The Valdivia culture (4400–1450 BC) corresponds to the Early Formative period of prehispanic Ecuador, with sites found across much of the western lowlands of the country (Supplemental Figure 1). Valdivia is characterized by one of the earliest ceramic traditions in the Americas (Hill Reference Hill1972–1974; Meggers et al. Reference Meggers, Evans and Estrada1965), the beginning of sedentary village life in the region (Lathrap et al. Reference Lathrap, Marcos and Zeidler1977), and the cultivation of domesticated plants (e.g., Pearsall Reference Pearsall, Silverman and Isbell2008).
Since excavation of the Valdivia type-site (G-31) in the 1950s (Meggers et al. Reference Meggers, Evans and Estrada1965), archaeologists have sought to clarify the temporal extent and identify social changes within the Valdivia tradition (for detailed discussion of the Valdivia absolute chronology, see Marcos Reference Marcos2008; Marcos and Michczynski Reference Marcos and Michczynski1996; Marcos and Obelic Reference Marcos, Obelic, Guinea, Marcos and Bouchard1998; Tabarev et al. Reference Tabarev, Yoshitaka Kanomata, Marcos, Popov and Lazin2016; and Zeidler Reference Zeidler, Raymond and Burger2003). The current chronology divides 11 phases into four periods: early, middle, late, and terminal (Supplemental Table 1). Most investigated sites were occupied for only one or two phases, which makes it difficult to distinguish regional differences from temporal change. The main exception to this is the Real Alto site (OGCh-12) on the semiarid Santa Elena Peninsula, which was occupied nearly the entirety of the Valdivia tradition. Here, changes to site layout, ritual and burial practices, expanded trade networks, and associated settlement patterns beginning in Middle Valdivia all suggest the development of incipient hierarchies in the region and in the Valdivia tradition more broadly (Damp Reference Damp1984; Lathrap et al. Reference Lathrap, Marcos and Zeidler1977; Marcos Reference Marcos1978; Zeidler Reference Zeidler1984). Nevertheless, it remains unclear whether these social changes are representative of the whole of the Valdivia tradition and territorial expanse.
Buen Suceso Excavations
Buen Suceso (OSE-M-2M-4) lies 9 km inland along the Manglaralto Valley in the Santa Elena Province of coastal Ecuador, on the flanks of the Chongon-Colonche hills. Local ecozones within a day's walk of the site include the maritime and littoral resources of the equatorial Pacific coast, such as mangrove swamps, as well as dry scrublands and tropical cloud forests. Average annual rainfall in the area is 530 mm, approximately twice that received on the Santa Elena Peninsula (Amado Garzaro Reference Amado Garzaro1990).
Buen Suceso is approximately 12 km north of the site of Loma Alta (OGSEMa-182; Norton Reference Norton, Marcos and Norton1982; Stahl Reference Stahl1984) via a modern footpath that crosses the intervalley hills. The Valdivia type-site is approximately 20 km away, following a path to the mouth of the valley and then continuing southward along the coast to the mouth of the Valdivia River. The proximity of these sites is such that their inhabitants could have been in semifrequent contact. Real Alto is located approximately 70 km to the south, in the Chanduy River drainage, and would have involved two or more days of travel to reach. It was thus likely part of the interaction zone for people at Buen Suceso but for more occasional interactions.
Buen Suceso measures 130 × 100 m and is characterized by a raised circular-shaped midden surrounding a cleared plaza area (Supplemental Figure 2). This spatial layout is characteristic of Early Valdivia sites (Raymond Reference Raymond, Scott Raymond and Burger2003). At Buen Suceso this spatial organization seems to have persisted throughout the 2,300-year occupation of the site presented here. The site is situated in a farmed field located on the lands of the comuna Dos Mangas. A modern dirt road cuts the western edge of the site, and the southern arm of the village midden is partially eroded by the Río Culebra, a tributary of the Manglaralto River.
Excavations in 2009 and 2017 (Rowe Reference Rowe2014, Reference Rowe2016, Reference Rowe and Cordero2018; Rowe and Duke Reference Rowe and Duke2018, Reference Rowe and Duke2019) recovered portions of three structures and numerous midden deposits that provide radiocarbon and ceramic evidence for Valdivia occupation of the site beginning around 3700 BC (Early Valdivia Phase Ib) and ending around 1425 BC (Terminal Valdivia Phase VIIIb). Together, these contexts indicate that Buen Suceso was a rare, multicomponent Valdivia site and is among the longest-occupied Valdivia sites investigated to date.
14C Contexts
The earliest dates at Buen Suceso come from excavation units on the northern arm of the midden ring surrounding the site, specifically from Units 5 and 6 excavated during the 2017 excavations (Table 1). Two carbon samples were tested from Unit 6: one each from Level 4 and Level 5 (Figure 1). The Level 4 sample (UCIAMS #211882) was recovered 60 cm below the surface from a brownish-yellow silty-loam midden matrix. The sample dated to the Early Valdivia period (Phase Ib, 3703–3637 cal BC). Level 4 contained two figurines (one stone and one ceramic), a piece of spondylus shell (genus Spondylus), and numerous ceramic and lithic items (Supplemental Figure 3). The Level 5 sample (UCIAMS #211885) was recovered 97 cm below the surface from a gray silty-ash matrix containing roots and stones. Its date is later than the sample from Level 4 (Early Valdivia, Phase IIa/IIb, 3265–2920 cal BC), although it is possible that it is actually associated with the large feature of dark gray soil associated with Level 4. The differentiation between this feature and Level 5 was indistinct during excavation.

Figure 1. Unit 3 and Unit 6, 2017 excavation profiles. Structure 1 floor plan and profile. (Color online)
Table 1. Radiocarbon Dates from Buen Suceso.
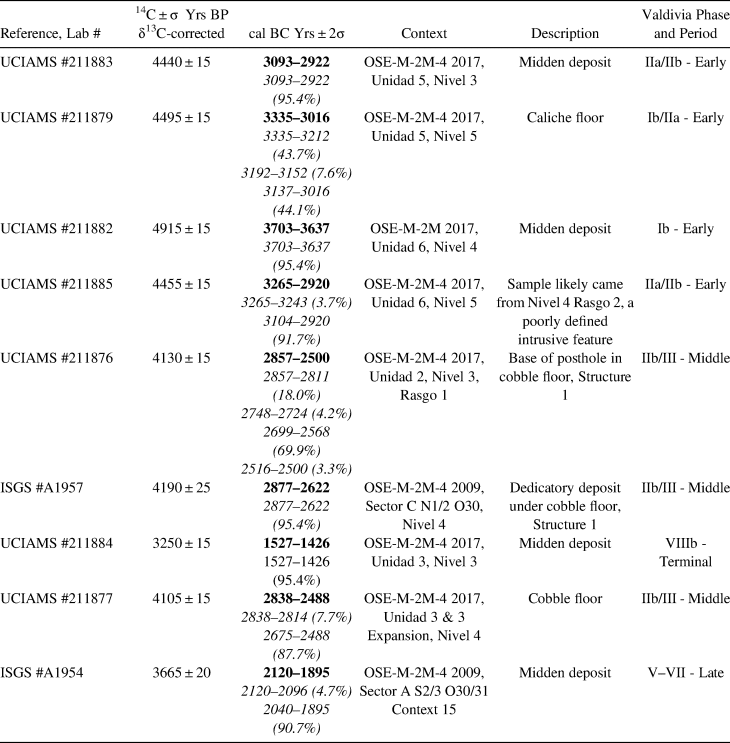
Notes: All dates are derived from charcoal samples and have been corrected for isotopic fractionation by the respective laboratories: the University of California Irvine Keck Carbon Cycle AMS Facility (UCIAMS) and the Prairie Research Institute Division of the Illinois State Geologic Survey (ISGS). Calibrations calculated in OxCal v4.3.2 (Bronk Ramsey Reference Bronk Ramsey2017) using the SHCal13 atmospheric curve (Hogg et al. Reference Hogg, Hua, Blackwell, Niu, Buck, Guilderson, Heaton, Palmer, Reimer, Reimer, Turney and Zimmerman2013).
Two carbon samples were recovered from Unit 5: one from Level 3 and another from Level 5 (Figure 2). The Level 3 sample dated to the Early Valdivia period (UCIAMS #211883; Phase IIa/IIb, 3093–2922 cal BC). It was recovered 58 cm below the surface in a grayish-brown silty-ash matrix. The sample from Level 5 (UCIAMS #211879) was recovered 77 cm below the surface from a chalky (caliche) floor and dated to the Early Valdivia period (Phase Ib/IIa, 3335–3016 cal BC). This may be the floor of a domestic structure.

Figure 2. Unit 5, 2017, and 2009 midden excavation profiles. (Color online)
Evidence for Middle Valdivia occupation of Buen Suceso comes from two locations. First, in Unit 3 (Figure 1) a sample was recovered from Level 4, a cobble floor 61 cm below the surface (UCIAMS #211877). This level includes the subfloor materials of coffee-colored silty loam mixed with small stones. This cobble floor likely represents a domestic structure. This sample dated to the Middle Valdivia period (Phase IIb/III, 2838–2488 cal BC).
The second location that exhibits evidence of Middle Valdivia occupation is a large cobble floor located near the center of the site, Structure 1, which immediately overlays sterile soil. Excavations in 2009 revealed a dedicatory deposit below the cobble floor (R1, Figure 1) consisting of two stacked and inverted vessel bases, a figurine fragment, and a charcoal sample (Supplemental Figure 4). This sample was dated to the Middle Valdivia period (ISGS #A1957; Phase IIb/III, 2877–2622 cal BC). Excavations in 2017 confirmed the Middle Valdivia date of Structure 1. A radiocarbon sample taken from the base of a large posthole (R4, Figure 1), 40 cm below the surface (UCIAMS #211876), was dated to the Middle Valdivia period (Phase IIb/III, 2857–2500 cal BC). There was no wall trench or enclosing postholes, so it was likely a prepared floor with no superstructure. Based on the size and position of this floor, we hypothesize that Structure 1 had a communal or ritual use.
The 2009 excavations included a 2 m deep unit in the south arm of the midden ring. A charcoal sample (ISGS #A1954), dating to the Late Valdivia period (Phase V/VI/VII, 2120–1895 cal BC), was recovered at a depth of 110 cm below the surface from a pit feature dug at the interface of Layers 4 and 5 (context 15; Figure 2). This pit was filled with a grayish-brown silty ash and contained two ceramic sherds and a few lithic artifacts. This Late Valdivia date was further supported by the ceramics found in adjacent levels of the midden (Rowe Reference Rowe2014:354–360).
Finally, the Unit 3, Level 3, sample (UCIAMS #211884) was recovered 50 cm below the surface in a coffee-colored midden deposit above the level of the cobble floor (Level 4; Figure 1). This sample dated to the Terminal Valdivia period (Phase VIIIb, 1527–1426 cal BC). Terminal Valdivia occupation has not previously been identified on the central Ecuadorian coast. Although this is a midden layer and not a feature, it is possible that future excavations will recover evidence of the transition between Valdivia and the subsequent Machalilla tradition, for which there are a few sherds collected from the surface of the site.
Discussion
In summary, in our excavations at Buen Suceso we identified three floors and numerous midden deposits that demonstrate multicomponent Valdivia occupation at the site (Figure 3). The circular layout of Buen Suceso originated in Early Valdivia and persisted through the life of the site. One caliche floor (in Unit 5) represents the Early Valdivia occupation. Two cobble floors (in Unit 3 and Structure 1) indicate Middle Valdivia occupation, whereas midden deposits provide evidence for all periods of occupation at the site. Further excavation is required to determine whether this occupation was continuous or episodic.

Figure 3. Radiocarbon calibration curves from Buen Suceso.
The only other investigated sites that approach or surpass the longevity of Buen Suceso are the Valdivia type-site and Real Alto. Due to the excavation methodology employed at the Valdivia type-site (Meggers et al. Reference Meggers, Evans and Estrada1965), it cannot be used as a reliable source of comparative information regarding social processes in the past. Thus, the most fruitful comparisons for Buen Suceso are the ongoing excavations at Real Alto. A dramatic spatial reorganization occurred in the Middle Valdivia period at Real Alto as it transformed into a regional center. Buen Suceso, in contrast, exhibits a remarkable degree of continuity throughout the 2,300 years of Valdivia occupation. This suggests that very different processes were behind the ongoing occupations at the two sites and that the Valdivia culture was marked by greater social and regional variability than previously recognized. Future work at Buen Suceso will explore this variation.
Acknowledgments
The 2009 excavations were funded by a Scholar Award from the Philanthropic Educational Organization and a Dissertation Travel Grant from the Graduate College of the University of Illinois. The 2017 excavations were funded by a Fulbright Scholar Award. Permits for excavation and sample export were granted by the Instituto Nacional de Patrimonio Cultural, Guayaquil (011.SRL.INPC.2009; 007.DR5.INPC.2017), Ecuador.
Data Availability Statement
All primary data were generated by the coauthors. Data are maintained by the Proyecto Arqueológico Ríos Culebra-Colín, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley.
Supplemental Materials
For supplemental material accompanying this article, visit https://doi.org/10.1017/laq.2020.43.
Supplemental Figure 1: Map of coastal Ecuador with Valdivia sites mentioned in the text.
Supplemental Figure 2: Buen Suceso site map with excavation units.
Supplemental Figure 3: Associated artifacts, Unit 6, Level 4: (a) stone figurine; (b) ceramic figurine; (c) front and back of Spondylus fragment; (d) pie-crust rim; (e) cut and bevel rim.
Supplemental Figure 4: Dedicatory deposit under Structure 1: (a) outer vessel; (b) inner vessel; (c) figurine fragment.
Supplemental Table 1. Correlation of Relative and Absolute Chronologies for Valdivia by Phase (Zeidler Reference Zeidler, Raymond and Burger2003:519).






