INTRODUCTION
The Schmidt hammer is used frequently in Quaternary geomorphological research to assess the surface-exposure age of landforms. By relating the compressive strength of bedrock and boulder surfaces to the degree of surface weathering, relative ages can be proposed for adjacent features (Matthews and Shakesby, Reference Matthews and Shakesby1984; Ballantyne, Reference Ballantyne1986; Dawson et al., Reference Dawson, Matthews and Shakesby1986; McCarroll, Reference McCarroll1989). This methodology has been adopted by some subsequent studies (McCarroll et al., Reference McCarroll, Ballantyne, Nesje and Dahl1995; Clark and Wilson, Reference Clark and Wilson2004; Winkler, Reference Winkler2005; Shakesby et al., Reference Shakesby, Matthews and Owen2006), while others have developed the technique into one of high-precision calibrated-age dating (Shakesby et al., Reference Shakesby, Matthews, Karlén and Los2011; Matthews and Wilson, Reference Matthews and Wilson2015; Matthews et al., Reference Matthews, McEwen and Owen2015, Reference Matthews, Winkler, Wilson, Tomkins, Dortch, Mourne, Hill, Owen and Vater2018; Tomkins et al., Reference Tomkins, Dortch and Hughes2016, Reference Tomkins, Dortch, Hughes, Huck, Stimson, Delmas, Calvet and Pallàs2018a, Reference Tomkins, Dortch, Hughes, Huck, Tonkin and Barr2018b, Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c; Wilson and Matthews, Reference Wilson and Matthews2016; Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Matthews and Mourne2017). Irrespective of the approach taken, Schmidt-hammer exposure-age dating (SHD) is used for landform age estimation in a wide variety of Quaternary geomorphic contexts—for example, fluvial terraces (Stahl et al., Reference Stahl, Winkler, Quigley, Bebbington, Duffy and Duke2013); flood sediments (Matthews and McEwen, Reference Matthews and McEwen2013); alluvial fans (White et al., Reference White, Bryant and Drake1998); debris flows (Boelhouwers et al., Reference Boelhouwers, Jager and De Joode1999; Wilson and Matthews, Reference Wilson and Matthews2016); glacial landforms (Winkler, Reference Winkler2005, Reference Winkler2009, Reference Winkler2014; Shakesby et al., Reference Shakesby, Matthews and Owen2006; Matthews and Winkler, Reference Matthews and Winkler2011; Kłapyta, Reference Kłapyta2013); active and relict rock glaciers (Kellerer-Pirklbauer et al., Reference Kellerer-Pirklbauer, Wangensteen, Farbrot and Etzelmüller2008; Rode and Kellerer-Pirklbauer, Reference Rode and Kellerer-Pirklbauer2012; Matthews et al., Reference Matthews, Nesje and Linge2013; Winkler and Lambiel, Reference Winkler and Lambiel2018); pronival ramparts (Matthews et al., Reference Matthews, Shakesby, Owen and Vater2011, Reference Matthews, Wilson and Mourne2017; Matthews and Wilson, Reference Matthews and Wilson2015); patterned ground (Cook-Talbot, Reference Cook-Talbot1991; Winkler et al., Reference Winkler, Matthews, Mourne and Wilson2016), blockstreams (Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Matthews and Mourne2017; Marr et al., Reference Marr, Winkler and Löffler2018), blockfields, boulder lobes, and talus (Wilson and Matthews, Reference Wilson and Matthews2016; Marr et al., Reference Marr, Winkler and Löffler2018); snow-avalanche impact ramparts (Matthews et al., Reference Matthews, McEwen and Owen2015); rock-slope failures (Clark and Wilson, Reference Clark and Wilson2004; Wilson Reference Wilson2007, Reference Wilson2009; Owen et al., Reference Owen, Hiemstra, Matthews and McEwen2010; Wilson and Matthews, Reference Wilson and Matthews2016; Marr et al., Reference Marr, Winkler and Löffler2018; Matthews et al., Reference Matthews, Winkler, Wilson, Tomkins, Dortch, Mourne, Hill, Owen and Vater2018); fault scarps (Tye and Stahl, Reference Tye and Stahl2018); chemically-weathered bedrock surfaces (Owen et al., Reference Owen, Matthews and Albert2007); raised boulder-dominated shorelines (Sjöberg and Broadbent, Reference Sjöberg and Broadbent1991; Shakesby et al., Reference Shakesby, Matthews, Karlén and Los2011); and shore platforms (Knight and Burningham, Reference Knight and Burningham2011).
Terrestrial cosmogenic nuclide (TCN) exposure-age dating is used much more widely than SHD for the numerical-age determination of landforms. The technique has a broad temporal range but is costly because of the necessity for analysis of several samples from a particular context in order to obtain a reliable age estimate for the landform or event under investigation. As a consequence, the number of samples analyzed from a landform is sometimes less than the optimum number that would be analyzed if cost were not a significant constraint. Nevertheless, the technique is employed extensively, particularly for age assessment of moraines (Chenet et al., Reference Chenet, Brunstein, Jomelli, Roussel, Rinterknecht, Mokadem, Biette, Robert and Léanni2016; Kiernan et al., Reference Kiernan, Fink and McConnell2017; Hughes et al., Reference Hughes, Fink, Rodés, Fenton and Fujioka2018; Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Rodés and Smith2018) and rock-slope failures (Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, Sandeman, Stone and Wilson2014a; Schleier et al., Reference Schleier, Hermanns, Rohn and Gosse2015; Grämiger et al., Reference Grämiger, Moore, Vockenhuber, Aaron, Hajdas and Ivy-Ochs2016; Southall et al., Reference Southall, Wilson, Dunlop, Schnabel, Rodés, Gulliver and Xu2017).
Several studies have utilized both SHD and TCN dating with the aim of establishing the accuracy and precision of the former technique (Sánchez et al., Reference Sánchez, Mosquera and Romaní2009; Winkler, Reference Winkler2009, Reference Winkler2014; Matthews and Winkler, Reference Matthews and Winkler2011). It is generally thought that SHD is a valuable complementary method to TCN dating over the period of the last deglaciation and Holocene, and that SHD data may be utilized in the selection of surfaces for TCN dating. This would introduce greater objectivity to the sample selection process and possibly require fewer samples, with the result that project costs could be reduced.
Because TCN dating is based on the measurement of in situ-produced nuclides with accelerator mass spectrometry, it is perhaps regarded as inherently more accurate, precise, and reliable than the low-tech and low-cost SHD, but this is not necessarily the case. There are several examples where TCN dating has failed to return statistically consistent ages for certain sites and landforms as a result of nuclide inheritance, transient sample shielding, enhanced post-exposure surface erosion, post-depositional reworking or introduction of younger rock surfaces, or simply too few samples (Everest et al., Reference Everest, Bradwell, Fogwill and Kubik2006; Principato et al., Reference Principato, Geirsdóttir, Jóhannsdóttir and Andrews2006; Sanhueza-Pino et al., Reference Sanhueza-Pino, Korup, Hetzel, Munack, Weidinger, Dunning, Ormukov and Kubik2011; Schmidt et al., Reference Schmidt, Hetzel, Kuhlmann, Mingorance and Ramos2011; Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, Wilson, Gheorghiu and Rodés2014b; Çiner et al., Reference Çiner, Sarıkaya and Yıldırım2017; Romundset et al., Reference Romundset, Akçar, Fredin, Tikhomirov, Reber, Vockenhuber, Christl and Schlüchter2017). In addition, a number of methodological issues concerning production rates and scaling factors continue to be discussed (Balco, Reference Balco2011; Darvill, Reference Darvill, Cook, Clarke and Nield2013; Marrero et al., Reference Marrero, Phillips, Borchers, Lifton, Aumer and Balco2016).
Presently, the most comprehensive attempt to link SHD and TCN dating is the study by Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Dortch and Hughes2016) in which Schmidt-hammer rebound values (R-values) obtained from 98 surfaces exposed by retreat of the last British-Irish Ice Sheet (BIIS) and dated using 10Be were reported. A multi-lithology approach was adopted but a robust calibration was only obtained for granite surfaces (n = 25). Nevertheless, this enabled Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Dortch and Hughes2016) to convert R-values from 31 undated granite erratics on Shap Fell, northwest England, to surface-exposure ages and to propose that local retreat of the last ice sheet had occurred at 16.5 ± 0.5 ka. This age is consistent within uncertainties with the 10Be exposure age estimate, from the same area, of 17.07 ± 0.9 ka (using the Loch Lomond production rate with Lal/Stone (LM) scaling and an erosion rate of 1 mm ka−1) or 16.65 ± 1.36 ka (using CRONUScalc with Lifton/Sato/Dunai (SA) scaling and an erosion rate of 1 mm ka−1) (Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Lord and Rodés2013; recalculated by Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Rodés and Smith2018).
It seems therefore that granite surfaces in northern Britain exposed by retreat of the last ice sheet can provide reliable surface-exposure ages from application of the Schmidt hammer and the granite calibration of Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Dortch and Hughes2016). Furthermore, the large number of surfaces targeted for SHD decreases the level of geomorphological uncertainty inherent in a sampling program in which only a few surfaces are selected, as is customary with TCN dating (Kirkbride and Winkler, Reference Kirkbride and Winkler2012). This suggests that multiple sampling of such surfaces for 10Be dating could become redundant, resulting in considerable project-cost savings.
Further work by Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c) provided an updated granite calibration through inclusion of a wider range of sites, including some of Holocene age. This calibration extends from 23.8 ka to 0.8 ka, is based on 54 granite surfaces, and indicates a strong linear relationship between 10Be ages and Schmidt-hammer R-values (R2 = 0.94, p = <0.01).
We tested the calibration of Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c) over a wider geographical area by applying SHD to glacially-transported granite boulders in parts of northern and western Ireland and southwest Scotland that had been exposed by retreat of the last BIIS or Younger Dryas (YD) ice masses. Retreat of the last BIIS in these areas was interrupted by several stillstands or readvances but occurred over the interval ~22–15 ka (Finlayson et al., Reference Finlayson, Merritt, Browne, Merritt, McMillan and Whitbread2010; Ballantyne and Ó Cofaigh, Reference Ballantyne, Ó Cofaigh, Coxon, McCarron and Mitchell2017). Similarly, the pattern and style of YD (12.9–11.7 ka BP) glaciation in these areas may not have been fully elucidated (Cornish, Reference Cornish1981; Ballantyne and Ó Cofaigh, Reference Ballantyne, Ó Cofaigh, Coxon, McCarron and Mitchell2017; Barr et al., Reference Barr, Roberson, Flood and Dortch2017). The granites we investigated formed at different times and are likely to differ texturally and mineralogically. However, such variations were deemed to be of limited significance by Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Dortch and Hughes2016). For the purposes of their study, time-dependent weathering rates were proposed to account for the recorded differences in surface hardness. We have adopted this premise with respect to our sites.
Seven of our sites had previously been dated using 10Be and these ages act as key comparators for the exposure ages determined with the Schmidt hammer and the granite calibration of Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c). The other eight sites we sampled have not been subjected to 10Be dating and therefore our SHD ages from these locations require independent assessment.
RESEARCH SITES
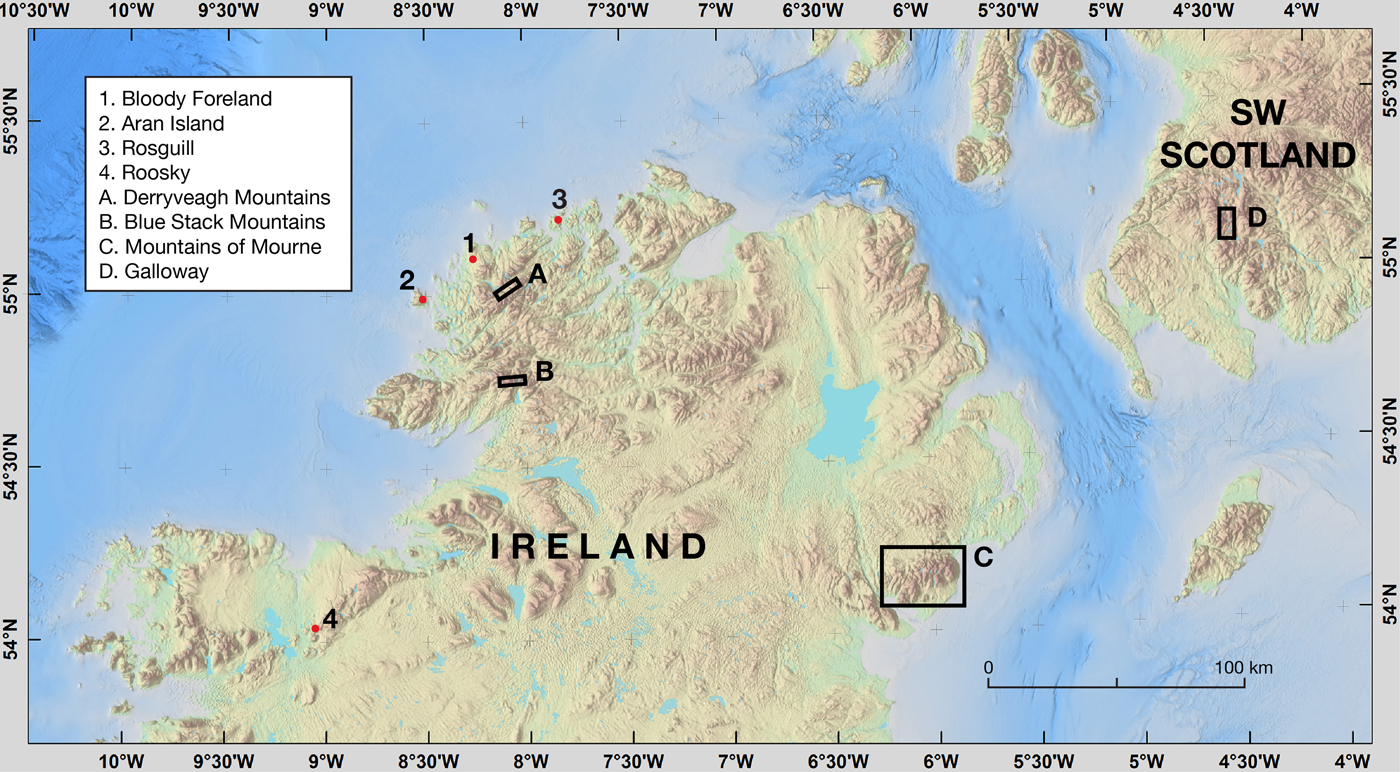
Thirteen sites in Ireland and two sites in Scotland were selected for SHD (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2). Six of the sites in Ireland and one site in Scotland had previously been dated using 10Be (Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, Rinterknecht and Gheorghiu2013; Schiele, Reference Schiele2017; Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Ballantyne, Benetti, Small, Fabel and Clark2019), and boulders at one Scottish site and two Irish sites had previously been inferred to be of YD age on morpho- or biostratigraphic grounds (Cornish, Reference Cornish1981; P. Wilson, Reference Wilson2004; Barr et al., Reference Barr, Roberson, Flood and Dortch2017). Of the six sites we sampled in northwest Donegal, Ireland, three are boulder-dominated moraines at Bloody Foreland (110 m above sea level (asl); Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, McCarroll and Stone2007; Clark et al., Reference Clark, McCabe, Schnabel, Clark, Freeman, Maden and Xu2009), the Poisoned Glen (75 m asl; Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Ballantyne, Benetti, Small, Fabel and Clark2019), and Croloughan Lough cirque (280 m asl; P. Wilson, Reference Wilson2004), with the latter two sites being in the Derryveagh Mountains (Fig. 3A). The other three sites are the ridge to the west of Dooish Mountain (520–650 m asl), also in the Derryveagh Mountains, the Rosguill headland on the north coast (100 m asl; Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Ballantyne, Benetti, Small, Fabel and Clark2019), and Aran Island off the west coast (100–220 m asl; Cullen, Reference Cullen2013; Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Ballantyne, Benetti, Small, Fabel and Clark2019) (Fig. 1); these sites are strewn with glacially-transported boulders. In the Blue Stack Mountains of south Donegal, a boulder-dominated cirque moraine bounding Cronloughan to the east of Glascairns Hill (290 m asl; Barth et al., Reference Barth, Clark, Clark, Roe, Marcott, McCabe, Caffee, He, Cuzzone and Dunlop2018), and the summit ridge running northeast from Croaghgorm Mountain (590–670 m asl) with numerous ice-transported perched boulders, were sampled (Fig. 3B). The Roosky site in Mayo (Fig. 1), Ireland (75 m asl; Schiele, Reference Schiele2017) is a boulder-strewn hillside at the southwestern end of the Ox Mountains. Four sites were sampled in the Mountains of Mourne, Ireland (Fig. 3C). These comprise a boulder-dominated moraine in the upper Annalong valley (275 m asl; Sutton, Reference Sutton1998; Barr et al., Reference Barr, Roberson, Wilson, Roberson, Barr and Cooper2016, Reference Barr, Roberson, Flood and Dortch2017), perched boulders on the upper slopes and summit ridge of Slievemoughanmore (450–560 m asl), boulders on moraine ridges in the valley of the Pigeon Rock River (225 m asl; Colhoun, Reference Colhoun1981; K.R. Wilson, Reference Wilson2004), and boulders of inferred YD age at the lip of the Pot of Pulgarve cirque (500 m asl; Barr et al., Reference Barr, Roberson, Flood and Dortch2017). The two sites sampled in Galloway, Scotland, are the boulder-strewn ridge of Rig of the Jarkness in upper Glen Trool (390 m asl; Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, Rinterknecht and Gheorghiu2013) and boulders within the margin of a YD glacier on the eastern slopes of Merrick (510 m asl; Cornish, Reference Cornish1981) (Fig. 3D).

Figure 1. (color online) Locations of sites for SHD in Ireland and southwest Scotland. Site locations in the Derryveagh Mountains (A), Blue Stack Mountains (B), Mountains of Mourne (C) and Galloway (D) are shown in greater detail in Figure 3.
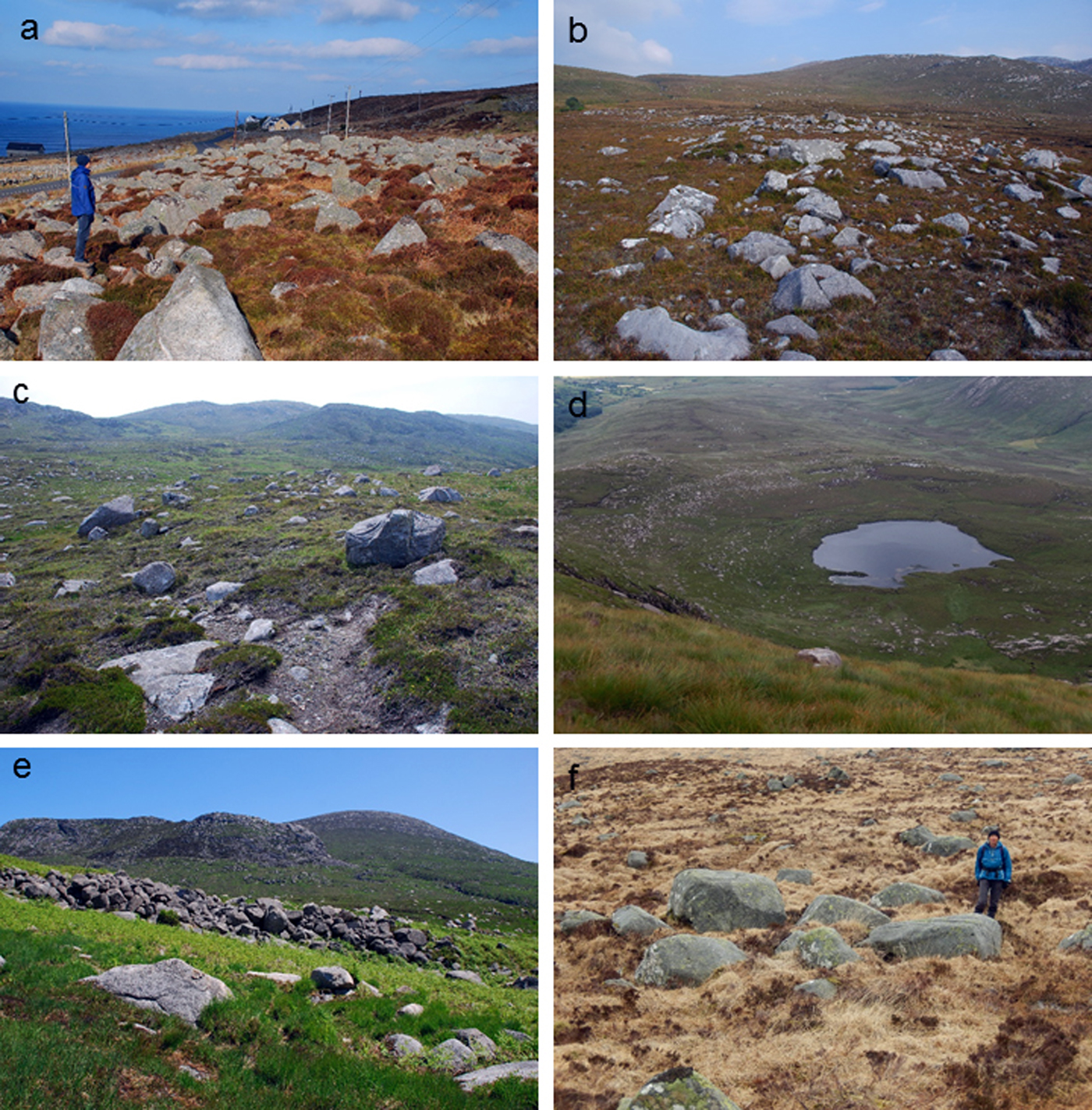

Figure 2. (color online) Selection of sites sampled for SHD. a: Part of the boulder moraine at Bloody Foreland, Donegal. b: Part of the boulder moraine in the Poisoned Glen, Donegal. c: Glacially-transported boulders at Rosguill, Donegal. d: Arcuate boulder moraine at Cronloughan, Donegal. e: Part of the boulder moraine in the Annalong valley, Mountains of Mourne. f: Glacially-transported boulders at Merrick, Galloway.

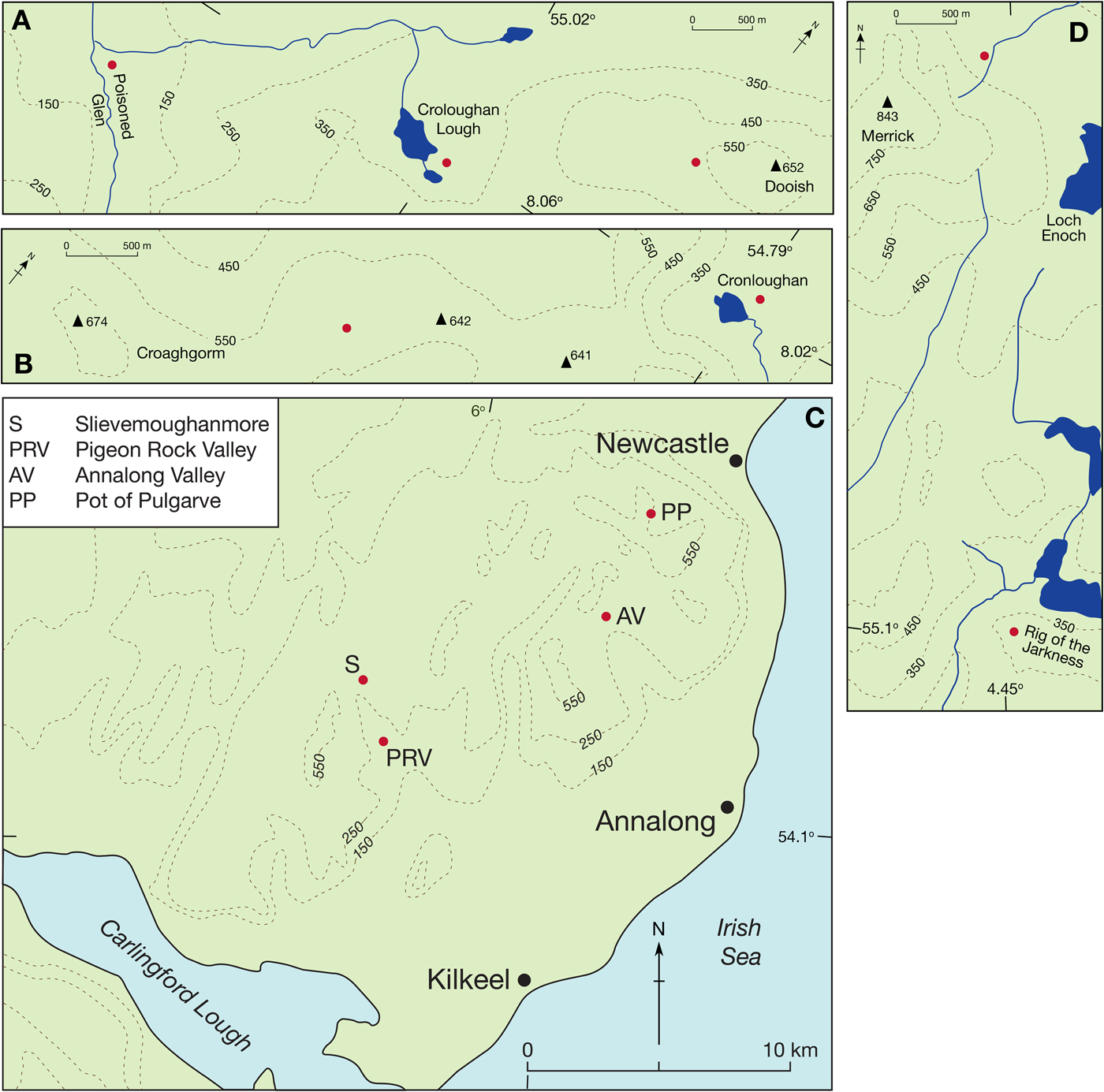
Figure 3. (color online) Locations of the SHD sites (red dots) in the Derryveagh Mountains (A), Blue Stack Mountains (B), Mountains of Mourne (C) and Galloway (D). Also indicated in C is the 14C dated coastal sediments site of Kilkeel reported by P.U. Clark et al. (Reference Clark, McCabe, Mix and Weaver2004) and J. Clark et al. (Reference Clark, McCabe, Bowen and Clark2012). Contours are in meters. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
METHODS
A single Schmidt-hammer R-value was obtained from each of 250 boulders at 12 sites. At the other three sites, with fewer available boulders, sample size was between 175 and 220 (Table 1). Upper, near-horizontal boulder surfaces that were free from cracks, obvious flaking, and lichen thalli and standing more than 0.5 m above the ground surface were sampled (Fig. 2). All measurement was performed by the same operator with a single mechanical N-type Schmidt hammer (Proceq, 2006) in dry conditions (P. Wilson). Boulder surfaces were not prepared before measurement. The hammer was periodically checked using the manufacturer's test anvil. No deterioration from the calibration value of 80 ± 2 was found during sampling, which extended over a 14-month period. A total of 3595 R-values was obtained.
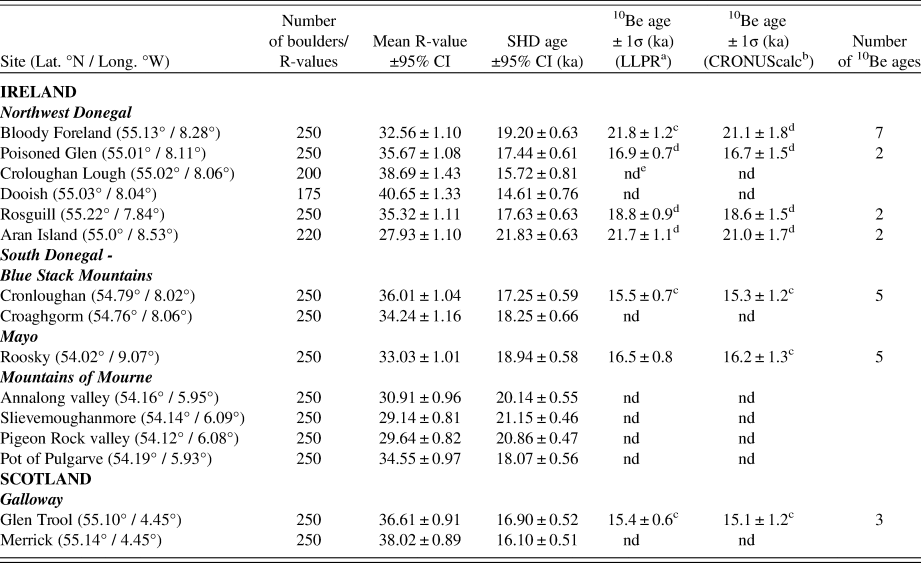
Table 1. Summary data pertaining to SHD ages for the 15 sites sampled and recalculated 10Be exposure ages for seven sites.

a Loch Lomond Production Rate, Lm scaling and 1 mm ka-1 erosion. Uncertainty weighted mean value and total uncertainty
b CRONUScalc, Lm scaling and 1 mm ka-1 erosion. Uncertainty weighted mean value and total uncertainty
c overlap at 2σ with SHD age range
d overlap at 1σ with SHD age range
e site not dated with 10Be
The R-values for each site were input into an Excel spreadsheet and the arithmetic mean, standard deviation, standard error, and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated using standard statistical procedures. Each mean R-value (±95%CI) was converted to an SHD age (±95%CI) using the granite calibration equation of Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c):
where y = SHD age and x = site mean R-value.
Other studies of weathering rates (Colman, Reference Colman1981; Colman and Dethier, Reference Colman and Dethier1986; Sánchez et al., Reference Sánchez, Mosquera and Romaní2009; Stahl et al., Reference Stahl, Winkler, Quigley, Bebbington, Duffy and Duke2013) lend support to the linear relationship established by Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c) for the period encompassing the last glaciation and Holocene (<25 ka) and justify its wider application to both dated and undated granite surfaces in Britain and Ireland.
The 10Be ages were calculated using two methods. First, ages were determined using version 3.0 of the online exposure age calculators formerly known as the CRONUS-Earth online exposure age calculators (Balco et al., Reference Balco, Stone, Lifton and Dunai2008; http://hess.ess.washington.edu/math/), using the independently-constrained Loch Lomond production rate (LLPR; 3.963 ± 0.094 atoms g−1 a−1; Fabel et al., Reference Fabel, Ballantyne and Xu2012) with time-dependent LM scaling (Lal, Reference Lal1991; Stone, Reference Stone2000) and assuming 1 mm ka−1 of post-depositional surface erosion (cf. André, Reference André2002; Nicholson, Reference Nicholson2008; Larsen et al., Reference Larsen, Linge, Håkansson and Fabel2012). Second, ages were calculated using CRONUScalc (http://cronus.cosmogenicnuclides.rocks/2.0/; Marrero et al., Reference Marrero, Phillips, Borchers, Lifton, Aumer and Balco2016) with the default global 10Be production rate of 3.92 atoms g−1 a−1 for LM scaling (Borchers et al., Reference Borchers, Marrero, Balco, Caffee, Goehring, Lifton, Nishiizumi, Phillips, Schaefer and Stone2016), again assuming an erosion rate of 1 mm ka−1.
The reduced chi-square statistic (χ2R) was applied to check within-site consistency of 10Be ages (Bevington and Robinson, Reference Bevington and Robinson2003). Where the χ2R value for a sample of ages from a single site exceeded the critical value (95% level), it was inferred that geological uncertainty contributed to the observed age scatter. In such cases, outlier ages were manually removed until a χ2R value less than the critical value was obtained; ages meeting this requirement were regarded as consistent with and representative of a single age population, with age scatter being due to measurement error alone (Balco, Reference Balco2011; Applegate et al., Reference Applegate, Urban, Keller, Lowell, Laabs, Kelly and Alley2012; Small and Fabel, Reference Small and Fabel2016; Small et al., Reference Small, Clark, Chiverrell, Smedley, Bateman, Duller, Ely, Fabel, Medialdea and Moreton2017). For each site the uncertainty-weighted mean of internally-consistent ages was determined and is regarded as providing the best estimate exposure age for the site.
The 10Be ages for three sites (Bloody Foreland, Cronloughan, and Glen Trool) have been published previously using different production rates from those used here and therefore the ages we report differ slightly from the original ones.
RESULTS
R-value frequency distributions
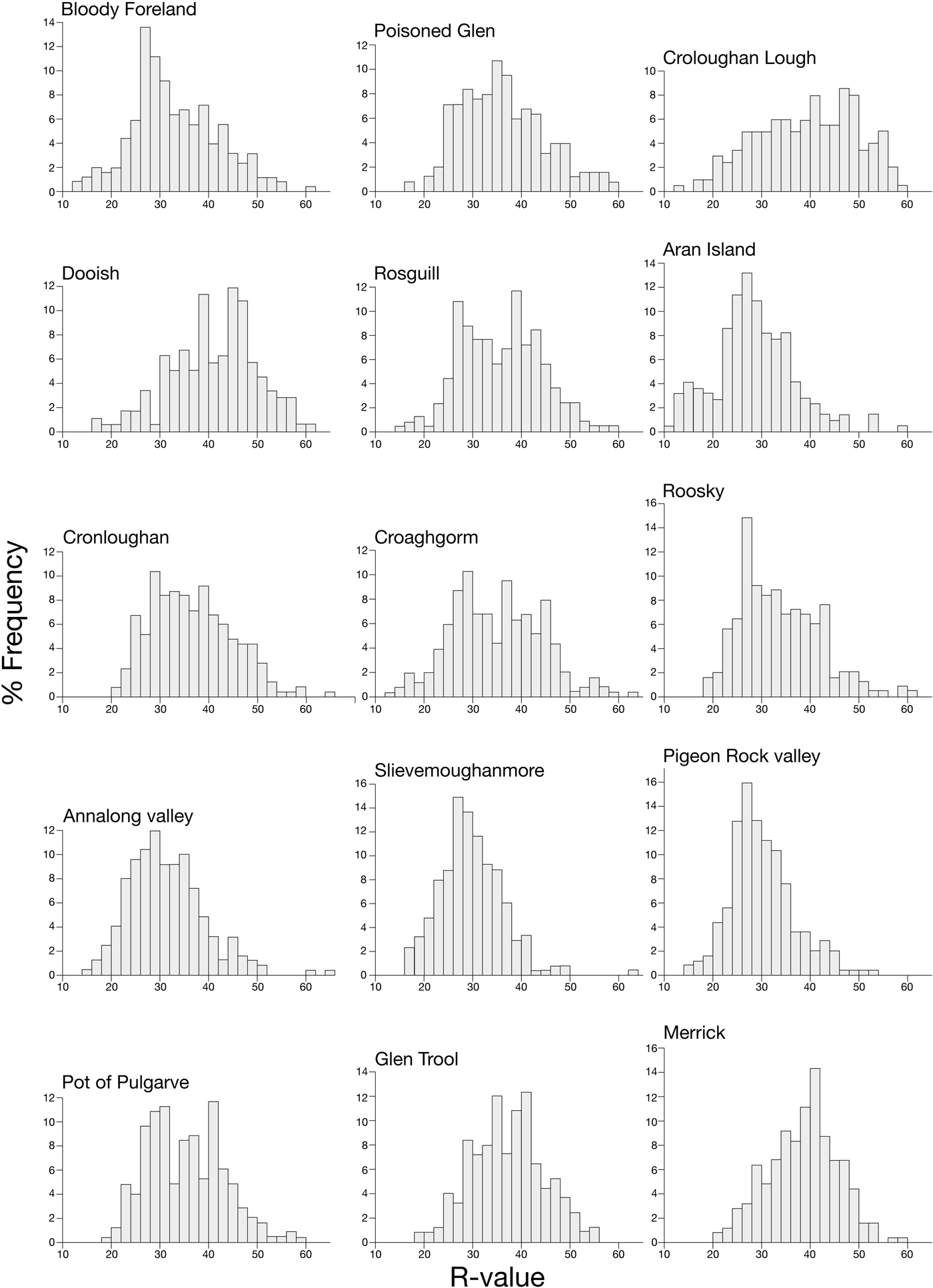
The frequency distributions of Schmidt-hammer R-values for the 15 sites are shown in Figure 4. Each site shows a broad range of R-values, with a maximum range of 51 for both Croaghgorm and Annalong valley and a minimum range of 37 for Glen Trool. Variability in R-value range is greater between the four sites in the Mountains of Mourne (39–51) than it is for the eight sites in Donegal (43–51); lowest variability (37–39) occurs for the Galloway sites. All distributions exhibit a small degree of skewness, with the majority (12) showing slight positive skew. This suggests that although the boulder populations may include small sub-populations of younger or older boulders, these are likely to make only minor contributions to the mean values.
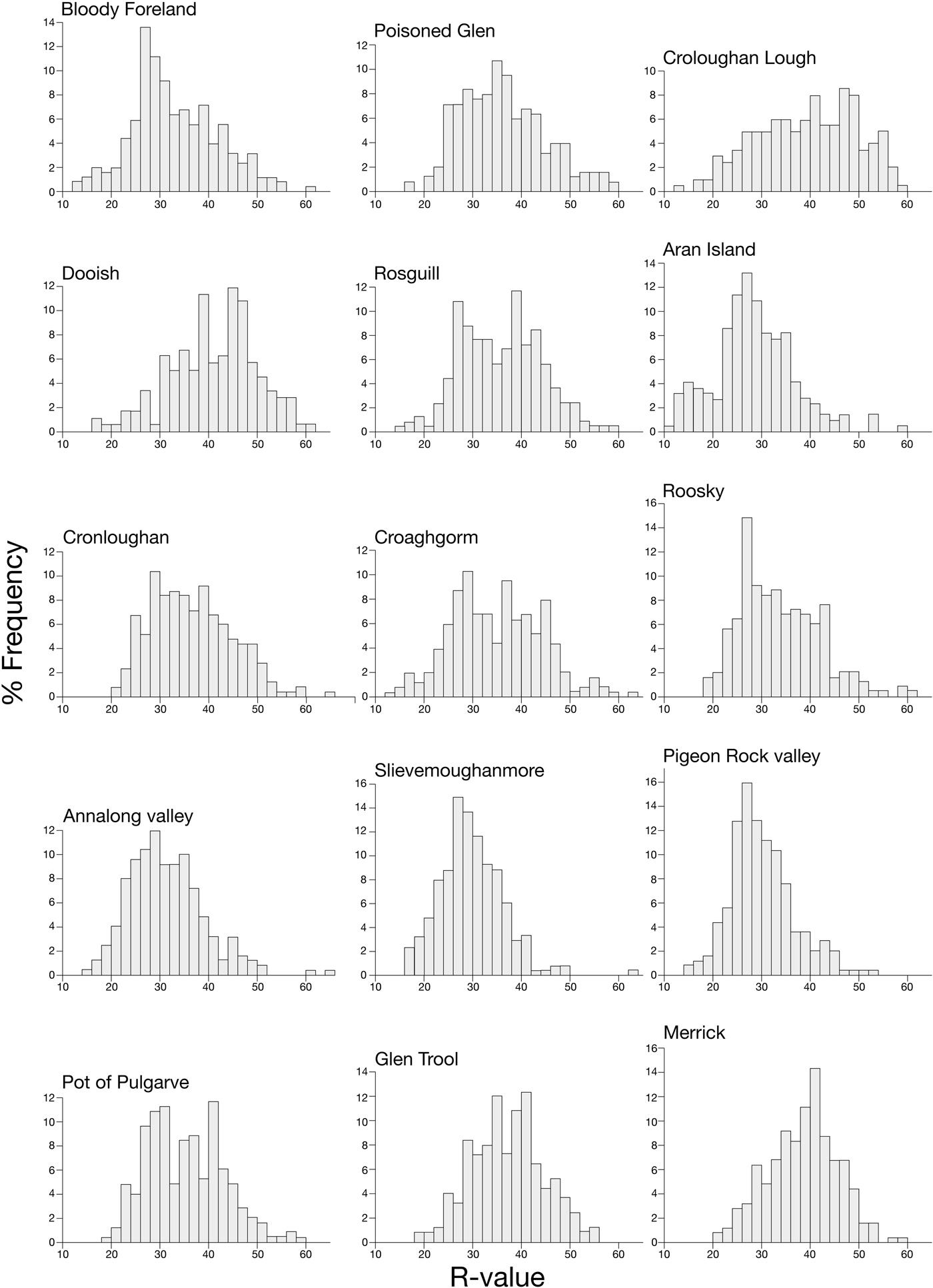
Figure 4. Frequency distributions of Schmidt-hammer R-values for the 15 sites. The class interval is two units.
SHD ages
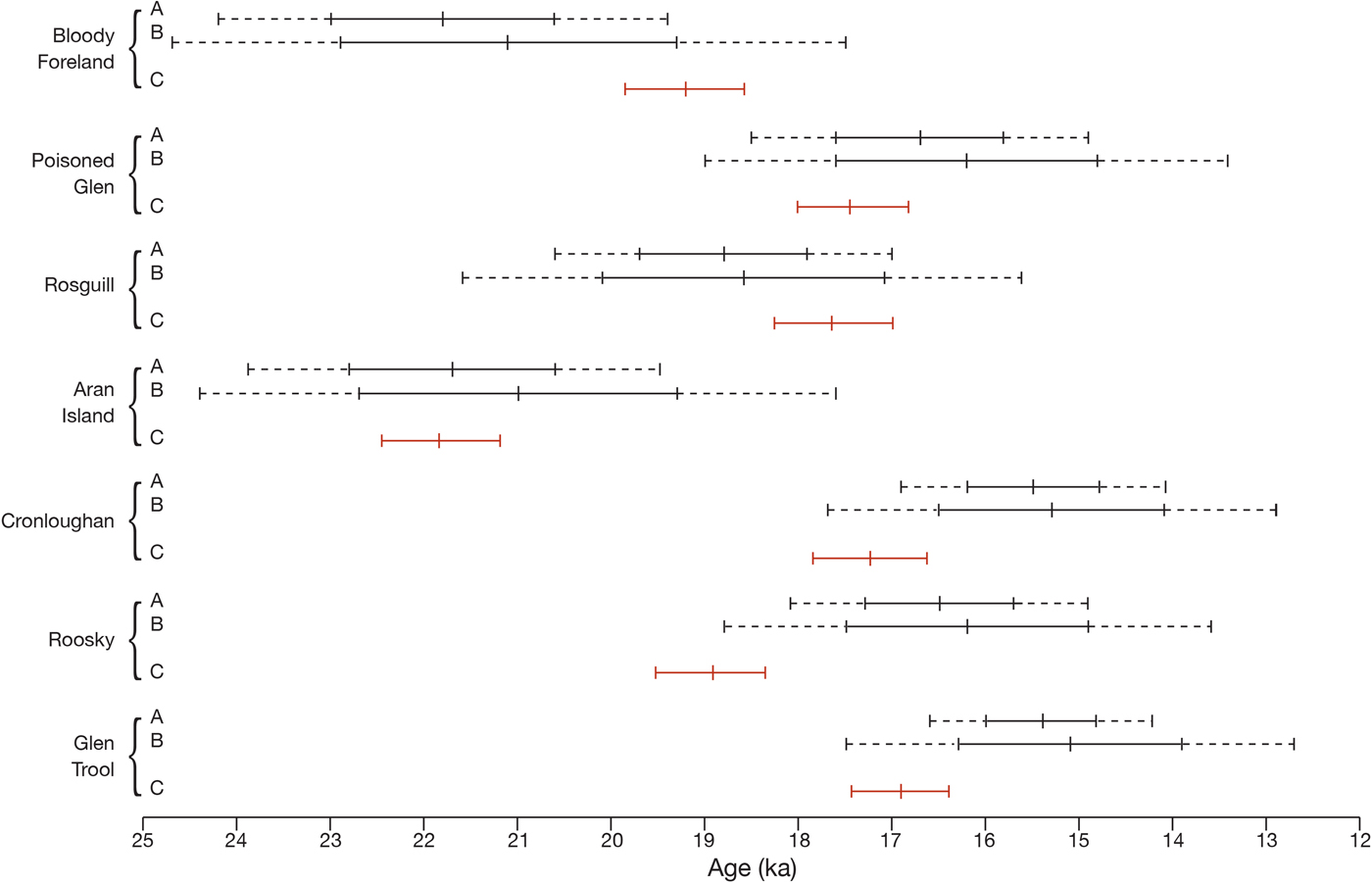
We have followed established convention in reporting uncertainties associated with mean R-values (±95%CI), SHD ages (±95%CI), and 10Be ages (±1σ) (Table 1). An indication of the degree of correspondence (overlap) between the SHD ages and 10Be ages is provided in Table 1 and illustrated in Figure 5. For three of the SHD/10Be pairings (Poisoned Glen, Rosguill, and Aran Island), age overlap is within one or both of the 1σ ranges of the respective 10Be ages; for two pairings (Cronloughan and Glen Trool), age overlap is only within the 2σ range of the 10Be ages; for Bloody Foreland, age overlap is within the 2σ range of the LLPR age and the 1σ range of the CRONUScalc age; and for Roosky age, overlap only occurs within the 2σ range of the CRONUScalc age. In all cases, the precision associated with the SHD ages (i.e., 95%CI) is greater than the 1σ precision determined for the 10Be ages. The significance of these results is explored below.

Figure 5. (color online) Illustration depicting the TCN ages (A = LLPR age; B = CRONUScalc age) and SHD ages (C) for the seven sites for which both ages exist. For the TCN ages the solid line represents the 1σ uncertainty, and both the solid line and the dashed extensions represent the 2σ uncertainty. The SHD ages are shown with 95% confidence intervals. The mid-point of each range is the mean age.
DISCUSSION
The close correspondence between ages at the seven sites for which both 10Be and SHD data are available suggests the Schmidt hammer can provide surface-exposure ages that are of equivalent accuracy, precision, and reliability as those obtained using 10Be. This, in turn, is a convincing argument for using SHD and the calibration of Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c) to obtain age estimates for glacially-transported granite boulders from various contexts in Ireland and Britain for which 10Be ages are not available. Nevertheless, it is still necessary to assess the accuracy of such SHD ages against the wider geological, geomorphological, and geochronological evidence before accepting or rejecting them and their implications. In the sub-sections below, we limit discussion to those sites from which SHD ages alone have been obtained.
Donegal
Three of the sites sampled for SHD do not have associated 10Be ages, and their SHD ages require evaluation. Boulders from the cirque moraine at Croloughan Lough (280 m asl), previously inferred to date from the YD Stadial (P. Wilson, Reference Wilson2004), returned a SHD age of 15.72 ± 0.81 ka (Table 1). This age estimate suggests the moraine formed somewhat earlier than had been supposed, perhaps during a stillstand or readvance related to the Killard Point Stadial/Readvance ((KPS/R) ~17.3–16.5 ka BP; Clark et al., Reference Clark, McCabe, Bowen and Clark2012). Support for this earlier age comes from the neighboring site of the Poisoned Glen (75 m asl), 3 km to the west, which has both SHD and 10Be ages from a boulder-dominated end moraine of a 3-km long valley glacier. These ages (SHD: 17.44 ± 0.61 ka; LLPR: 16.9 ± 0.7 ka; CRONUScalc: 16.7 ± 1.5 ka; Table 1) are also consistent with the KPS/R and indicate that the Derryveagh Mountains hosted at least one valley glacier at that time. Therefore, given its higher elevation, we consider that a small cirque glacier is likely to have existed in the Croloughan Lough cirque during that interval and that the SHD age can be regarded as an accurate and reliable indicator for the timing of ice withdrawal from or stabilization of the moraine.
An SHD age of 14.61 ± 0.76 ka for glacially-transported boulders was obtained for the Dooish Mountain ridge (520–650 m asl; Table 1). This site is 2–5 km east of the Croloughan Lough and Poisoned Glen sites and is at higher elevation. Dating evidence from the uplands of Ireland and Britain indicates a top-down model of post-last glacial maximum (LGM) deglaciation, with summits and ridges becoming ice-free before cirques and valleys (Fabel et al., Reference Fabel, Ballantyne and Xu2012; Hughes et al., Reference Hughes, Glasser and Fink2016; Ballantyne and Ó Cofaigh, Reference Ballantyne, Ó Cofaigh, Coxon, McCarron and Mitchell2017; Barr et al., Reference Barr, Roberson, Flood and Dortch2017). The converse situation would have applied in this part of north Donegal if the SHD age from Dooish were correct. The age also suggests that plateau ice persisted on Dooish into the lateglacial (Woodgrange) Interstadial (14.7–12.9 ka). However, this seems an unlikely scenario because chironomid-inferred mean July temperatures for Lough Nadourcan (60 m asl), 8 km east-northeast of Dooish, reached ~13°C early in the Interstadial (Watson et al., Reference Watson, Brooks, Whitehouse, Reimer, Birks and Turney2010). Therefore, on the balance of evidence we consider that it is unlikely that glacier ice remained on Dooish until ~14.6 ka, and we regard the SHD age as being anomalously young.
From the summit ridge of Croaghgorm (590–670 m asl), in the Blue Stack Mountains, 30 km to the south of Dooish, a SHD age of 18.25 ± 0.66 ka (Table 1) indicates the apparent timing of summit emergence from the downwasting Donegal ice dome. We consider this age to be an accurate and reliable indicator of ice-free conditions because it is consistent with TCN ages from elsewhere in Ireland and Britain for the emergence of mountain ridges as nunataks from independent ice centers (Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, Stone and Fifield2009; Hughes et al., Reference Hughes, Glasser and Fink2016; Ballantyne and Ó Cofaigh, Reference Ballantyne, Ó Cofaigh, Coxon, McCarron and Mitchell2017). In addition, on lower ground (~150 m asl) on the southern flanks of the Blue Stack Mountains, Wilson et al. (Reference Wilson, Ballantyne, Benetti, Small, Fabel and Clark2019) reported a 10Be mean age of ~15.0 ka for glacially-transported boulders. Together with the Croaghgorm SHD age, these support a top-down model of deglaciation for the region.
Mountains of Mourne
None of the four sites sampled in the Mountains of Mourne have 10Be ages associated with them. Three of the sites (Annalong valley, Slievemoughanmore, and Pigeon Rock valley) yielded SHD ages in the range 21.15 ± 0.46 ka to 20.14 ± 0.55 ka (Table 1), indicating that summits and ridges had emerged as nunataks by that time but that valley glaciers continued to exist. Support for early deglaciation of the Mournes and our SHD ages is provided by P.U. Clark et al. (Reference Clark, McCabe, Mix and Weaver2004) and J. Clark et al. (Reference Clark, McCabe, Bowen and Clark2012) using geomorphological and dating evidence from the coast at Kilkeel (Fig. 3C). Following deglaciation of the coastal plain, broad channels up to 12 m in depth were cut into glacigenic sediments by rivers flowing southeast from the mountains. The channels were then filled by fossiliferous marine muds as a consequence of relative sea level rise. Five 14C ages from different levels in the muds are statistically consistent, with a mean of 20.1 ka BP (recalibrated by Ballantyne and Ó Cofaigh, Reference Ballantyne, Ó Cofaigh, Coxon, McCarron and Mitchell2017). Therefore, deglaciation of the coastal plain and subsequent sediment channelling occurred prior to that time. Our SHD ages from Annalong, Slievemoughanmore, and Pigeon Rock are consistent with this and we propose that downwasting of mountain ice and retreat of glaciers into the Mourne valleys began >22–21 ka. Other mountain masses adjacent to the Irish Sea and elsewhere in Ireland provide further support for early deglaciation of the Mournes. In Wales, the Lake District, Isle of Man, Wicklow, the Blackstairs, and Kerry-Cork mountains, 10Be exposure ages indicate the emergence of summits ~23–18 ka (Ballantyne et al., Reference Ballantyne, McCarroll and Stone2006, Reference Ballantyne, Stone and Fifield2009, Reference Ballantyne, McCarroll and Stone2011; Ballantyne and Stone, Reference Ballantyne and Stone2015; Hughes et al., Reference Hughes, Glasser and Fink2016; Chiverrell et al., Reference Chiverrell, Smedley, Small, Ballantyne, Burke, Callard and Clark2018; Glasser et al., Reference Glasser, Davies, Hambrey, Davies, Gheorghiu, Balfour, Smedley and Duller2018).
The SHD age for boulders at the lip of the Pot of Pulgarve cirque is 18.07 ± 0.56 ka. This suggests that the boulders do not date from the YD Stadial as favored by Barr et al. (Reference Barr, Roberson, Flood and Dortch2017). Rather, a considerably earlier age is indicated and this fits with the pattern of SHD ages from Annalong, Slievemoughanmore, and Pigeon Rock for top-down post-LGM deglaciation. We consider it unlikely that a YD glacier developed in the cirque. Our SHD age suggests that the boulders we sampled relate to cirque glacier activity prior to the YD Stadial.
In contrast to our results from the Mountains of Mourne, SHD ages reported by Barr et al. (Reference Barr, Roberson, Flood and Dortch2017) for the Annalong, Pigeon Rock, and Pot of Pulgarve moraines are, respectively, 10.97 ± 1.65 ka, 9.93 ± 1.6 ka, and 8.63 ± 1.61 ka. These ages are considerably younger than ours and are difficult to interpret in a post-LGM/YD deglaciation context.
Galloway
The SHD age of 16.1 ± 0.51 ka for boulders within the limit of the YD glacier at Merrick seems, at face value, to be too old. One of two possible reasons may account for this. First, the glacier may have been substantially smaller than indicated by Cornish (Reference Cornish1981), and the boulders sampled for SHD may have been beyond rather than within the glacier limit. If so, the boulders will relate to post-LGM deglaciation. Large numbers of granite boulders do exist outside of the proposed glacier limit, especially adjacent to Loch Enoch, 1.5 km to the south (Fig. 3D). Consequently, this reason for the SHD age is not easily dismissed. Second, if the mapped YD ice margin is correct, the boulders may have been deposited earlier during post-LGM deglaciation, weathered, and then reworked passively by YD ice. It is not easy to establish which of these scenarios might have applied and given rise to the SHD age.
WIDER IMPLICATIONS
Where we have used SHD at sites that had previously been dated with TCN, we have found good correspondence between the ages derived by both methods within the limits imposed by the respective statistical uncertainties. This suggests that for granite surfaces influenced by the BIIS, SHD is a valid and reliable technique for establishing surface-exposure ages, supporting the conclusions reached in the pioneering work of Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Dortch and Hughes2016, Reference Tomkins, Dortch, Hughes, Huck, Stimson, Delmas, Calvet and Pallàs2018a, Reference Tomkins, Dortch, Hughes, Huck, Tonkin and Barr2018b, Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c). Given that granites are widespread in areas inundated by the BIIS, the potential for rapid field determination of deglaciation age is high and, significantly, the method can be used to extend and refine the developing chronology of deglaciation of the BIIS and YD ice masses. The age range (0.8 ka to 23.8 ka) of the SHD calibration established by Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c) is also appropriate for the age determination of extra-glacial and post-glacial granite landforms in Britain and Ireland, such as rock-slope failures, talus, boulder lobes, pronival ramparts, and flood-related deposits. The ages of many of these features are little known beyond the generality of stating that they formed in the lateglacial or Holocene; establishing more accurate and precise ages is important because they are archives of valuable paleoclimatic information and landscape change.
There is also the potential for extending the use of SHD to granite landforms elsewhere in the world. This has been done by Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Dortch, Hughes, Huck, Stimson, Delmas, Calvet and Pallàs2018a) for the Pyrenees where a TCN/SHD calibration extending from 25 ka to 60 ka has been developed. In this region and over this longer timescale, a curvilinear weathering trend has been shown to apply. It seems likely that similar applications of TCN/SHD calibration to late Pleistocene granite landforms will yield results of significance to wider understanding of the timing and nature of environmental change.
Because the majority of our results are consistent with either the previously obtained 10Be ages or the wider geological, geomorphological, and geochronological evidence, we consider the methodology applied to be robust and appropriate for age determination of glacially-transported granite boulders in a British-Irish context. Two factors contribute significantly to these findings: (1) the adoption of a statistically sound SHD calibration curve based on a large number of sites that have associated 10Be ages (Tomkins et al., Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c), and (2) the large number of Schmidt-hammer R-values obtained at each of our sites. This latter aspect is important in order to minimize potential sources of error such as lithological variations and post-depositional disturbance, thereby enhancing the statistical significance of the results.
CONCLUSIONS
Application of SHD to glacially-transported granite boulders at seven sites exposed by retreat of the last BIIS has yielded ages that show good correspondence (within uncertainties) with previously acquired 10Be ages for the same general surfaces. This provides strong support for the more extensive use of SHD, in combination with the granite calibration equation of Tomkins et al. (Reference Tomkins, Huck, Dortch, Hughes, Kirkbride and Barr2018c), for obtaining age estimates for granite surfaces from different glacial contexts in Ireland and Britain that have not been dated with 10Be.
Evaluation of the SHD ages determined for glacially-transported granite boulders at eight sites that lack 10Be ages suggests that most can be considered reliable because they are consistent with current theory and the broader field evidence. However, as with all dating techniques, the reliability and implications of surface-exposure ages obtained using SHD should be assessed using the wider geological, geomorphological, and geochronological evidence prior to using such ages for chronology building and correlation of landforms and events.
The Schmidt hammer can provide surface-exposure ages that are comparable in accuracy, precision, and reliability to those obtained using 10Be dating. As such, this relatively low-cost technique of rapid data collection deserves to be utilized more widely, both with and without 10Be.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Aaron Barth (University of Wisconsin) for allowing us to use his 10Be results for Cronloughan, and Dr. Derek Fabel (SUERC AMS Laboratory, East Kilbride) and Dr. David Small (University of Durham) for calculating the 10Be ages. The figures were prepared by Anna Ratcliffe. Two anonymous referees are thanked for their comments that helped us to clarify certain issues.