Rice is one of the most important cereals produced in the world. It is cultivated mainly in paddy fields (Kim et al. Reference Kim, Gutierrez, Jeong, Lee, Haque and Kim2014) using a continuous flood (IRGA 2016). A continuous flood enhances crop development by eliminating drought stress and reducing weed interference by suppressing weed germination and emergence (Chauhan and Johnson Reference Chauhan and Johnson2010). However, it requires a nearly continuous supply of water, which can lead to high irrigation usage (Avila et al. Reference Avila, Martini, Mezzomo, Refatti, Campos, Cezimbra, Machado, Massey, Carlesso and Marchesan2015). An alternative to continuous rice flooding is alternate wetting and drying, or intermittent flooding (Bouman et al. Reference Bouman, Lampayan and Tuong2007; Liu et al. Reference Liu, Wan, Tao, Li, Zhang, Li and Fang2013). With intermittent flooding, the flood is initiated and established as normal and is followed by one or more drying cycles where ponded water is allowed to subside to a predetermined level before re-establishment of the flood. The extent and number of wetting–drying cycles depends on prevailing weather, edaphic, and field conditions, producer comfort level, and purpose of using intermittent flooding (Massey et al. Reference Massey, Walker, Smith, Anders and Avila2014). For example, if the goal is to reduce methane emissions, more extensive drying is generally required than that required to reduce irrigation use. When carefully managed, intermittent flooding reduces irrigation pumpage by 30% or more compared to continuous flooding (Farooq et al. Reference Farooq, Kobayashi, Wahid, Ito and Basra2009; Susi et al. Reference Susi, Marasi and Soekrasno2016) with no reduction in grain yield (Avila et al. Reference Avila, Martini, Mezzomo, Refatti, Campos, Cezimbra, Machado, Massey, Carlesso and Marchesan2015; Borojeni and Salehi Reference Borojeni and Salehi2013).
Pesticides are indispensable components of modern rice production, helping to provide high crop productivity and economic returns (Wei et al. Reference Wei, Wu, Wang and Yang2015). However, the use of pesticides may also be associated with water contamination that can be harmful to environmental safety and human health (Bhanti and Taneja Reference Bhanti and Taneja2007; Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Zhang, Liu, Jiang and Wu2010). As a result, paddy fields in southern Brazil are a source of water contamination, with frequently used herbicides (e.g. clomazone, imazapyr, and imazapic) being detected in rivers, lakes, and groundwater in Rio Grande do Sul (RS) State (Silva et al. Reference Silva, Avila, Agostinetto, Magro, Oliveira, Zanella and Noldin2009).
Clomazone is a selective, early PRE or POST herbicide used to control a wide range of weeds in rice (Andres and Machado Reference Andres and Machado2004). It belongs to the isoxazolidinones chemical group, and inhibits the desoxixilulose phosphate synthase (DOXP synthase; 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate) enzyme. DOXP synthase is responsible for the synthesis of isoterpenoids, basic precursors of carotenoids (Ferhatoglu and Barret Reference Ferhatoglu and Barret2006). This herbicide is among the more frequently detected pesticides in paddy water studies conducted in Australia, Arkansas (United States), and southern Brazil (Marchesan et al. Reference Marchesan, Zanella, Avila, Camargo, Machado and Macedo2007; Mattice et al. Reference Mattice, Skulman, Norman and Gbur2010; Quayle Reference Quayle2003). It is characterized as persistent, being detected, on average, up to 30 d after being applied (Cumming et al. Reference Cumming, Doyle and Brown2002). Thereby, the maintenance of clomazone at high concentration in fields enhances the possibility of environmental contamination, which can pollute water bodies and have harmful effects on fish (Crestani et al. Reference Crestani, Menezes, Glusczak, Miron, Spanevello, Silveira, Gonçalves, Zanella and Loro2007; Miron et al. Reference Miron, Crestani, Shettinger, Morsch, Baldisserotto, Tierno, Moraes and Vieira2005).
Pesticide dissipation in paddy water has been studied extensively (Martini et al. Reference Martini, Mezzomo, Avila, Massey, Marchesan, Zanella, Peixoto, Refatti, Cassol and Marques2013; Reimche et al Reference Reimche, Machado, Zanella, Vicari, Piccinini, Golombieski and Reck2014; Santos et al. Reference Santos, Marchesan, Machado, Avila, Zanella and Gonçalves2008; Tomco et al. Reference Tomco, Holstege, Zou and Tjeerdema2010; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Wang and Fan2006; Watanabe et al. Reference Watanabe, Nguyen, Souphasay, Vu, Phong, Tournebize and Ishihara2007; Wei et al. Reference Wei, Wu, Wang and Yang2015). However, the impact of water-saving flood management practices, such as intermittent flooding, on pesticide dissipation has not been determined. If intermittent flooding were found to decrease the aquatic persistence of a pesticide relative to a conventional (i.e., continuous) flood, the efficacy of the pesticide might be affected. Conversely, if intermittent flooding increases persistence in the flood, risks associated with environmental contamination might be increased.
The objective of the present study was to investigate the effect of intermittent flood (IF) and continuous flood (CF) irrigation management regimes on the dissipation of clomazone, imazapyr, and imazapic in paddy water.
Material and Methods
Field Experiment
The experiment was established on an Albaquaf soil at the Federal University of Pelotas (UFPEL), Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil (31°52′00′′S, 52°21′24′′W) in the 2012/2013 cropping season. The soil properties were as follows: pHwater (1:1), 5.1; clay content, 15%; organic matter content, 1.2%; P, 4.3 mg dm−3; K, 30 mg dm−3; Ca, 1.8 cmolcdm−3; Mg, 1 cmolcdm−3; and Al, 0.2 cmolcdm−3. The experimental area had not been sprayed with herbicides for five years prior to this study.
The study investigated the interactions between two irrigation systems and the dissipation of three herbicides in paddy water. It was arranged in a completely randomized design with four repetitions per sampling time. The study was repeated at two sowing dates intended to bracket the normal sowing window for rice produced in RS. Experimental plots measuring 15 by 4 m (60 m2) and were separated by 0.3-m soil levees. Zero-grade leveling (i.e., no slope in paddies) was used. The rice cultivar “INTA Puitá CL” was sown on September 24 and November 12 in a no-till residue management regime. The seeding rate was 100 kgha−1, and the row spacing was 0.17 m. The seeds were pre-treated with a mixture of fipronil (Standak®, 250 gaiL−1, Basf A/S), carboxin plus thiram (200+200 gaiL−1) and dietholate (800 g ai L−1) at doses of 38, 200, and 800 g ai per 100 kg seed, respectively. Three hundred kilograms per hectare of fertilizer was applied at planting (5-25-25 N-P2O5-K2O). An additional 80 kgha−1 N was applied at V4/V6 (Counce et al. Reference Counce, Keisling and Mitchell2000). Pest control was performed according to local recommendations for rice cropping systems (SOSBAI 2014).
Irrigation was initiated on November 18 and December 19 in 2012 for the first and second sowing dates, respectively. In the CF plots, a flood depth of 10 cm was maintained throughout the growing season until immediately prior to harvest. For the IF treatments, a 10-cm flood depth was established, but afterwards the flood was allowed to subside naturally until soil moisture was near field capacity (10 kPa). Soil moisture was measured using one soil moisture sensor (Watermark™ , M-900, Irrometer) installed 5 cm below the soil surface in the center of each plot. The level of dryness targeted in this study was similar to that suggested in the method developed by the International Rice Research Institute (Bouman et al. Reference Bouman, Lampayan and Tuong2007). Once soil moisture was 10 kPa, irrigation was resumed so as to re-establish a 10-cm flood. The irrigation system was automated and irrigation was distributed by pumps according to the requirements of each plot. Flood depths were recorded daily for each plot.
Clomazone (800 g ai L−1) was applied PRE using a rate of 792 g ai ha−1 on October 1 and November 18 for the first and second sowing date, respectively. A commercial mixture of imazapyr and imazapic (525+175 g ai kg−1) was applied POST at V3/V4 at rates of 73.5 and 24.5 g ai ha−1 on November 2 and December 18, respectively, for the first and second sowing dates. Control plots that received no herbicide applications were maintained for both irrigation regimes and sampled for each sowing date. Herbicide applications were made using a CO2-pressurized backpack sprayer using TeeJet® XR 110015 flat fan nozzles at 140 kPa pressure and 150 L ha−1 spray volume. Physicochemical characteristics of the herbicides are listed in Table 1.
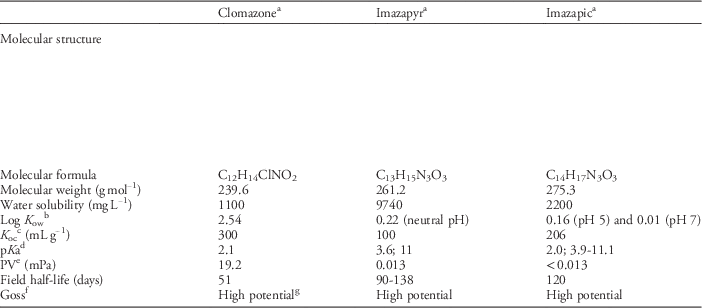
Table 1 Molecular structure and formula, physicochemical properties, and surface water contamination probability (Goss) for clomazone, imazapyr, and imazapic herbicides.

a Data source (IUPAC 2016)
b Partition coefficient between n-octanol and water (Harper Reference Harper1994)
c Partition coefficient between soil organic matter and soil solution (Harper Reference Harper1994)
d Indicates the pH value at which 50% of total molecules are associated in soil and 50% of total molecules are dissociated (Harper Reference Harper1994)
e Compound volatility measured by vapor pressure (Gavrilescu Reference Gavrilescu2005)
f Method of classification of potential surface water contamination (high, medium, and low)
g Criteria for solution transport classification: Low potential: DT50soil>35 days; K oc<100.000 mg L−1; solubility>1 mg L−1; or high potential: K oc≤700 mg L−1; 10 mgL−1≤solubility≤100 mgL−1 (Goss Reference Goss1992)
Sampling
One-liter paddy water samples were randomly collected in amber glass bottles from each plot at 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 15, 20, 30, and 60 d after beginning irrigation (DABI). After sampling, the bottles were placed on ice and transported to the laboratory, where they were stored at 4 C prior to extraction and analysis.
Reagents and Chemicals
Analytical standards of the herbicides were obtained from Dr. Ehrenstorfer (Augsburg, Germany). Full-scan mass spectrometric analysis was used to confirm the chemical identities of the herbicides, which had chemical purities >95%. HPLC grade methanol (MeOH), acetonitrile (MeCN), and optima grade acetic acid (HOAc) were purchased from J. T. Baker (Phillipsburg, NJ). Ammonium acetate was purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Ultrapure water was prepared using a Milli-Q Direct UV3® system from Millipore (Molsheim, France). A vortex mixer model QL-901 was purchased from Microtécnica (Curitiba, Brazil). The polymeric sorbent cartridges Oasis® HLB (60 mg, 3 mL) used in solid phase extraction (SPE) were acquired from Waters (Wexford, Ireland).
Standard Solutions and Calibration Curves
Stock solutions of each herbicide were prepared using residue-grade MeOH. Solutions of the herbicides were prepared using the individual stock solutions to yield concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0, 50.0, 100.0, and 200.0 μgL−1 for each herbicide. The standard solutions were stored at −18C prior to use. In all sample extracts, the herbicides concentrations were quantified based on external calibration curves. Subsequently, the data were adjusted to determine the concentration (μgL−1) of each compound in water.
Analytical Procedures
Considering that the herbicide concentrations were low, the samples were concentrated in SPE cartridges (Oasis®HLB) to quantify these compounds (Donato et al. Reference Donato, Martins, Munaretto, Prestes, Adaime and Zanella2015). The cartridges were conditioned in sequence with 3 mL methanol, 3 mL ultrapure water, and 3 mL water (pH 2.5). Thereafter, 250 mL of each aliquot, previously acidified to pH 2.5 with aqueous phosphoric acid (1:1 by volume) and filtered (PTFE filters, 0.45 µm; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA), was transferred to an SPE cartridge positioned in a vacuum manifold. The cartridge flow rate ranged from 2 to 5 mLmin−1. After the sample passed through the cartridge, 3 mL purified water was passed through the cartridge. The herbicides were eluted from the cartridge using 2 mL of a 1:1 (v/v) methanol–acetonitrile mixture that was prepared with 1% acetic acid. Next, 200 µL eluate was diluted with water (800 µL) prior to chromatographic separation. A concentration factor of 25 times was obtained using this procedure.
Chromatographic separation was performed according to the methods of Donato et al. (Reference Donato, Martins, Munaretto, Prestes, Adaime and Zanella2015), with some modification using a liquid chromatography--mass spectrometry and mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) system equipped with a UPS Pursuit C18 column (100 by 2.0 mm; 2.8 µm particle size). Mobile-phase components A and B consisted of 5 mmolL−1 ammonium formate aqueous solution and methanol, respectively. The initial mobile phase contained 10% solvent B held constant for 3 min, which was then increased to 50% for 1 min, to 95% for 4 min, to 98% for 3 min, held constant for 2 min, and returned to the initial condition over 2 min. The flow rate was 0.150 mLmin−1, resulting in a total run time of 15 min. The sample injection volume was 10 µL. Compound quantification was operated in electrospray ionization positive mode using selected reaction monitoring (SRM). The MS source conditions were as follows: capillary voltage, 2.0 kV; source temperature, 50C; and desolvation temperature, 250C.
The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were estimated using the signal-to-noise ratio method, where the LOD was defined as the lowest concentration at which the analytical signal could be reliably differentiated with a signal-to-noise ratio of 3:1, and the LOQ was defined as the lowest spike concentration that produced a signal-to-noise ratio of 10:1 (SANTE 2015). The instrumental LOD and LOQ were 0.01 and 0.02 µgL−1, respectively. The analytical selectivity of the LC method was tested by analyzing blank samples collected from the non-herbicide-treated control plots. No interfering peaks were detected (data not shown), and analytical calibration curves presented good linearity, with R 2 values being greater than 0.99 for all compounds (data not shown). Extraction recoveries ranged from 78.3% to 103.6 %, with relative standard deviation ≤15.9% obtained for all herbicides at the 500 µgL−1 fortification level.
Data Analysis
The concentrations of each herbicide detected in paddy water were normalized to a water volume corresponding to a 10-cm flood depth, thus allowing comparisons between irrigation systems. The data were tested for normality and homogeneity of variance, and then fit to three different kinetic models: single first order (SFO), first-order multicompartment, and dual first order in parallel. A flow to sink compartment was used to describe the degradation patterns of each herbicide and to obtain the correct endpoints (FOCUS 2006). Based on curve-fitting results (e.g., dg-adj R 2) and the resulting error distribution, the SFO model was selected. This model is represented by Equation 1:
where C is the herbicide concentration at time t, C 0 is initial herbicide concentration, and k is the dissipation rate. Thus, using the assumption that the reaction kinetics were first order, herbicide half-lives (DT50) were calculated with Equation 2:
where DT50 is the time required for 50% herbicide dissipation, and k is the dissipation rate constant from Equation 1. Data analyses and construction of 95% confidence intervals were performed with R software (2013), enabling comparisons between irrigation treatments and crop sowing dates.
Results and Discussion
The mean daily air temperature recorded during the experimental period was higher for the second than it was first sowing date (Figure 1). Moreover, precipitation events were more frequent during the second sowing date (Figure 2). Consequently, the need for irrigation in both the IF and CF treatments was decreased for the second sowing date. In the IF treatment, four wetting-drying cycles occurred during the first sowing period, while only three occurred during the second sowing period. This suggests that for the first sowing date aerobic conditions were more often present, which may have affected herbicide degradation.

Figure 1 Daily average of air temperature (C) and precipitation (mm) at two sowing dates: September 24 (first sowing date) and November 12 (second sowing date).

Figure 2 Flood heights and rainfall events for plots managed using either continuous or intermittent flooding, in days after the beginning of irrigation treatments, in the first (a) and second (b) sowing date.
In terms of the dissipation model fit, the SFO model gave the best description of the herbicide dissipation pattern for both irrigation treatments. In general, R 2 adj values were high and the errors were <15% (FOCUS 2006). The estimated parameters from Equation 1 and the corresponding degradation end points (DT 50, DT 90) are shown in Table 2. Herbicide dissipation in paddy water under two irrigation systems (CF and IF) and two sowing dates is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3 Dissipation curves of clomazone, imazapyr, and imazapic herbicides in paddy water under continuous and intermittent flooding systems at two sowing dates: September 24 (first sowing date) and November 12 (second sowing date).
Table 2 Parameters from Equation 1 for clomazone, imazapyr, and imazapic herbicides applied under intermittent flood (IF) and continuous flood (CF) irrigation management systems at two sowing dates (September 24 and November 12).

a Days before the beginning of irrigation
b 95% confidence intervals
The concentrations of each herbicide in paddy water under both irrigation regimes increased between 5 and 10 DABI. This could be explained by the soil-applied herbicides becoming solubilized by flood water, with concomitant increase in concentration in paddy water. Thus, herbicide dissipation from soil to water is described by a linear pattern until approximately 10 DABI, when maximum concentrations were achieved. Thereafter, concentrations in water decreased at differing rates for the different herbicide and sowing date combinations. This decrease in concentration is partly associated with the dissipation of the compounds, and partly due to low rates of herbicide loading in the irrigation water.
Imazapic and imazapyr are weak acids (Table 1), and therefore their bioavailability in soil is influenced by pH (Loux and Reese Reference Loux and Reese1993). Areas cultivated with rice in RS have predominantly low soil pH values, which favor the adsorption of these herbicides (Oliveira et al. Reference Oliveira, Colonna, Prates, Mantovani, Gomide and Oliveira2004). Therefore, the low pH (5.1) and soil moisture present at time of PRE herbicide applications favored adsorption of the herbicides. However, upon establishment of the rice flood, soil pH would be expected to rise to values close to 6.0 (Silva and Ranno Reference Silva and Ranno2005), causing more of the herbicide to be in anionic form, which would have increased water solubility. Thus, increases in soil pH with flooding increased water solubility, resulting in the gradual increase in herbicide concentrations in paddy water soon after flood initiation.
The maximum herbicide concentrations recovered from paddy water were higher under IF than they were under CF, which may be associated with the more frequent changes in soil water content with IF (Martini et al. Reference Martini, Mezzomo, Avila, Massey, Marchesan, Zanella, Peixoto, Refatti, Cassol and Marques2013). These variations in water content can affect the microorganism populations, thus slowing down degradation of the herbicides. Furthermore, under CF the herbicides are more vulnerable to dissipation via leaching and surface runoff, which could contribute to their lower concentrations in paddy water. These results are in accordance with a previous study comparing the transport of imazethapyr and imazapic under CF and IF, in which a transport reduction of approximately 80% for both herbicides was observed under IF (Martini et al. Reference Martini, Mezzomo, Avila, Massey, Marchesan, Zanella, Peixoto, Refatti, Cassol and Marques2013). The use of IF has also been reported to reduce the transport of other herbicides, such as simetryn, mefenacet and thiobencarb, by approximately 90% (Watanabe et al. Reference Watanabe, Nguyen, Souphasay, Vu, Phong, Tournebize and Ishihara2007).
At the first sowing date, maximum concentrations observed for clomazone, imazapyr, and imazapic under IF were 11.9, 5.4, and 0.86 µgL−1, respectively, while those under CF were 8.3, 4.7, and 0.79 µgL−1, respectively. Higher maximum concentrations were observed for the second sowing date, which can be attributed to the smaller period between herbicide application to soil and the beginning of irrigation when compared to that of the first sowing date. The maximum concentrations observed under IF for the second sowing date for clomazone, imazapyr and imazapic were 16.9, 6.0, and 0.98 µgL−1 respectively. While in CF, the recovered concentrations were 13.8, 5.2, and 0.9 µgL−1, respectively. Differences in the recovered maximum concentrations between the different herbicides are explained by the initial rates applied: 792, 73.5, and 24.5 gaiha−1 for clomazone, imazapyr, and imazapic, respectively.
Imazapic was less persistent in water than were the other herbicides, with lower DT50 values at both sowing dates. Herbicide DT50 values under CF were 3.20 and 3.10d for the first and second sowing dates, respectively, with a dissipation rate of approximately 0.21d−1. Under an IF regime, the half-life of imazapic was higher than it was under CF, with DT50 values of approximately 5d for both sowing dates. Similar results were found by others, who estimated the DT50 for imazapic to be approximately 4 d under CF (Reimche et al. Reference Reimche, Machado, Zanella, Vicari, Piccinini, Golombieski and Reck2014).
Imazapyr DT50 values under CF were approximately 6 d for both sowing dates. The half-life of this herbicide was higher under IF than it was under CF, with 11.30 and 12.00d for the first and second sowing dates, respectively. The degradation of imazapyr was previously studied under different soil water contents, with half-life in soil under aerobic and anaerobic conditions varying between 26 and 44 d and 3 and 10d, respectively (Wang et al. Reference Wang, Wang and Fan2006). Others report that shallow flooding results in imazapyr half-life values of from 5 to 15 d (Mangels and Ritter Reference Mangels and Ritter2000). These results agree with those that show that imazapyr biodegradation is faster under anaerobic conditions than it is under aerobic conditions, and are in accordance with the results achieved in the field experiment, where imazapyr half-life in water was found to be <13d for all treatment combinations.
When imidazolinone herbicides are near water surfaces, photolysis can be an important dissipation pathway (Avila et al., Reference Avila, Massey, Senseman, Armbrust, Lancaster, McCauley and Chandler2006). Photodegradation has been reported as a dominant process for imazapyr, occurring relatively quickly with a half-life of <3d (Mallipudi et al. Reference Mallipudi, Stout, Cunha and Lee1991). Furthermore, this process may be particularly important in tropical and subtropical countries, where intense solar radiation and high temperatures are predominant (Santos et al. Reference Santos, Marchesan, Machado, Avila, Zanella and Gonçalves2008). However, photodegradation occurs only when the herbicides remain exposed, on the soil surface or in clear water (Ramezani et al. Reference Ramezani, Oliver, Kookana, Gill and Preston2008). In this study, the paddy water of the CF treatments was visually clearer than that in the IF plots, owing to less soil disturbance caused by irrigation events. This could have contributed to faster dissipation of these herbicides under a CF regime.
The dissipation of clomazone did not show significant differences under the two irrigation regimes. Under CF, DT50 values were 5.00 and 7.50 d for the first and second sowing dates, respectively. With IF, DT50 values were higher than they were in CF, at 21.70 and 10.10d for the first and second sowing dates, respectively. Half-life values of 47 and 8d have been reported for clomazone under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, respectively (Tomco et al. Reference Tomco, Holstege, Zou and Tjeerdema2010). However, another study found faster dissipation of this herbicide, with DT50 values of 14 and 7 d in soil and water, respectively (Quayle et al. Reference Quayle, Oliver and Zrna2006). Thus, results of the present field study are in accordance with those previously reported.
Physicochemical characteristics of clomazone indicate that photolysis and microbial degradation are important processes mediating the herbicide’s environmental fate, with microbial degradation expected to play a greater role (Tomco and Tjeerdema Reference Tomco and Tjeerdema2012). Furthermore, clomazone has a tendency to volatilize, and environmental conditions such as high soil moisture tend to accelerate the losses of this herbicide, mainly due to competition between water and herbicide molecules for soil adsorptive sites (Cumming et al. Reference Cumming, Doyle and Brown2002).
Temperature and rainfall differences between sowing dates may partly explain the variation in the dissipation behavior of the herbicides and resulting herbicide half-lives. Clomazone was found to dissipate nearly twice as fast for the second sowing date compared to the first. For most compounds, higher temperatures generally result in higher dissipation rates owing to enhanced water solubility and microbial activity (Castillo and Tortensson Reference Castillo and Torstensson2007).
Our hypothesis that dissipation of herbicides occurs at slower rates under intermittent irrigation, and when the crop is sown earlier in the cropping season, was only partly supported. Clomazone dissipation was not affected by irrigation regime. In contrast, the two imidazolinone herbicides dissipated more slowly under IF than they did under CF. Sowing date did not affect the dissipation of imazapyr and imazapic in paddy water, while clomazone dissipation was reduced during the cooler planting season.
Another important aspect to be determined is the potential impacts of IF on grain yield. This study did not find any differences in grain yield between irrigation systems for two sowing dates (Figure 4). Similar results were reported by others, where satisfactory grain yield under IF was explained by the fact that plants were not submitted to water deficits, as the soil was kept always at least saturated (Avila et al. Reference Avila, Martini, Mezzomo, Refatti, Campos, Cezimbra, Machado, Massey, Carlesso and Marchesan2015; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Wang and Fan2006).

Figure 4 Rough rice grain yield (dry) under two irrigation systems (intermittent and continuous flood) and at two sowing dates: September 24 and November 12.
The overall conclusions from this study are that the aquatic dissipation rates of two imidazolinone herbicides are faster under CF than they are under IF, while the dissipation of clomazone did not differ between CF and IF management. This is likely due to greater offsite runoff of the herbicides from paddies irrigated using a continuous flood, and, to a lesser degree, potential changes in oxygen status between the CF and IF.
Among the herbicides studied, imazapic was the least persistent in water. At the warmer sowing date (second), the dissipation of clomazone was faster than in the first sowing date under both irrigation systems. Irrigation method did not affect grain yield. However, to ensure crop productivity, it is important that soil water content does not drop significantly below field capacity. This investigation has shown that the dissipation behaviors of commonly used rice herbicides can differ under different irrigation regimes. Thus, changes in irrigation management, which will be required to produce more rice grain with less water to avoid future scarcity, should be made with consideration of the impacts of flood management on herbicide persistence and environmental behavior.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Research Support Foundation of Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS) and the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education (CAPES) for funding this research.