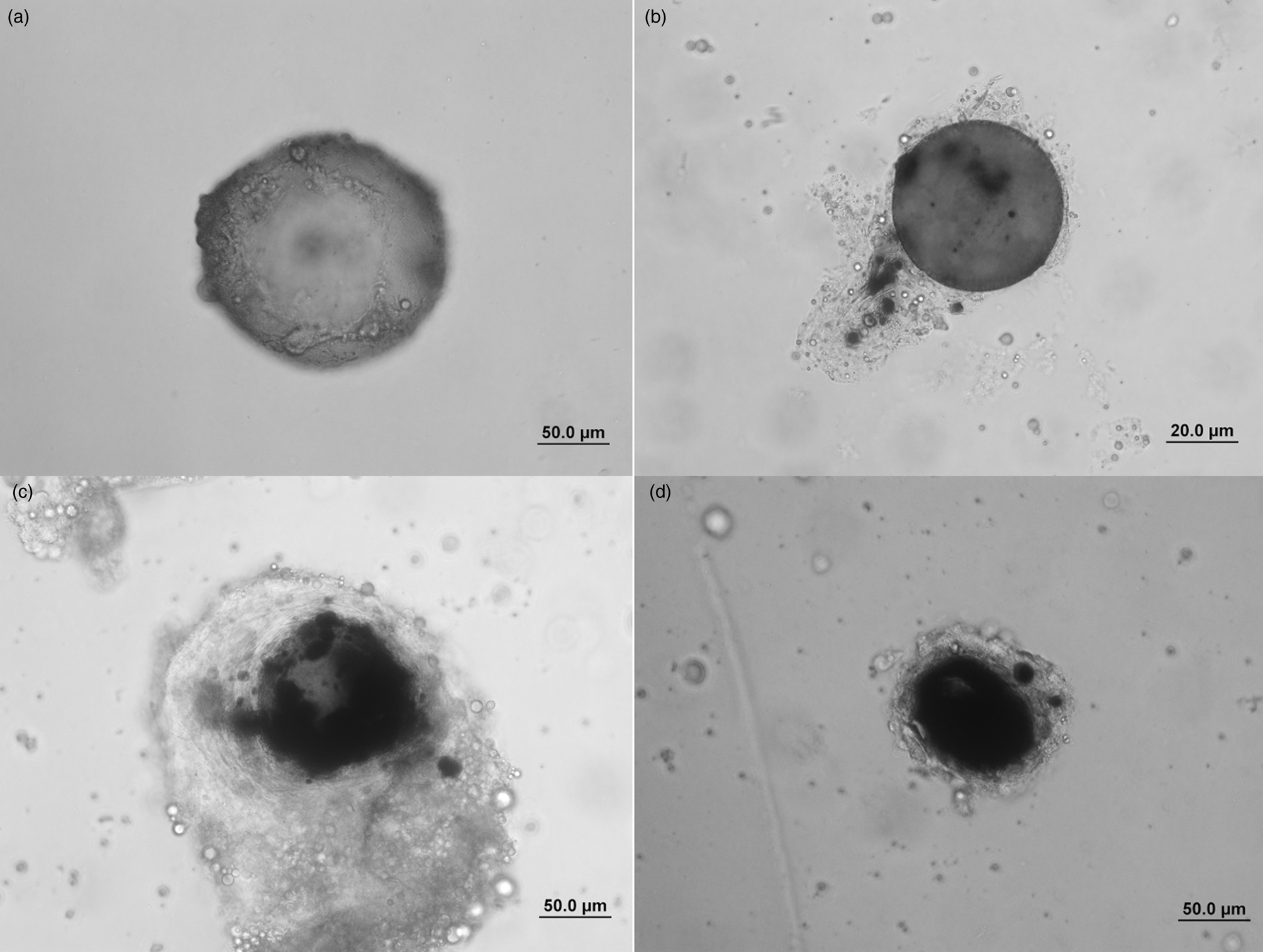
Figure 2. Encapsulation of Sephadex A-25 beads in G. mellonella larvae. (a) Non-encapsulated bead (zero to two cell layer) and non-melanized (zero melanized area), (b) weak encapsulated (2–10 cell layers) and weak melanized (melanization level <20%), (c) strong encapsulated bead (more than 10 cell layers) and middle melanized (melanization levels between 20 and 70%), (d) strong encapsulated and strong melanized bead (more than 10 cell layers and melanized area covers more than 70% of the bead).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were made with SPSS (SPSS, version 19.0 for Windows; IBMM SPSS Statistics, Armonk, NY, USA) program. Tukey's HSD test in one-way ANOVA was used to compare the mean of the data. Arcsine transformation was performed to evaluate percentage data values before analysis.
Results
Total hemocyte count
In vivo and in vitro studies revealed that total hemocyte numbers of G. mellonella decreased significantly after treatment with P. turionellae calyx fluid except for 0.1 FEC dose in a concentration-dependent manner (fig. 3). The minimum hemocyte counts were detected as 16.95 × 106 cell ml−1 in vivo and 17.94 × 106 cell ml−1 in vitro at the highest dose of 1 FEC. The null-injected and PBS-injected groups were similar to the untreated groups.
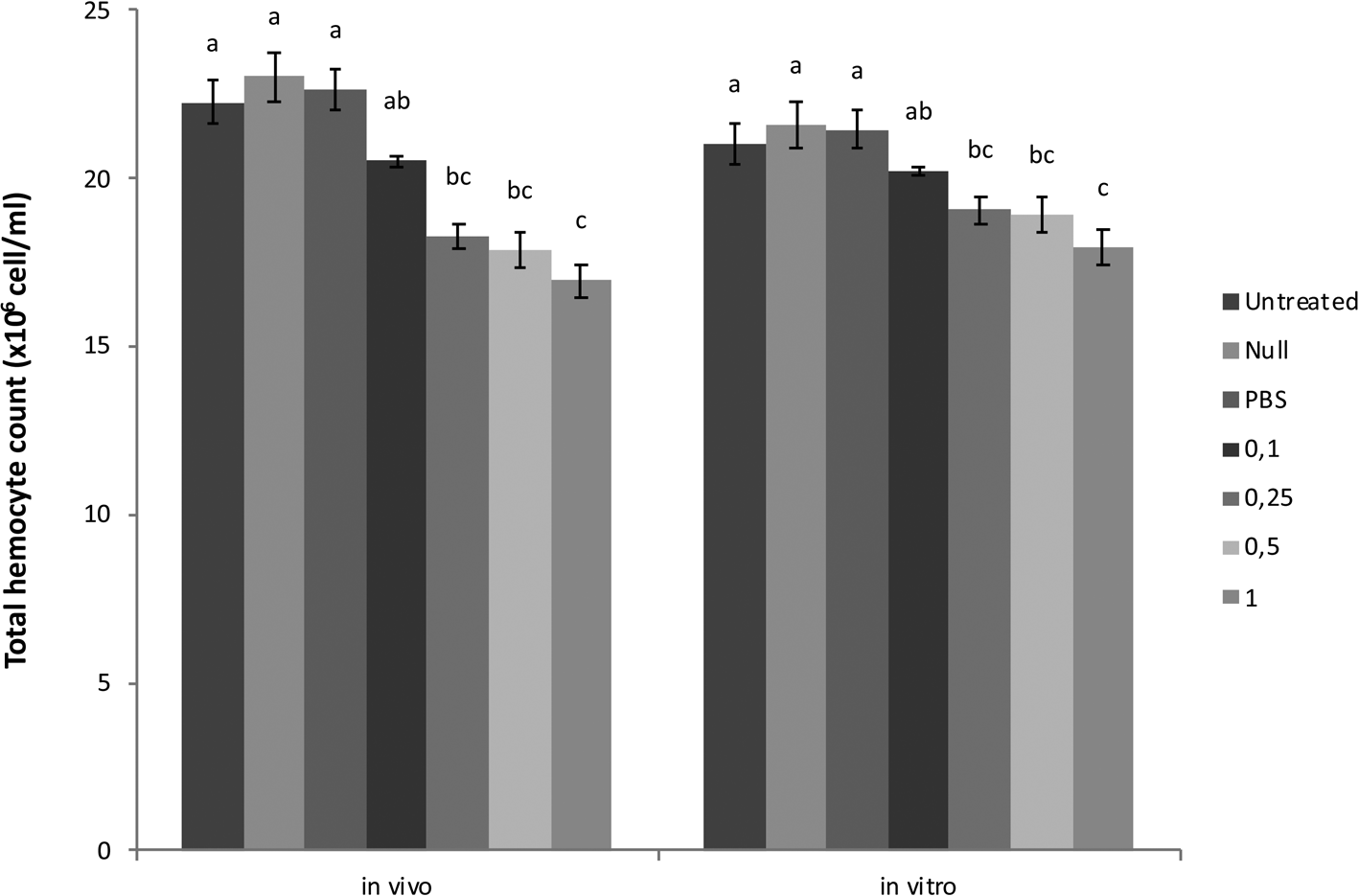
Figure 3. Effects of calyx fluid on THC in vivo and in vitro. Data are expressed as the mean × 106 cell ml−1 (n = 15). For each treatment, values followed by different letters are significantly different (P ≤ 0.05) according to one-way ANOVA and tested with Tukey's HSD (in vivo F: 10.364, dF: 6, P: 0.00; in vitro F: 16.591, dF: 6, P: 0.00).
Hemocyte viability and mitotic indices
The microscopic analyses of AO/EB double-stained slides revealed that apoptotic and necrotic indices of experimentally calyx fluid-injected G. mellonella larvae increased in a dose-dependent manner compared to untreated control both in vivo and in vitro (table 1). The ratio of early apoptotic, late apoptotic, and necrotic hemocytes in the null-injected and PBS-injected groups was similar to that of the untreated controls. More than 91% of hemocytes were viable in untreated, null, and PBS-injected G. mellonella larvae (table 1). Significant reductions in cell viability were observed at all calyx fluid doses both in vivo and in vitro.
Table 1. Calyx fluid-related changes of apoptotic indices (%) of G. mellonella larvae in vivo (A) and in vitro (B)
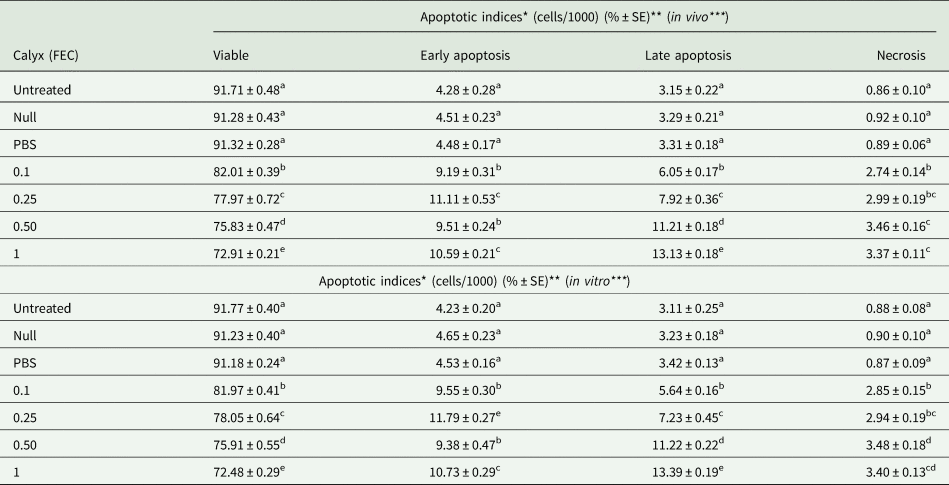
The same letters indicate no significant differences between experimental groups (one-way ANOVA followed Tukey's HSD, P ≤ 0.05). Each data was the mean of five larvae in three replicates (n = 15).
*Represent apoptotic cell percentage.
**Each data symbolize the mean ± Standard Error (%) of 15 larvae in three replicates.
***In vivo: viable F: 290.114, dF: 6, P: 0.00; early apoptotic F: 106.751, dF: 6, P: 0.00; late apoptotic F: 336.578, dF: 6, P: 0.00; necrotic F: 92.468, dF: 6, P: 0.00. In vitro: viable F: 339.023, dF: 6, P: 0.00; early apoptotic F: 127.199, dF: 6, P: 0.00; late apoptotic F: 282.497, dF: 6, P: 0.00; necrotic F: 86.428, dF: 6, P: 0.00.
The mean ratios of mitotic hemocytes in the control and experimentally calyx fluid-injected groups are given in fig. 4. The frequency of mitosis was detected to be similar within the untreated, null, PBS-injected groups and 0.1 FEC is the lowest calyx fluid dose both in vivo and in vitro. However, the ratio of mitotic hemocytes significantly decreased in a dose-dependent manner in the calyx fluid-injected groups except for 0.1 FEC compared to the controls.
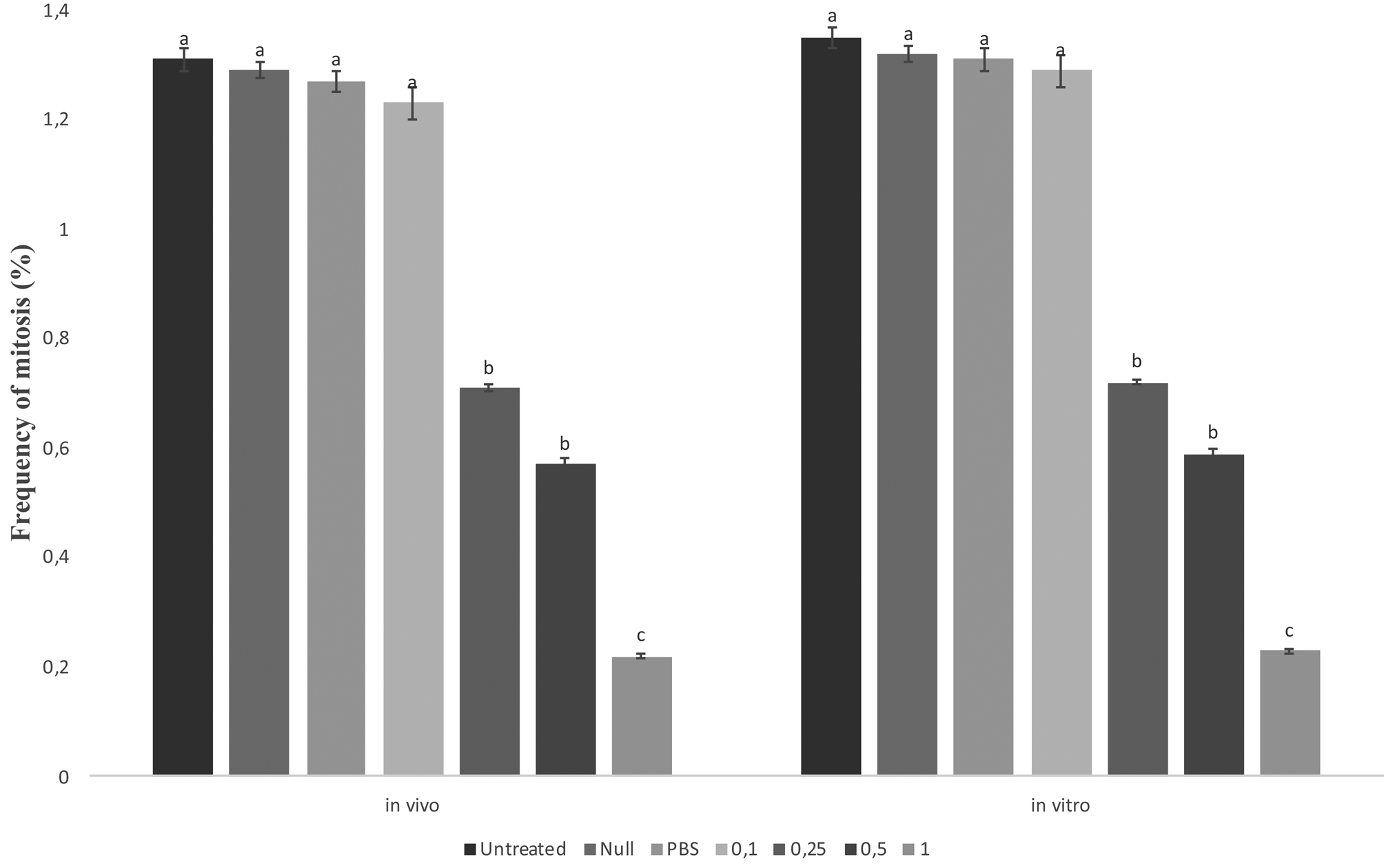
Figure 4. Effects of calyx fluid on mitotic indices of G. mellonella larval hemocyte in vivo and in vitro. Data are expressed as the mean × 106 cell ml−1 (n = 15). For each treatment, values followed by different letters are significantly different (P ≤ 0.05) according to one-way ANOVA and tested with Tukey's HSD (in vivo: F: 55.455, dF: 6, P: 0.00; in vitro: F: 48.348, dF: 6, P: 0.00).
Encapsulation and melanization
Sephadex A-25 beads elicited the encapsulation reaction at 4 and 24 h post bead injection in the hemocoel of G. mellonella larvae (table 2). The encapsulation response in the null and PBS-injected groups was identical with untreated host larvae. Calyx fluid injection progressively reduced the percentage of strong encapsulation reaction associated with increasing doses. Of the 192 beads dissected from 15 G. mellonella larvae injected with the highest calyx dose of 1 FEC, none of the beads were strongly encapsulated while only 10.79 ± 1.59 (% ± Standard Error) beads were weakly encapsulated 24 h post injection.
Table 2. Effects of calyx fluid on encapsulation response level
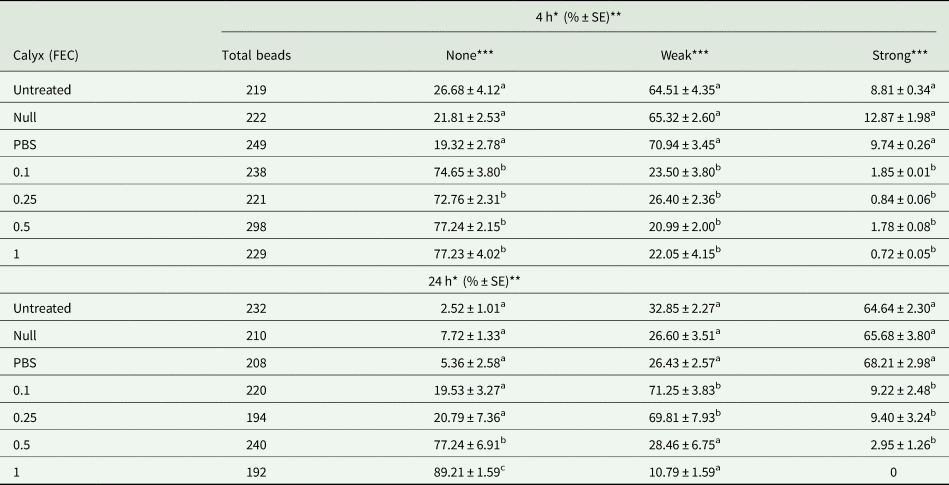
Data are expressed as the mean percentage (n = 15). The same letters indicate no significant differences between experimental groups (one-way ANOVA followed Tukey's HSD, P ≤ 0.05). Each data was the mean of five larvae in three replicates (n = 15).
*Represent (4 h) short time and long time (24 h) response.
**Each data symbolize the mean ± Standard Error (%) of 15 larvae in three replicates.
***4 h. None F: 41.197, dF: 6, P: 0.00; weak F: 45.586, dF: 6, P: 0.00; strong F: 7.863, dF: 6, P: 0.00. 24 h. None F: 56.850, dF: 6, P: 0.00; weak F: 22.371, dF: 6, P: 0.00; strong F: 130.726, dF: 6, P: 0.00.
The percentage of melanized capsules did not demonstrate significant variations among the untreated, null-injected, PBS-injected, and low-dose calyx (0.1 FEC) injected experimental groups at 4 and 24 h post treatments (table 3). By contrast, the ratio of strongly melanized beads significantly reduced at doses more than 0.1 FEC compared to the untreated controls. The highest calyx fluid dose (1 FEC) completely inhibited the strong melanization response 24 h after treatment.
Table 3. Calyx fluid effect on melanization levels are expressed as the mean percentage (n = 15)
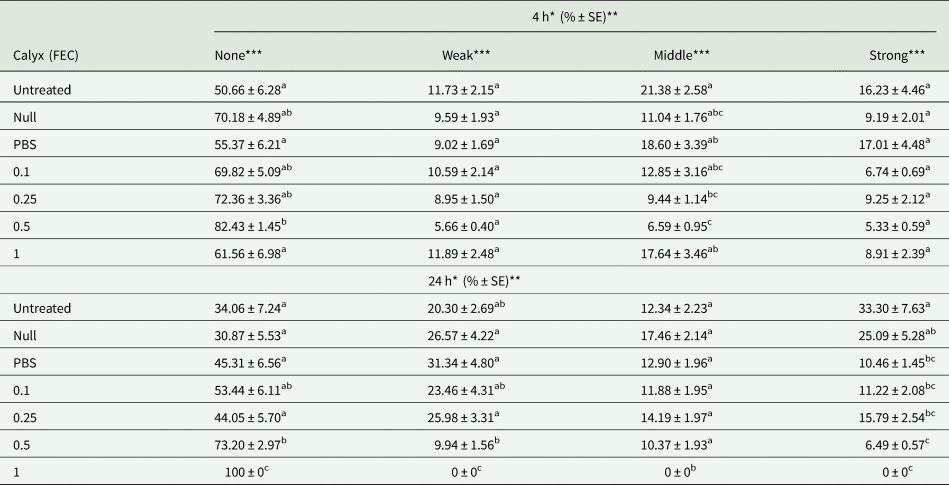
The same letters indicate no significant differences between experimental groups (one-way ANOVA followed Tukey's HSD, P ≤ 0.05). Each data was the mean of five larvae in three replicates (n = 15).
*Represent (4 h) short time and long time (24 h) response.
**Each data symbolize the mean ± Standard Error (%) of 15 larvae in three replicates.
***4 h. None F: 4.891, dF: 6, P: 0.00; weak F: 1.291, dF: 6, P: 0.269; middle F: 4.375, dF: 6, P: 0.001; strong F: 2.574, dF: 6, P: 0.023. 24 h. None F: 7.402, dF: 5, P: 0.00; weak F: 3.952, dF: 5, P: 0.003; middle F: 1.427, dF: 5, P: 0.223; strong F: 6.067, dF: 5, P: 0.00.
Discussion
In order to complete their development successfully into their host insects, parasitic wasps require protection from their host immune system. Especially endoparasitoid species, which develop inside the hemocoel of larval or pupal stages of their hosts, must avoid various cell-mediated immune reactions (Schmidt et al., Reference Schmidt, Theopold and Strand2001). The most common features shared among many endoparasitoids are suppression of host hemocyte quality, quantity, and also behavior which are modulated by complex mechanisms (Teng et al., Reference Teng, Xu, Gan, Chen, Fang and Ye2016). These complex mechanisms mostly rely on maternally derived secretions produced in specialized glands of parasitoid females and injected at the time of oviposition (Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers, Ergin and Sak2010). Pimpla turionellae is an idiobiont and solitary endoparasitoid that lacks PDVs which inflict the venom injection before oviposition and apparently discussed to depend on maternal venom for host manipulation in previous studies (Ergin et al., Reference Ergin, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2006; Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers, Ergin and Sak2010, Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011; Uçkan et al., Reference Uçkan, Er and Ergin2010). Venom includes typical parasitoid enzymes such as carboxylesterase, laccase, phenoloxidase, S1A superfamily trypsin domain, glycoside hydrolase family 1, metallopeptidase M12B, and venom acid phosphatase, cysteine-rich peptides, several mid to high range molecular weight proteins, and also a new ICK peptide family (pimplin 2) that resembles a neurotoxic factor (Ergin et al., Reference Ergin, Uçkan, Rivers, Rivers and Yoder2007; Özbek et al., Reference Özbek, Wielsch, Vogel, Lochnit, Foerster, Vilcinskas and von Reumont2019). Venom-induced paralytic activity, cytotoxicity in cultured cells (Ergin et al., Reference Ergin, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2006), and immune-suppressive effects of P. turionellae venom on G. mellonella (Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers, Ergin and Sak2010, Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011; Uçkan et al., Reference Uçkan, Er and Ergin2010) were demonstrated. However, venom-related immune-suppressive effects were seen only in venom doses greater than LD50 calculated for G. mellonella in previous studies (Ergin et al., Reference Ergin, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2006; Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers, Ergin and Sak2010). The fact that venom-induced encapsulation suppressive activity detected in our previous study (Uçkan et al., Reference Uçkan, Er and Ergin2010) was not close to that found in natural parasitization levels has shown that another supplementary factor such as calyx fluid of P. turionellae females would be effective for the complete immunosuppression of the host.
The experimental injection of the isolated calyx fluid of P. turionellae into host larvae resulted in a reduction in THCs in the circulation depending on calyx fluid doses compared to the controls. In vitro assays with isolated G. mellonella hemocytes also revealed that the addition of calyx fluid doses more than 0.25 FEC reduced hemocyte counts similar to in vivo studies. In our previous observations on the parasitizing behavior of P. turionellae, we detected that the wasp oviposits up to four different G. mellonella at a certain time, so we chose doses under and below 0.25 FEC in our experimental design. The findings here are in accordance with the behavioral observation and the 0.25 FEC we used in our study seemed to be the amount required for successful parasitism of P. turionellae. In the current study, the reduction in hemocyte numbers seemed to be due to cell death via apoptotic pathways and also inhibition of mitosis. AO and EB staining indicated that the artificial injection of the isolated calyx fluid of P. turionellae to the host resulted in an elevated apoptotic ratio in the circulating hemocytes. Both early-late apoptotic and also necrotic hemocyte ratios increased more than 100% compared to the controls. In vitro experiments also supported the results. In many host/parasitoid systems, there are diverse arrays of studies demonstrating the elevations or reductions in THCs due to parasitism (Strand and Noda, Reference Strand and Noda1991; Yu et al., Reference Yu, Chen, Chen, Huang, Lou and Liu2007; Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers, Ergin and Sak2010; Teng et al., Reference Teng, Xu, Gan, Chen, Fang and Ye2016). In many cases, hemocyte viability and numbers may be affected by PDVs. Apoptosis of host hemocytes, triggered by symbiotic viruses of parasitoid wasps, has already been reported in M. demolitor/P. includes (Strand and Pech, Reference Strand and Pech1995), C. kariyai/P. separata (Teramoto and Tanaka, Reference Teramoto and Tanaka2004), and M. pulchricornis/P. separate (Suzuki and Tanaka, Reference Suzuki and Tanaka2006) parasitoid/host systems. However, to the best of our knowledge, there seems to be no report showing the significant effects of calyx fluid of an endoparasitoid that lacks PDVs on total count and viability of the host hemocytes. Injected A. japonica calyx fluid that is devoid of symbiotic viruses did not cause a reduction in hemocyte numbers while venom + calyx fluid significantly reduced total hemocyte numbers in D. melanogaster circulation (Mabiala-Moundoungou et al., Reference Mabiala-Moundoungou, Doury, Eslin, Cherqui and Prevost2010). Li et al. (Reference Li, Lu, Feng, Ke and Fu2007) demonstrated that venom and ovarian proteins of M. cingulum (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) that lacks PDVs had no significant effect on the hemocyte viability of the host O. furnacalis (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae).
In our previous study, parasitism and venom from P. turionellae induced hemocyte death via apoptotic and/or necrotic pathways in G. mellonella (Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011). In vitro studies with P. turionellae venom also demonstrated that venom induces apoptosis in hemocytes by a pathway dependent on extracellular calcium influx (Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011). Nevertheless, the highest rate of apoptotic cells was observed when pupae were naturally parasitized compared to venom injection. However, it is obvious in the current study that, in order to achieve the apoptotic ratio induced by natural parasitization, calyx fluid is needed as a complementary factor of venom. Injection of complementary proteins produced in the calyx region of the ovaries in a large quantity of host–parasitoid systems is required to guarantee successful parasitism (Moreau and Asgari, Reference Moreau and Asgari2015). Variations in circulating hemocyte numbers are also maintained by mitosis (Ratcliffe et al., Reference Ratcliffe, Rowley, Fitzgerald and Rhodes1985). Current in vivo and in vitro studies demonstrate that the calyx fluid of P. turionellae is also responsible for the reduction of G. mellonella hemocytes in the mitotic phase. It was previously showed that venom and parasitization of P. turionellae cause a significant decline in the ratio of mitotic hemocytes in host G. mellonella (Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011). Calyx fluid of P. turionellae may act as a complementary factor of venom in order to suppress the cell cycle. In C. kariyai/P. seperata parasitoid–host system, venom and PDV injection have been shown to suppress the cell cycle (Teramoto and Tanaka, Reference Teramoto and Tanaka2004). Though there are only limited numbers of studies on the effects of parasitism-associated factors on the cell cycle of the host hemocytes, further investigation is needed to clarify the mechanism involved in mitotic events.
The major threat toward foreign objects that enter the insect hemocoel is encapsulation in which hemocytes form a multilayer sheath around internal parasites or parasitoid eggs (Teng et al., Reference Teng, Xu, Gan, Chen, Fang and Ye2016). Termination of capsule formation is accompanied by melanin and reactive oxygen species production that finally kills the encapsulated organism (Nappi et al., Reference Nappi, Vass, Frey and Carton1995). It is a known fact that many parasitoids must protect their eggs from encapsulation by injecting maternally derived fluids at the time of oviposition which modifies the number and the adhesion properties of the hemocytes. In this report, we demonstrate that the calyx fluid of P. turionellae significantly suppressed the melanization and encapsulation of Sephadex A-25 beads in G. mellonella hemocoel. We previously showed that the number of Sephadex A-25 beads strongly encapsulated and melanized were reduced by 50% after the highest dose venom injection in the larvae of G. mellonella (Uçkan et al., Reference Uçkan, Er and Ergin2010). Maintaining the ability of hemocytes to encapsulate and melanize half of the beads injected into envenomated groups prove with the present study that the ovarian proteins are required as supplementary factors for successful parasitization. Our results agree with those reported in the host–parasitoid systems that lack PDVs where calyx fluid was demonstrated to prevent encapsulation (Li et al., Reference Li, Lu, Feng, Ke and Fu2007; Mabiala-Moundoungou et al., Reference Mabiala-Moundoungou, Doury, Eslin, Cherqui and Prevost2010). In the majority of parasitoid–host systems, the efficacy of encapsulation response is known to be affected by a number of parameters such as hemocyte number, cell spreading, and aggregation behavior of hemocytes. The decrease in THCs due to cell death that we observe in the current study may be linked to the suppressed encapsulation function. It is also possible that the active molecules in the ovarian components of P. turionellae may have functions to evade the encapsulation of G. mellonella hemocytes.
Combined with our previous study (Er et al., Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers, Ergin and Sak2010, Reference Er, Uçkan, Rivers and Sak2011; Uçkan et al., Reference Uçkan, Er and Ergin2010), we can conclude that P. turionellae calyx fluid may have complementary effects on venom to regulate and overcome the host immunity. A series of candidate molecules in P. turionellae venom that have potential roles in venom-induced immunosuppression have been characterized in several studies (Ergin et al., Reference Ergin, Uçkan, Rivers, Rivers and Yoder2007; Özbek et al., Reference Özbek, Wielsch, Vogel, Lochnit, Foerster, Vilcinskas and von Reumont2019). However, we could detect no report identifying the calyx fluid components of endoparasitoids that are devoid of symbiotic viruses and their possible mechanisms of action in parasitoid–host interactions. The characterization of ovarian proteins with a genomic approach and the possible host regulatory mechanisms of these bioactive components need further investigations.
Financial support
This work was supported by Kocaeli University Scientific Research Coordination Unit. Project number: 2012/25.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants by any of the authors.










