I. INTRODUCTION
N,N-Dimethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine (Figure 1) is an extract of herbal medicine Cryptotaenia japonica, which was isolated for the first time by Liu et al. (Reference Liu, Zhang and Liang2018). It is one of the special components in this plant, which has not been found in other plants. It is recorded in the pharmacopeia of traditional Chinese medicine that C. japonica has many medicinal values, such as anti-inflammatory, detoxification, promoting blood circulation, reducing swelling, treating lung disease, gonorrhea, toothache, anti-infection, and anti-virus (Yang and Xia, Reference Yang and Xia2010). For example, crude flavonoids extracted from this plant have antioxidant activity in vitro (Lu et al., Reference Lu, Xu, Yang, Fu, Luo and Li2015). Its methanol extract has protective effects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo (Kang et al., Reference Kang, Bang, Lee, Lew, Eom, Li and Choi2012). Kaempferol-7-O-β-D-glucuronide and tilianin, isolated from this plant, show anti-melanogenic potential (Seong et al., Reference Seong, Lee, Poudel, Oh and Lee2016). Hence, it can be speculated that the title compound may play a key role in the pharmacological activity of the designated plant. At present, the detailed X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) data for it have not been reported.
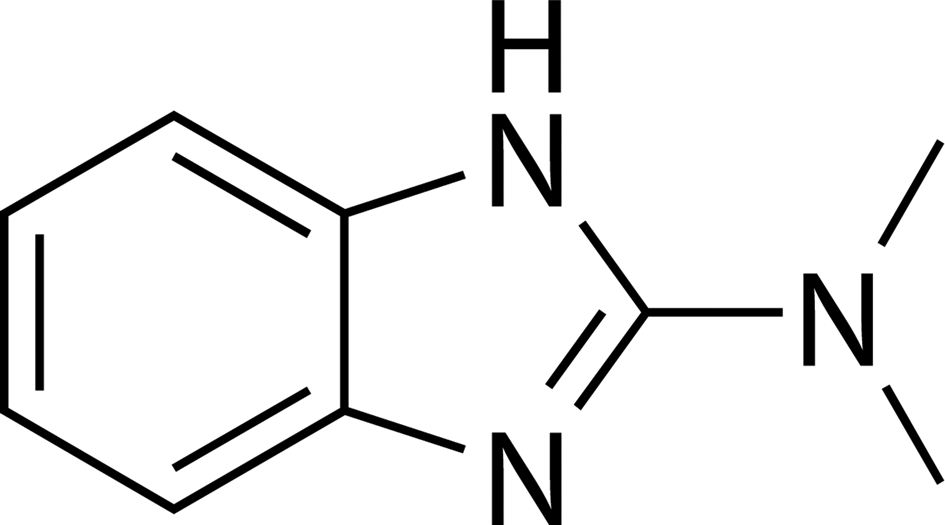
Figure 1. Chemical structure of N,N-dimethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine.
II. EXPERIMENTAL
A. Sample preparation
The sample (Figure 1) was extracted (60% ethanol, heating reflux), isolated, and purified (ethyl acetate extracted, then separated by silica gel column, hydroxypropyl dextran gel column, octadecyl silane bonded silica gel column) from C. japonica. The natural sample was analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). As seen in Figure 2, the chromatogram shows that its purity is satisfactory. The melting point and measured density of it are 325.17 °C (Figure 3) and 1.271 g cm−3, respectively. The crystallization of the title compound at room temperature was successful using chloroform-ethyl acetate (10:1, v/v) as a solvent. Then, the crystals were dried, smashed, and mounted on a flat zero background plate.

Figure 2. HPLC pattern of N,N-dimethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine.

Figure 3. DSC pattern of N,N-dimethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine.
B. Diffraction data collection and reduction
XRD measurement was performed at room temperature using a Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer (Bruker, AXS, Germany) with a LynxEye array detector and CuKα radiation (generator setting: 40 kV and 40 mA). The diffraction data were collected over the angular range from 5 to 50° 2θ with a step size of 0.020464° 2θ (time of diffraction measurement ~10 min) (Figure 4).

Figure 4. XRD pattern of N,N-dimethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine using CuKα radiation.
The software package Material Studio 8.0 (Accelrys Co., Ltd., CA, USA) was used to process the data in the multi-function computing platform (Guangxi University, Nanning). The XRD pattern was processed by subtracting the background, smoothing, and stripping off the Kα 2 component. Automatic indexing results were obtained by the DICVOL91 method (Boultif and Louër, Reference Boultif and Louër1991). The following figures of merit were achieved: F 20 = 19.9 (0.0157, 46) (Smith and Snyder, Reference Smith and Snyder1979) and M 20 = 15.6 (de Wolff, Reference de Wolff1968). The indexing results were then refined using Pawley (Reference Pawley1981), which involves assigning the Miller indices (h, k, l) to each observed peak in the experimental powder XRD pattern.
III. RESULTS
Pawley refinement results confirmed that the title compound is orthorhombic with space group P21212 and unit-cell parameters: a = 11.379(3) Å, b = 10.227(5) Å, c = 7.151(1) Å, α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 90°, unit-cell volume V = 832.318 Å3, Z = 4, ρ cal = 1.286 g cm−3. The values of 2θ obs, d obs, I obs, h, k, l, 2θ cal, d cal, and Δ2θ are listed in Table I.
TABLE I. Indexed X-ray powder diffraction data for N,N-dimethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine.

The d-values were calculated using CuKα 1 radiation (λ = 1.5405981 Å).
IV. DEPOSITED DATA
CIF and or RAW data files were deposited with ICDD. You may request this data from ICDD at info@icdd.com.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the 2017 basic ability improvement project for young and middle-aged teachers in colleges and universities in Guangxi (Grant No. 2017KY1226).








