Article contents
A fluid mechanical view on abdominal aortic aneurysms
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 November 2010
Abstract
Abdominal aortic aneurysms are a dilatation of the aorta, localized
preferentially above the bifurcation of the iliac arteries, which increases in
time. Understanding their localization and growth rate remain two open questions
that can have either a biological or a physical origin. In order to identify the
respective role of biological and physical processes, we address in this article
these questions of the localization and growth using a simplified physical
experiment in which water (blood) is pumped periodically (amplitude
a, pulsation ω) in an elastic membrane (aorta) (length
L, cross-section A0 and elastic
wave speed c0) and study the deformation of this
membrane while decharging in a rigid tube (iliac artery; hydraulic loss
K). We first show that this pulsed flow either leads to a
homogenous deformation or inhomogenous deformation depending on the value of the
non-dimensional parameter
c02/(aLω2K).
These different regimes can be related to the aneurysm locations. In the second
part, we study the growth of aneurysms and show that they only develop above a
critical flow rate which scales as
A0c0/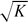 .
.
JFM classification
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2010
References
REFERENCES
- 9
- Cited by


