Introduction
Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma of minor salivary gland origin is a malignant neoplasm that was described in 1984 as being a distinct entity from other salivary gland tumours.Reference Evans and Batsakis1 It was later adopted into the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of tumours.Reference Luna, Wenig, Barnes, Eveson, Reichart and Sidransky2 It is a slow-growing tumour with indolent biology that presents on average in the fifth decade of life.Reference Evans and Luna3, Reference Castle, Thompson, Frommelt, Wenig and Kessler4
To date, there have only been three reports of polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma in the second decade of life.Reference Tsang, Tung and Chan5–Reference Arora, Sreedharanunni and Dey7 These 3 cases were in patients aged 12, 16 and 18 years at diagnosis. Two of these patients were found to have regional lymph node metastasis at presentation. The authors reported greater papillary cystic growth patterns in the tumours than is usually seen in polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma, suggesting that this is the cause of the uncharacteristically aggressive behaviour.Reference Kumar, Stivaros, Barrett, Thomas, Bounds and Newman6, Reference Arora, Sreedharanunni and Dey7 Similarly, Luna and Wenig reviewed 40 polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma cases and reported that the rate of metastasis was unusually high.Reference Luna, Wenig, Barnes, Eveson, Reichart and Sidransky2
In 2011, Skalova et al. reported on a series of 23 cases of distinct, poorly recognised, low-grade adenocarcinomas that principally affected the tongue, all of which had previously been diagnosed as polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma.Reference Skalova, Sima, Kaspirkova-Nemcova, Simpson, Elmberger and Leivo8 They found that these tumours were different to polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma in terms of location, histology and behaviour. In light of the predominantly solid and cribriform architecture of this tumour, it has been termed ‘cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary glands’. It is currently a provisional entity in the WHO classification.Reference Luna, Wenig, Barnes, Eveson, Reichart and Sidransky2
In this report, we describe the case of a 13-year-old girl with cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland of the palate, with cervical lymph node metastasis at presentation. This represents the first case in the literature of an adolescent with cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland. Prior to this paper, the youngest reported case was in a patient aged 21 years.Reference Michal, Kacerovska and Kazakov9
A literature search was performed to identify all relevant previous case reports and literature reviews. This involved a search of the terms ‘polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma’ and ‘cribriform adenocarcinoma’ on Medline, in articles published from 1946 to January 2014.
Case report
An 11-year-old girl presented to her general practitioner with a left, level II neck lump and symptoms of intermittent nausea. Initially, she was referred on to paediatric medicine. At the age of 13 years, she was seen by an otolaryngologist. There had been no interval change in the size of the lump and the patient was asymptomatic.
An ultrasound scan indicated a prominent level II cervical lymph node with slightly suspicious features, including hypoechogenicity. An excisional biopsy was subsequently performed. Histological analysis revealed appearances of polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma within a lymph node, with no evidence of parotid gland tissue; as such, the findings represented metastasis from an as yet unidentified primary tumour.
The patient was subsequently referred to our head and neck centre. Examination of the oral cavity demonstrated a firm, irregular mass of the left hard and soft palate, with normal overlying mucosa (Figure 1). The head and neck examination findings were otherwise normal.

Fig. 1 Pre-operative view of the left palatal lesion.
Computerised tomography and magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated a large lesion in the soft and hard palate that extended inferio-anteriorly, causing bony destruction and erosion of the maxilla adjacent to the maxillary premolar roots. Superiorly, the lesion extended into the maxillary antrum, eroding the medial and posterior walls of the antrum and the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone. The tumour measured 37 × 30 × 24 mm (Figures 2 and 3).

Fig. 2 Coronal, T1-weighted, post-contrast magnetic resonance imaging scan demonstrating the left palate lesion.

Fig. 3 Axial, T1-weighted, post-contrast magnetic resonance imaging scan demonstrating the left palate lesion.
Biopsies of the primary lesion were taken via an endoscopic nasal approach. The morphological and immunophenotypical features of the lesion appeared consistent with polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma.
Following discussion in the multidisciplinary team meeting, radical surgical resection was deemed the most appropriate form of management. The patient underwent left maxillectomy via a Weber–Ferguson approach (Figure 4), with left, level I–IV selective neck dissection. A composite fibula free flap was harvested to reconstruct the defect.

Fig. 4 View of the resected mass, following left maxillectomy.
After appropriate post-operative management, the patient made a good recovery with no immediate or early complications.
Histopathological analysis of a maxillectomy resection specimen showed extensive involvement by an unencapsulated, malignant tumour. The tumour had a nodular arrangement composed of solid, cribriform and microcystic structures, with invasion into the maxillary bone. In the solid areas, the tumour nests were detached from an outer layer of peripheral cells, forming clefts; this gave a glomeruloid appearance (Figure 5). The tumour nuclei had a pale, optically clear, vesicular appearance, resembling the nuclei of papillary thyroid carcinoma (Figure 6). There was mild nuclear atypia. Mitotic figures were rare.
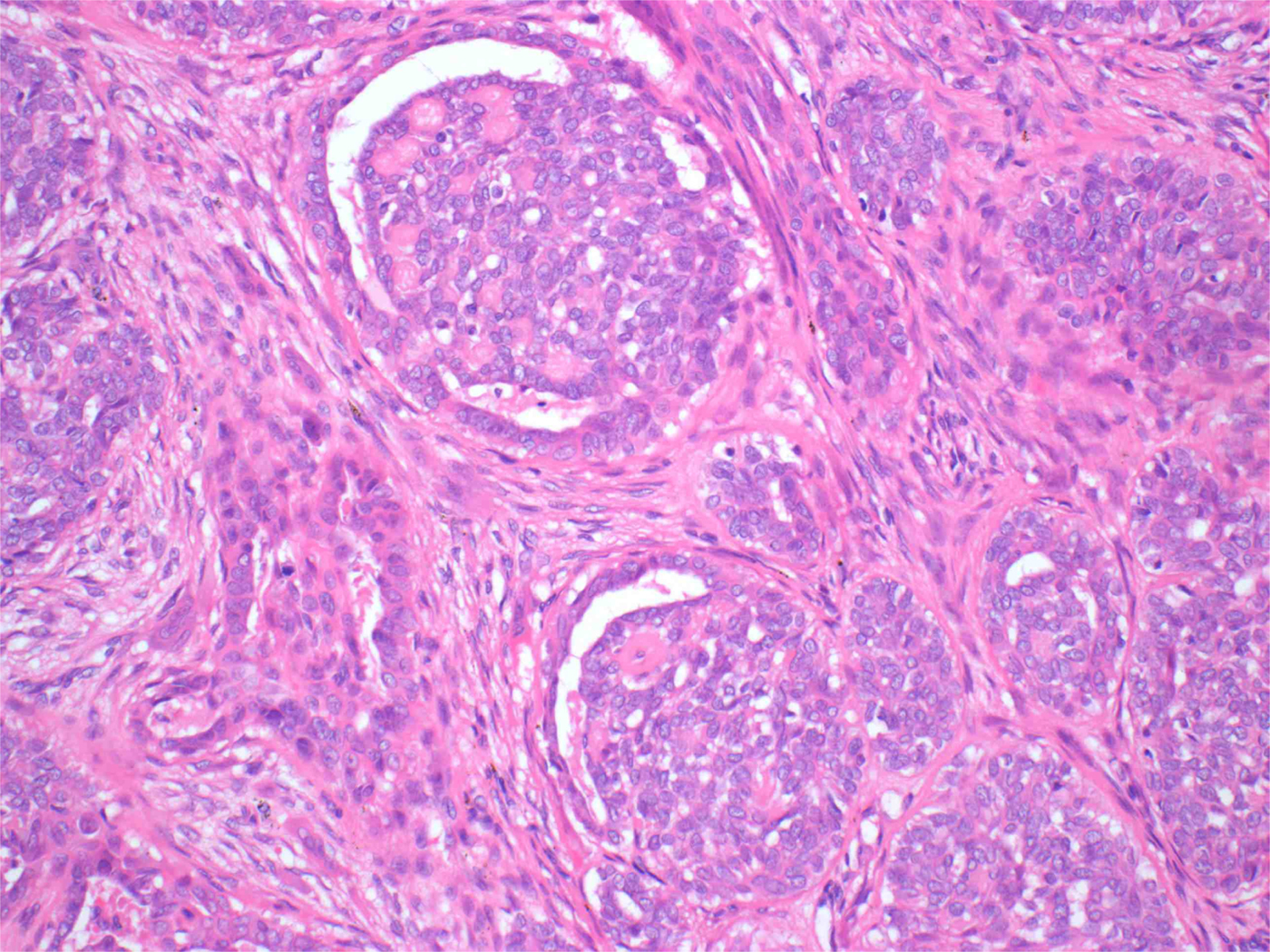
Fig. 5 Photomicrograph of the tumour revealing a composition of nests of solid and cribriform structures. The solid structures contain lobules of cells separated from an outer layer of peripheral cells by a narrow cleft, giving a glomeruloid appearance. The peripheral cells contain hyperchromatic nuclei with a hint of palisading. (H&E; ×200)
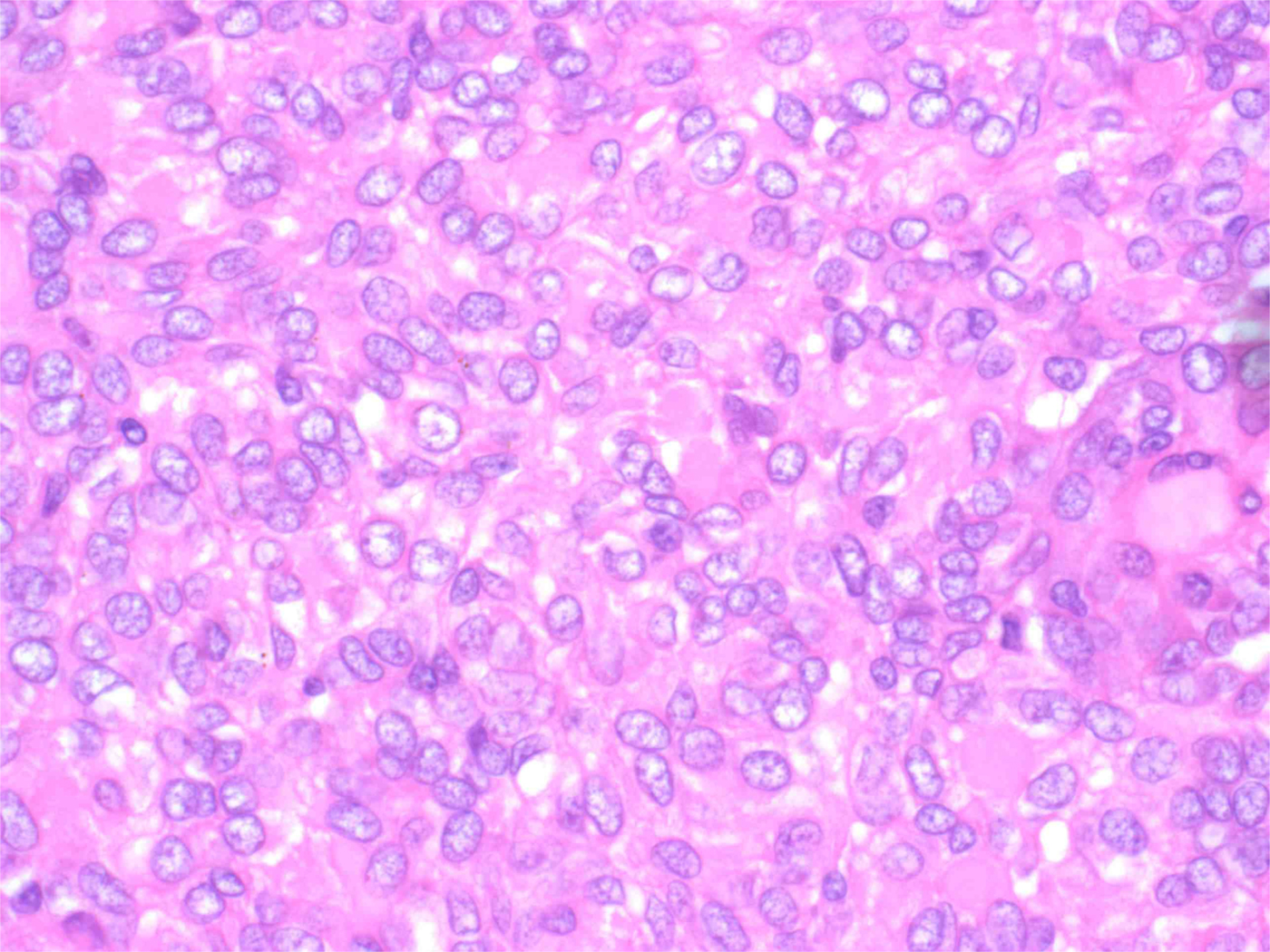
Fig. 6 Photomicrograph of the tumour cells, which contain pale vesicular nuclei with mild atypia. Mitotic figures are rare. (H&E; ×600)
Immunohistochemistry was positive for vimentin, CAM5.2, AE1/3, CK7, CK19 and S100. It was negative for TTF1 and thyroglobulin.
The growth pattern, with predominantly solid and cribriform patterns, suggested that the primary tumour could be more accurately described by the term cribriform adenocarcinoma of minor salivary gland origin, as recently described.Reference Skalova, Sima, Kaspirkova-Nemcova, Simpson, Elmberger and Leivo8 Further review of the prior biopsies from the patient indicated that the growth patterns were similar to that in the resection specimen. This led to the revision of the initial diagnosis (of polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma) to cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland.
The tumour was fully excised. Neck dissection revealed two positive level I nodes and one positive level II node. There was no extracapsular spread. Neither the primary tumour nor the lymph node metastasis demonstrated perineural invasion. The patient subsequently underwent adjuvant radiotherapy.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this paper describes the youngest patient diagnosed with cribriform adenocarcinoma of tongue or minor salivary gland origin. Of the 31 cases previously reported in the literature, the average age of patients was 56.8 years, with the youngest of these patients being 21 years old.Reference Luna, Wenig, Barnes, Eveson, Reichart and Sidransky2, Reference Skalova, Sima, Kaspirkova-Nemcova, Simpson, Elmberger and Leivo8, Reference Prasad, Kaniyur, Pai and Nesari10–Reference Laco, Kamaradova, Vitkova, Sehnalkova, Dvorakova and Vaclavokova13
The tumours originated in the tongue in 21 out of the 31 previously reported cases. This is in contrast to the findings of 2 large case series focusing on polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma, where, in 130 of 204 cases, the tumour originated in the hard or soft palate.Reference Evans and Luna3, Reference Castle, Thompson, Frommelt, Wenig and Kessler4 There appears to be a clear preponderance for cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland to principally affect the tongue (compared to polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma); this makes the presentation of our case, which involved the palate, uncharacteristic.
The rate of cervical lymph node metastasis in the 31 previously reported cases of cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland was 61.2 per cent at presentation, compared to reported rates of 6–35 per cent in a number of case series of polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma.Reference Evans and Batsakis1, Reference Evans and Luna3, Reference Hannen, Bulton, Feston, Wienk and de Wilde14–Reference Vincent, Hammond and Finkelstein17 The higher rate of metastasis at presentation is one of the behavioural features of cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland that differentiates it as an entity from polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma. In two of the three previous case reports of adolescents with polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma, there was cervical lymph node metastasis at presentation.Reference Tsang, Tung and Chan5–Reference Arora, Sreedharanunni and Dey7 This indicates more aggressive behaviour than is normally characteristic of polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma, which rarely metastasises. It has been suggested that a proportion of those cases reported as polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma with metastasis are in fact cases of cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland.Reference Michal, Kacerovska and Kazakov9
For the 31 previously reported cases of cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland, treatment entailed surgical excision; 14 patients also received radiotherapy.Reference Luna, Wenig, Barnes, Eveson, Reichart and Sidransky2, Reference Skalova, Sima, Kaspirkova-Nemcova, Simpson, Elmberger and Leivo8, Reference Prasad, Kaniyur, Pai and Nesari10–Reference Laco, Kamaradova, Vitkova, Sehnalkova, Dvorakova and Vaclavokova13 In the 21 cases where there were follow-up data (ranging from 2 months to 13 years), all patients were alive and without signs of metastasis or further recurrence at the time of the last follow up. These tumours are likely to be chemo-resistant, so adjuvant radiotherapy appears to form a suitable part of the management.
Histologically, polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma classically has a wide range of architectural appearances, including lobular, papillary or papillary cystic, cribriform, and trabecular structures. Particularly characteristic is the occurrence of streaming columns of single file or narrow trabeculae of cells forming concentric whorls, creating a targetoid appearance.Reference Michal, Kacerovska and Kazakov9 However, cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland is described as a solid mass divided by fibrous septa into irregularly shaped and sized nodules. These nodules are composed of solid, cribriform and microcystic structures, as was the case with our resection specimen. The solid component is often arranged in tumour nests detached from surrounding peripheral cells by clefts, giving a glomeruloid rather than a targetoid appearance.Reference Skalova, Sima, Kaspirkova-Nemcova, Simpson, Elmberger and Leivo8
At a cellular level, one of the key distinguishing features between polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma and cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland is the appearance of the nuclei. In cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland, the nuclei often overlap each other. The nuclei are pale, optically clear and vesicular, with a ground-glass appearance.Reference Skalova, Sima, Kaspirkova-Nemcova, Simpson, Elmberger and Leivo8 In polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma, the nuclei are uniformly round to ovoid. They contain open vesicular nuclear chromatin, and inconspicuous to small nucleoli.Reference Castle, Thompson, Frommelt, Wenig and Kessler4 In both tumour types, nuclear pleomorphism and mitotic figures are rarely found. The nuclear appearances of cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland with focal papillary growth can closely resemble the pattern of papillary carcinoma of the thyroid, as described in our case.
In both the previously published cases of polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma occurring in adolescents with metastasis, the authors comment on the presence of focal papillary cystic growth areas.Reference Kumar, Stivaros, Barrett, Thomas, Bounds and Newman6, Reference Arora, Sreedharanunni and Dey7 It is not clear from the discussion of the morphological appearances whether these could actually represent other cases of cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland in adolescence, especially as the authors only comment on cytological findings.Reference Arora, Sreedharanunni and Dey7
There have been cases of delayed diagnosis of cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland, resulting in unnecessary surgery such as total thyroidectomy. In one study, this occurred because of the similarities to papillary thyroid cancer and the incorrect diagnosis of an earlier floor-of-mouth lesion as ‘proliferating pleomorphic adenoma’.Reference Laco, Kamaradova, Vitkova, Sehnalkova, Dvorakova and Vaclavokova13 The routine use of TTF1 and thyroglobulin stains would normally differentiate these lesions, as these stains will be negative in cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland cases.
• Paediatric patients with lymphadenopathy should undergo a full ENT examination
• Cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary glands is considered a separate entity from polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma
• It behaves differently, with higher rates of cervical lymph node metastasis at presentation, but has a favourable prognosis if appropriately managed
• This paper describes the first reported case of cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland in the paediatric population
As highlighted by the current case, a full ENT examination and relevant investigation should never be overlooked in a paediatric patient with a persistent neck lump. This will ensure that unusual pathology is not missed, thereby avoiding delays in diagnosis and treatment. It is widely accepted that affected patients should be managed with wide local excision and adjuvant radiotherapy if necessary.
The current case provides additional evidence to support the argument that cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland is a distinct entity from polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma. At least two of the three previously reported cases of polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma in adolescence may have actually been cases of cribriform adenocarcinoma of the tongue and minor salivary gland.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr Samih Mady (Consultant Head and Neck Surgeon) and Mr Kavin Andi (Consultant Maxillofacial Head and Neck Surgeon) for their involvement in the care of the patient.








