Introduction
A plunging ranula is an uncommon condition characterised by a pseudocyst in the neck formed by mucus extravasation from the sublingual gland. This mucus extravasation may enter the neck, either posterior to the mylohyoid muscle or through a dehiscence in the muscle.Reference Morton, Ahmad and Jain 1
Plunging ranulas typically present as painless, gradually enlarging neck swellings. Acute presentation of ranulas is rare.Reference Zhao, Jia, Chen and Zhang 2 This article describes a rare case of an acute presentation of a plunging ranula that progressed rapidly to cause respiratory distress, requiring urgent treatment. A PubMed literature search was conducted. To the best of the author's knowledge, such a case has not previously been reported.
Case report
A 14-year-old male student presented to the otolaryngology clinic complaining of a left-sided neck swelling. The swelling had appeared two days before presentation and had progressively enlarged. It had started to become painful, and the patient had difficulty swallowing. However, there was no dyspnoea at presentation.
On examination, the vital signs were normal. The neck swelling was located in the left upper neck and measured approximately 9 cm in diameter. It was fluctuant and the overlying skin showed no sign of inflammation. Examination of the oral cavity showed no evidence of tonsillitis or dental caries. However, there was a cystic, reddish swelling in the left sublingual area over the site of the sublingual gland (Figure 1).
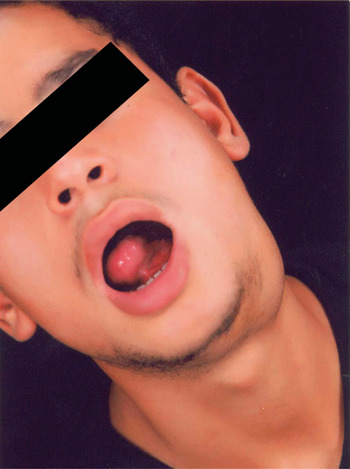
Fig. 1 Clinical photograph of patient at presentation, showing the neck and intra-oral swellings. Published with patient's permission.
The patient was admitted. Urgent ultrasound and computed tomography scans were arranged. The ultrasound scan showed the neck swelling to be a multilocular cyst. The computed tomography scan revealed a large, cystic neck mass measuring 80 × 45 × 90 mm, communicating with a sublingual component through a dehiscence in the mylohyoid muscle. The wall of the cyst was thin and showed no contrast enhancement (Figure 2).

Fig. 2 Axial computed tomography scan after admission, showing the cyst. R = right; P = posterior
Over the next few hours, the patient's condition deteriorated rapidly. His neck swelling became very tense and his tongue was pushed upwards and backwards by the sublingual component, causing respiratory distress.
The patient was urgently taken to the operating theatre. Under sedation, a wide-bore cannula was inserted into the neck cyst. A gush of clear, yellow fluid emanated from the cannula. Approximately 150 ml of fluid was aspirated, following which the sublingual component of the mass shrank markedly. The cyst cavity was repeatedly irrigated with 70 per cent alcohol as a sclerosant, and then the contents of the cavity were completely aspirated. Following aspiration of the neck cyst, the anaesthetist was able to intubate the patient nasotracheally, and a throat pack was applied after inducing general anaesthesia. The left sublingual gland was excised, preserving the lingual nerve and the submandibular duct. The intra-oral ranula cavity was noted to lie posterior to the sublingual gland. The sublingual gland was sent for histopathological analysis and the neck cyst aspirate was sent for cytology, biochemistry and bacteriology studies.
Histopathological analysis of the gland showed an inflammatory cellular infiltrate around the acini (Figure 3). Bacteriological culture of the aspirate grew no bacteria, and no acid-fast bacilli were evident. Cytological examination of the aspirate revealed macrophages, lymphocytes, neutrophils and red blood cells against a proteinaceous background.

Fig. 3 Photomicrograph of the excised sublingual gland showing an inflammatory cellular infiltrate around the acini. (H&E; ×150)
The results of biochemical analysis of the aspirate are shown in Table I.
Table I Biochemical profile of neck aspirate

The patient was closely monitored on the ward for five days, after which he was discharged.
He was seen in the clinic two weeks later, at which time he was completely symptom-free (Figure 4). On review four months after presentation, there was no recurrence of the ranula.

Fig. 4 Clinical photograph of the patient two weeks after discharge. Published with patient's permission.
Discussion
A ranula is an extravasation mucocele that arises from the sublingual gland, either from a ruptured main duct or from ruptured acini following obstruction. The sublingual gland is a spontaneous secretor and produces a continuous flow of mucus, even in the absence of nervous stimulation. The extravasated mucus excites an inflammatory reaction.Reference Harrison 3 The presented case showed inflammatory cells on cytological examination of the aspirate and on histological examination of the sublingual gland after excision.
A plunging ranula typically presents as a painless, gradually enlarging swelling in the neck, associated with a swelling in the floor of the mouth.Reference Zhao, Jia, Chen and Zhang 2 The differential diagnosis includes branchial cleft cyst, dermoid cyst and cystic hygroma. If the lesion is rapidly enlarging, an acute deep neck space infection should be suspected.Reference Gossett, Smith, Sullivan and Harsha 4
Imaging studies using ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging help to exclude the diagnosis of deep neck space infection, and also allow delineation of the extent of the lesion. Fine needle aspiration confirms the presence of saliva in the cyst, based on the high amylase content of the aspirate.Reference Mahadevan and Vasan 5
The case presented in this report is very unusual because of its rapidly progressive course. After presentation to our hospital, the diagnosis of a deep neck space infection was refuted by the radiologists, who suggested that the radiological appearances were more in favour of a ranula. The rapid progression of symptoms, to the extent of respiratory distress, necessitated urgent intervention. Aspiration of the cyst and excision of the ipsilateral sublingual gland were performed as an emergency, and the patient was closely monitored in the hospital for five days.
-
• Acute presentation of a plunging ranula is rare
-
• The presented case had an acute, progressive course with respiratory distress, requiring urgent intervention
-
• Treatment should include sublingual gland excision
Another case of a plunging ranula presenting with acute sublingual and submandibular swellings has been described.Reference Gossett, Smith, Sullivan and Harsha 4 That case was managed by repeated aspiration and, ultimately, by a marsupialisation procedure.
The acute and progressive clinical course in the presented patient is difficult to explain. The biochemical profile of the cyst aspirate was that of acinar salivary secretion unmodified by the ductal system (Table I). The dramatic high flow rate of saliva suggests acinar injury in the sublingual gland. In a recent histological study on excised sublingual glands, McGurk et al. Reference McGurk, Eyeson, Thomas and Harrison 6 suggested a traumatic aetiology for the development of oral ranulas. These authors showed that the ranula develops from a discrete area in the sublingual gland, and that it was not necessary to remove the whole sublingual gland for cure. In a discrete area of acinar rupture, local hypersecretion is associated with increased blood flow.Reference McClatchey, Haley Appelblatt, Zarbo and Merrel 7
One hypothesis for the acinar hypersecretion seen in the present case is aberrant parasympathetic nerve discharge. Parasympathetic nerve stimulation to the sublingual gland is known to cause increased blood flow and acinar hypersecretion through the kallikrein-bradykinin system.Reference Guyton, Hall, Guyton and Hall 8
Different modes of treatment have been proposed for plunging ranulas. However, any treatment should include excision of the ipsilateral sublingual gland to achieve minimal recurrence rates.Reference Zhao, Jia, Chen and Zhang 2 , Reference Mahadevan and Vasan 5 , Reference Huang, Liao, Chin and Chen 9 Recently, non-surgical modes of treatment have been described, including injection of botulinum toxin to cause chemical denervation to the glandReference Chow, Chan and Lam 10 and injection of OK-432 as a sclerosant.Reference Ohta, Fukase, Watanabe, Ito and Aoyagi 11 In the presented patient, irrigation of the cavity with alcohol as a sclerosant was preferred because of its safety.
Conclusion
Plunging ranulas rarely present in an acute fashion. Diagnosis should include imaging and fine-needle aspiration. Urgent surgery may be required if there is respiratory distress. Recurrence rates are minimal if excision of the sublingual gland is included in the management protocol.







