1. Introduction
The Mesozoic–Cenozoic geology of SE China is characterized by extensive magmatism, contractional and extensional deformation related, large-scale structures (i.e. SE China fold-and-thrust belt, Xuefeng Uplift, East China Rift System, Yangtze Fold Zone) and strike-slip fault systems (Figs 1, 2). Southeast China consists of two continental blocks, Yangtze and Cathaysia, making up the South China Block, which constitutes a significant component of the tectonic mosaic of SE Asia. The South China Block is separated from the North China Block to the north by the Qinling–Dabie–Sulu orogenic belt, from the Songpan Ganzi terrane to the NW by the Longmenshan fault system, from the Indochina Block to the SW by the Ailaoshan – Song Ma suture zone, and from the Luzon island arc (part of the Philippine Sea plate) to the E-SE by an active collision zone, exposed on the island of Taiwan (Fig. 1).
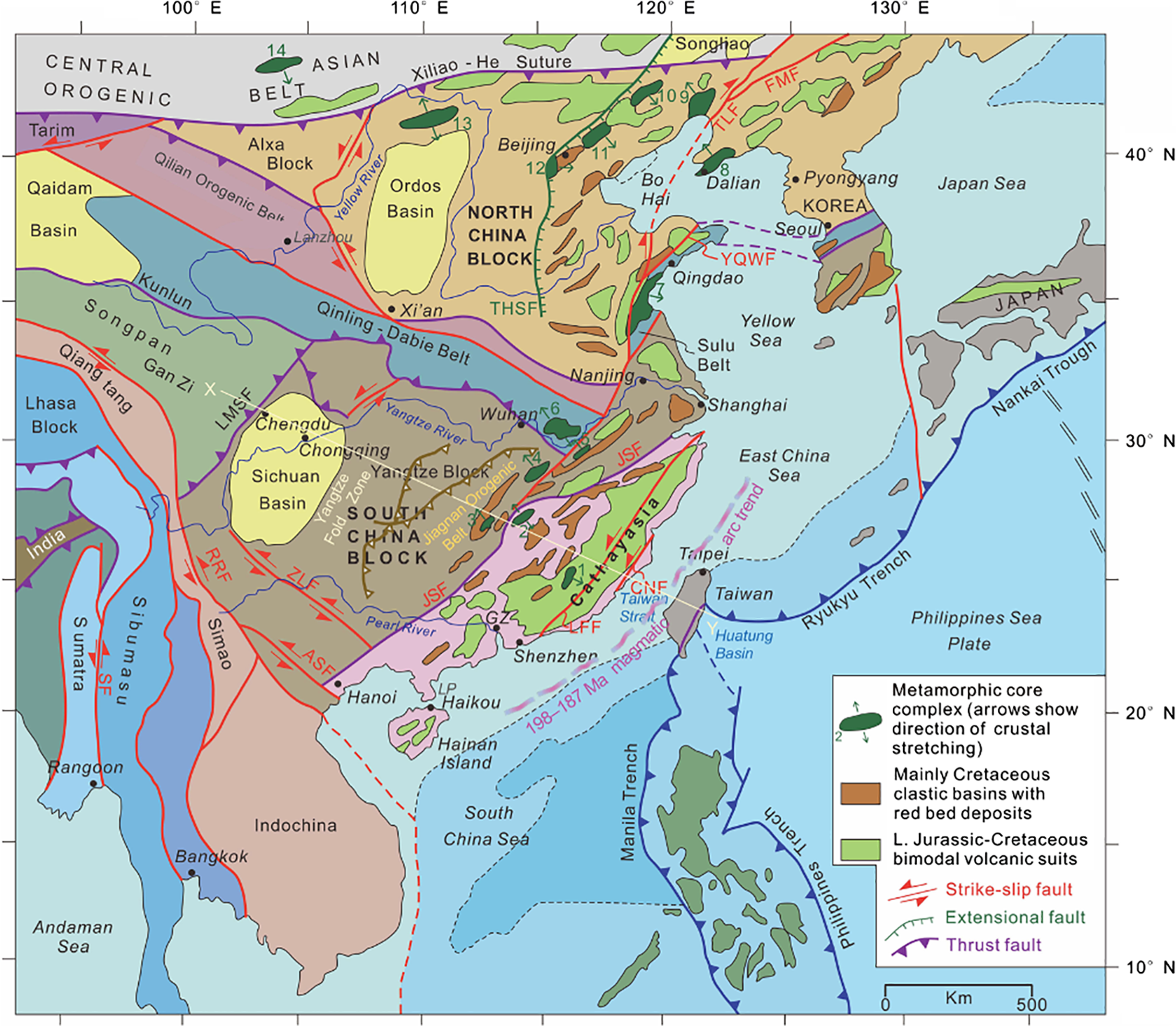
Fig 1. Simplified tectonic map of eastern and central China, Indochina and the western Pacific realm, showing the distribution of major continental blocks, suture zones, fault systems and modern trenches. Also shown, related to the topic of this paper, are latest Jurassic – Early Cretaceous metamorphic core complexes, Cretaceous clastic basins with red bed deposits, and Late Jurassic – Cretaceous bimodal volcanic sequences in eastern China. Metamorphic core complexes (listed from south to north): 1. Zhuguang–Nanxiong (102–96 Ma); 2. Wugongshan (131 Ma); 3. Yuechengling (140–120 Ma and 100–85 Ma); 4. Lushan (126 Ma); 5. Hongzhen (135–125 Ma); 6. North Dabieshan (125 Ma); 7.Wulian (135–122 Ma); 8. Liaoning (125 Ma); 9. Yiwulushan (126 Ma); 10. Kalaqin (120 Ma); 11. Yunmengshan (126 Ma); 12. Xishan (132 Ma); 13. Hohhot (125–121 Ma); 14. Yagan–Onch Hayrhan Fault (126 Ma). Abbreviations for the major fault systems: ASF – Aliaoshan Fault; CNF – Changle–Nanao Fault; FMF – Fushun–Mishan Fault; LFF – Lishui–Haifang Fault, LMSF – Longmenshan Fault; NJF – Nenjiang Fault; RRF – Red River Fault; SF – Sagaing Fault; THSF – Taihangshan Fault; YQWF – Yantai–Qingdao Wulian Fault; ZLF – Ziyun–Luodian Fault. LP – Leizhou (Liuchow) Peninsula. Data are from Faure et al. (Reference Faure, Sun, Shu, Monié and Charvet1996), Wang et al. (Reference Wang, Shu, Faure and Sheng2001), Lin & Wang (Reference Lin and Wang2006), Hall (Reference Hall2012), Ni et al. (Reference Ni, Liu, Tang, Yang, Xia and Guo2013), GW Zhang et al. (Reference Zhang, Xu, Zhao and Badal2013), Li & Li (Reference Li and Li2015), CH Xu et al. (Reference Xu, Zhang, Shi, Brix, Huhma, Chen, Zhang and Zhou2017) and Chu et al. (Reference Chu, Lin, Faure, Xue, Ji and Feng2019).
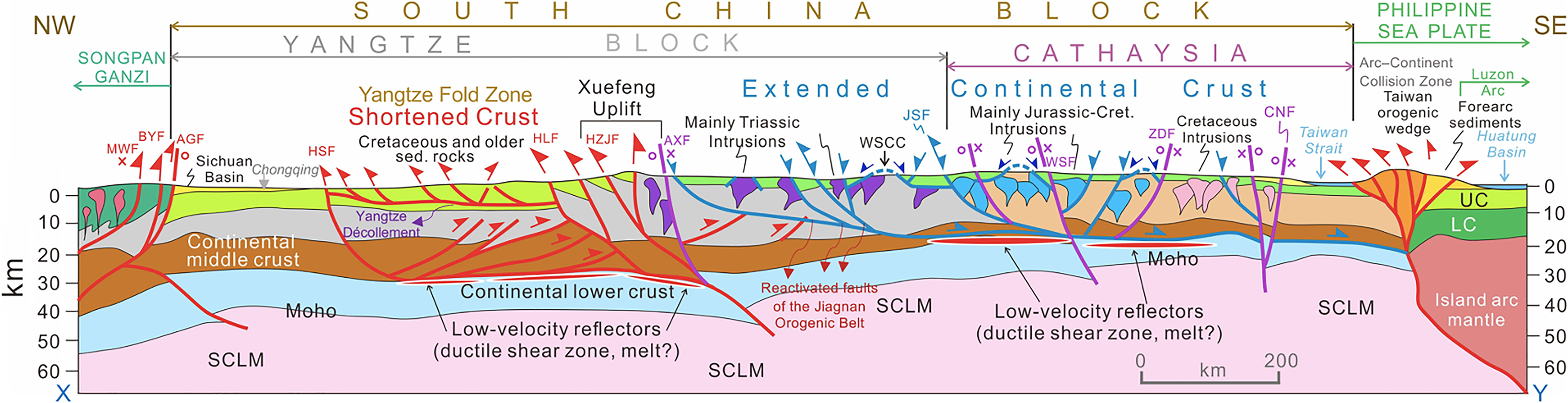
Fig 2. WNW–ESE-oriented lithospheric-scale tectonic cross-section, depicting the main modes of crustal and mantle deformation structures across the South China Block, extending into the Songpan Ganzi terrane in the NW and to the modern arc–continent collision zone in Taiwan and the Philippine Sea Plate in the SE. The Xuefeng Uplift Zone separates the folded and thrust-faulted Cretaceous and older sedimentary rocks of the Yangtze block (Shortened Crust) in the west from the Extended Crust of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks in the east. Geometries and locations of the main fault systems are based on seismically determined profile by Zhang et al. (Reference Zhang, Xu, Zhao and Badal2013). Other data are from XH Li (Reference Li2000), Li & van der Hilst (Reference Li and van der Hilst2010), Wang & Shu (Reference Wang and Shu2012), Li et al. (Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016), CH Xu et al. (Reference Xu, Zhang, Shi, Brix, Huhma, Chen, Zhang and Zhou2017), Zhang et al. (Reference Zhang, Wu, Gao, Fu, Sun, Wu and Ding2017) and JH Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018). Abbreviations for the major fault systems: AGF = Anxian–Guanxian Fault; AXF = Anhua–Xupu Fault; BYF = Beichuan–Yingxiu Fault; CNF = Changle–Nanao Fault; GJF = Ganjiang Fault; HLF = Hefeng–Laifeng Fault; HSF = Huayingshan Fault; HZJF = Huayuan–Zhangjiajie Fault; JSF = Jiangshan–Shaoxing Fault; LLF = Lishui–Faifang Fault; MWF = Maowan Fault; WSF = Wuchuan–Sihui Fault; ZDF = Zhenghe–Dapu Fault. Other abbreviations: LC = lower continental crust; SCLM = subcontinental lithospheric mantle; UC = upper continental crust; WSCC = Wugongshan core complex (131 Ma). Note that some of the E-dipping extensional normal faults in the eastern Yangtze Block are reactivated W-directed Triassic (?) thrust faults. Notice the significantly thinned nature of the lithosphere, particularly the middle to lower crust, in eastern Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks, and the existence of low-velocity reflectors (representing ductile shear zones and/or melt lenses) near the top of the lower crust in Cathaysia.
Although the tectonic boundaries of the South China Block with the surrounding continental blocks are well defined both geologically and geophysically, our understanding of the internal, lithospheric-scale architecture of this major cratonic block is still evolving as more data become available. Controversies and different interpretations exist, for example, as to what geological phenomena caused significant shortening of the crust in SE China during the Triassic, and what the driving forces were for the generally NW–SE-oriented extensional deformation, particularly within Cathaysia, during the Middle Jurassic through Cretaceous. Similarly, the heat and melt sources of extensive continental magmatism in SE China during the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous periods and the potential drivers of these discrete magmatic episodes with different geochemical signatures remain controversial despite a vast amount of extant geochemical, geochronological and petrological data.
A major shortening event in the Triassic produced a NE-trending, ~1000 km wide fold-and-thrust belt (Fig. 1), which shows NW-younging ages for contractional structures (Faure et al. Reference Faure, Lin, Chu and Lepvrier2016; Li et al. Reference Li, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Dong, Koppers, Miggins, Sun, Wang and Xin2017, Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018, and references therein). Interpretations for the cause of this deformation include: (1) far-field stress effects of the collisions between the North and South China blocks in the Early Palaeozoic (Faure et al. Reference Faure, Lin, Monié and Meffre2008) or in the Late Triassic (Meng & Zhang, Reference Meng and Zhang1999); (2) the collision of the Indochina and South China blocks in the Early to Middle Triassic (Zhang & Cai, Reference Zhang and Cai2009; Xu et al. Reference Xu, Zhang, Shu and Jia2011; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Fan, Zhang and Zhang2013; Faure et al. Reference Faure, Lepvrier, Nguyen, Vu, Lin and Chen2014; Shu et al. Reference Shu, Wang, Cawood, Santosh and Xu2015; Qiu et al. Reference Qiu, Yan, Yang, Wang, Tang and Ariser2017); and (3) flat subduction along the active continental margin of East Asia (Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Sun, Shen, Shu and Niu2006; Li & Li, Reference Li and Li2007; JH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018; Tao et al. Reference Tao, Li, Danisik, Evans, Li, Pang, Li, Jourdan, Yu, Liu, Batt and Xu2019).
Extensional tectonic and magmatic features in SE China include normal fault systems, metamorphic core complexes, and volcanic–plutonic belts with diverse compositions and geochemical affinities (Figs 1, 2; LS Shu et al. Reference Shu, Wang, Sha, Jiang, Yu and Wang2009; Wang & Shu, Reference Wang and Shu2012; JH Li et al. Reference Li, Zhang, Dong and Johnston2014; J Li et al. Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016; Wei et al. Reference Wei, Song, Hou, Chen, Faure and Yan2018). The main interpretations and models for the origin of these magmatic suites and the extensional fault systems include: (1) post-collisional collapse of thick continental crust (Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Sun, Shen, Shu and Niu2006; Li & Li, Reference Li and Li2007); (2) large-scale aesthenospheric upwelling associated with the break-up of Gondwana ~190 Ma, leading to lithospheric thinning and magmatism between ~180 and 80 Ma (Wilde et al. Reference Wilde, Zhou, Nemchin and Sun2003; Wang et al. 2017); (3) an extended continental arc origin (e.g. Zhou & Li, Reference Zhou and Li2000); and (4) rollback of the subducting palaeo-Pacific plate and associated extensional deformation and magmatism in the continental upper plate (Li et al. Reference Li, Zhang, Dong and Johnston2014, and references therein). The post-orogenic collapse models are problematic because: (a) granitic plutons and their volcanic counterparts in E-SE China are much more extensive in their areal coverage beyond the collision zones (i.e. Qinling–Dabie, Sulu, Ailaoshan and Jiang Saho sutures and fault zones), and these plutonic–volcanic rocks are spatially and temporally associated with extensional tectonic features (see, for example, Shu et al. (Reference Shu, Wang, Sha, Jiang, Yu and Wang2009) and Wei et al. (Reference Wei, Song, Hou, Chen, Faure and Yan2018) for Jurassic, and Yang et al. (Reference Yang, Jiang, Jiang, Zhao and Fan2011), Zhao et al. (Reference Zhao, Yu, Jiang, Mao, Yu, Chen and Xing2019) and C Wang et al. (2017) for Cretaceous magmatic suites and related extensional tectonics); (b) their emplacement times are at least ~60–80 Ma after the collisional events, which represents a very large time window in comparison to an average timespan for the initiation of post-collisional magmatism in other Mesozoic and Cenozoic orogenic belts (for some examples, see Dilek & Moores, Reference Dilek and Moores1999; Dilek & Whitney, Reference Dilek, Whitney, Panayides, Xenophontos and Malpas2000; Dilek, Reference Dilek, Dilek and Pavlides2006; Dilek et al. Reference Dilek, Imamverdiyev and Altunkaynak2010; Jamali et al. Reference Jamali, Dilek, Daliran, Yaghubpur and Mehrabi2010); and (c) there is no viable explanation for the heat source to drive the lithospheric-scale magmatism. Significant variations in the geochemistry and melt origin of the plutonic and volcanic rocks do not support the second and third models above. The slab rollback model is still debatable because of the perceived problems with the timing of the onset of the palaeo-Pacific plate subduction beneath the continent, the nature of the slab dynamics (flat vs high-angle) and the apparent absence of a Jurassic–Cretaceous continental arc system in mainland SE China.
In this study, we investigate the Mesozoic structural architecture and magmatic record of Hainan Island in the South China Block, and the geochemical characteristics and melt evolution of its Triassic through Cretaceous granitoids. We show that the Mesozoic granitoids in Hainan display characteristic trends and patterns as a result of time-progressive evolution of their mantle melt sources and melt development through time that are highly similar to those of their counterparts in mainland SE China. Hence, we consider Hainan Island a microcosm of the Mesozoic geology of SE China. The Mesozoic Hainan granitoids provide a unique opportunity to evaluate the spatial and temporal relationships between magmatism and the regional tectonics. In the first part of the paper, we discuss the crustal architecture and geology of Hainan, specifically the Mesozoic granitoids and the spatially associated intrusive rocks. Next, we present our geochemical and isotopic data on the Mesozoic granitoids on Hainan in comparison to the available data from coeval and similar granitoids in SE China. We then discuss the structural architecture and magmatic make-up of Mesozoic SE China in order to evaluate the nature of the spatial and temporal relationships between the regional tectonics and magmatism through time. The following section on the crustal and mantle structure beneath modern SE China helps us better understand the extreme heterogeneity in the crustal make-up of the South China Block that was reworked significantly during the Mesozoic. This heterogeneous continental crust in SE China strongly influenced the melt evolution of the Cretaceous granitoids and their volcanic counterparts. In the last part of the paper we present our new geodynamic model and propose that a slab-driven tectonic mode switch (Lister & Foster, Reference Lister and Foster2009; Schellart et al. Reference Schellart, Stegman, Farrington, Freeman and Moresi2010) from push-over geodynamics in the Triassic – Early Jurassic to pull-away geodynamics in the later Jurassic–Cretaceous along the active margin of East Asia produced the contrasting tectonic regimes and styles in Mesozoic SE China. Our model differs from other existing tectonic switch models suggesting various external causes, and shows, instead, that changes in subducting slab widths, subduction velocities and the degree of coupling–decoupling between the lower and upper plates played a major role in driving tectonic mode switches during the Mesozoic evolution of SE China. We propose the late Cretaceous–Eocene tectonics of the Western US Cordillera as an analogue for the Mesozoic tectonics of SE China. We present this geodynamic model as a working hypothesis, which should be tested by future integrated studies in SE China.
2. Review of the regional geology of SE China
The regional geology of the South China Block displays two major suture zones along a NW–SE-oriented, lithospheric-scale tectonic profile (Fig. 2) that attest to its eastward growth via collisional events through time. These events are the Neoproterozoic amalgamation of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks (Charvet et al. Reference Charvet, Shu, Shi, Guo and Faure1996; Faure et al. Reference Faure, Shu, Wang, Charvet, Choulet and Monié2009; ZX Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Wu, Zhang, Fan, Zhang, Zhang, Peng and Yin2012; Shu et al. Reference Shu, Jahn, Charvet, Santosh, Wang, Xu and Jiang2014), and the 6.5 Ma collision of the Luzon volcanic arc of the Philippine Sea plate with the SE China Block (Byrne et al. Reference Byrne, Chan, Rau, Lu, Lee, Wang, Brown and Ryan2011; Van Avendonk et al. Reference Van Avendonk, McIntosh, Kuo-Chen, Lavier, Okaya, Wu, Wang, Lee and Liu2016; Chen et al. Reference Chen, Huang, Yan, Dilek, Chen, Wang, Zhang, Lan and Yu2017; Malavieille et al. 2020). In the opposite, NE–SW direction, the South China Block also underwent a series of collisional orogenic events as it sutured with the North China Block to the NE in the Late Triassic (Meng & Zhang, Reference Meng and Zhang1999) or perhaps earlier in the Palaeozoic (Faure et al. Reference Faure, Lin, Monié and Meffre2008), and with Indochina to the SW in the Early to Middle Triassic (Qiu et al. Reference Qiu, Yan, Yang, Wang, Tang and Ariser2017). Here, we consider the lithospheric-scale structures of the South China Block between its NW and SE tectonic boundaries against the Songpan Ganzi terrane to the NW and the arc–continent collision zone in Taiwan to the SE, because we are interested in observing the crustal structure and magmatic record of SE China in the general direction of its major crustal growth (Figs 1, 2).
The NE–SW-oriented Jiang Shao fault zone (JSF) marks the main tectonic boundary between the Cathaysia and Yangtze continental blocks, and the nearly 150–200 km wide Jiagnan orogenic belt to the west of this fault zone (Figs 1, 2) represents a protracted period of multiple oceanic plate subduction and island arc collision events between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks throughout the Proterozoic, prior to their final suturing (Li et al. Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016, and references therein). The Proterozoic basement rocks within this Jiagnan orogenic belt include metamorphosed granitoid intrusions, mafic–ultramafic rock sequences, pelitic rocks and flysch deposits. The structural fabric in the orogenic belt is characterized by W-NW-vergent thrust faults, which were largely reactivated as low-angle normal faults in the Cretaceous (Li et al. Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016). Superimposed on the Jiagnan orogeny were the Triassic Indosinian orogeny and a Middle–Late Jurassic contractional event in the Yangtze Block. Interpretations of the mechanics and the causes of the Indosinian orogeny are diverse. It is mainly interpreted as an intracontinental event that produced NW-directed thrust faulting and folding, greenschist metamorphism and alkaline magmatism (Lin et al. Reference Lin, Faure, Monié, Schärer and Panis2008; Shu et al. Reference Shu, Wang, Sha, Jiang, Yu and Wang2009; Zhang & Cai, Reference Zhang and Cai2009; XB Xu et al. Reference Xu, Zhang, Shu and Jia2011; Chu et al. Reference Chu, Faure, Lin, Wang and Ji2012), although alternative explanations invoking the continental collisions with the North China (Zhang & Cai, Reference Zhang and Cai2009) or Indochina blocks (Faure et al. Reference Faure, Lepvrier, Nguyen, Vu, Lin and Chen2014) have also been proposed. Carter & Clift (Reference Carter and Clift2008) have argued that the Indosinian orogeny was a reactivation event caused by the accretion of the Shibumasu Block to Indochina further south in Vietnam, rather than a major mountain-building episode between the Indochina and South China blocks.
To the west of the Jiagnan orogenic belt is the Middle Triassic Xuefeng Uplift (Fig. 2), which is characterized by NW-directed shortening (Ma et al. Reference Ma, Wang, Huang and Xie2019), NW–SE-oriented mineral lineation and NE–SW-trending folds. The timing of NW-directed thrusting, which involved the Proterozoic basement rocks and the Mesozoic metasedimentary rock sequences, was 243–226 Ma based on monazite dating of sheared micaschists (Chu et al. Reference Chu, Faure, Lin, Wang and Ji2012).
A Middle–Late Jurassic contractional event was responsible for the development of a broad fold-and-thrust belt (SE China Fold and Thrust Belt; Fig. 3) and décollement surfaces at depth (Yang & Yu, Reference Yang and Yu1994; Yan et al. Reference Yan, Zhou, Song, Wang and Malpas2003; Ding et al. Reference Ding, Guo, Liu and Zhai2007; Li et al. Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016). NE-trending folds were cross-cut by Late Jurassic granitic intrusions, indicating that folding and associated shortening must have developed in the Middle to Late Jurassic at the latest (Li et al. Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016). This event has been interpreted to have resulted from retroarc deformation above the palaeo-Pacific slab subducting beneath SE China (Li et al. Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016, and references therein).
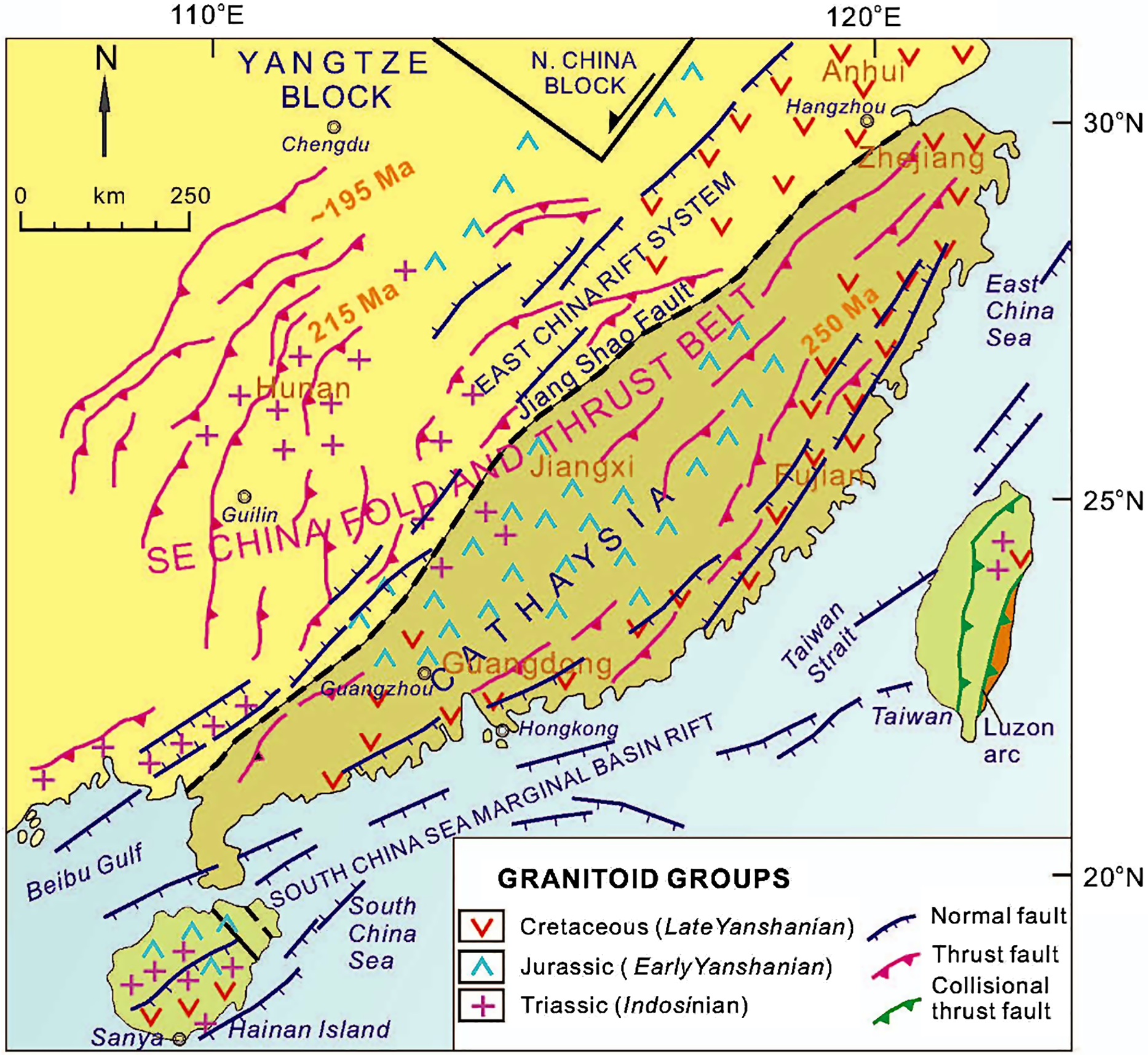
Fig 3. Simplified tectonic map of SE China, showing the distribution of major Mesozoic structural systems and granitoid groups. Data are from ZY Tian et al. (Reference Tian, Han and Xu1992), Yang & Yu (Reference Yang and Yu1994), Li (Reference Li2000), Xiao & He (Reference Xiao and He2005), Jiang et al. (Reference Jiang, Jiang, Zhao and Ling2006), Li et al. (Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016), Wei et al. (Reference Wei, Song, Hou, Chen, Faure and Yan2018) and Wang et al. (Reference Wang, Wang, Lia, Seagrenc, Zhang, Zhang and Qian2020).
The Yangtze Fold Zone (Fig. 1) to the west of the Xuefeng Uplift represents a long-wavelength crustal shortening zone, which is characterized by thin-skinned, NW-vergent imbricate faulting and folding, underlain by a regional-scale décollement structure (Main Yangtze Décollement), which shows a down-dip flat–ramp–flat geometry to the SE on seismic reflection profiles (Fig. 2; JH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018). This décollement zone separates the highly deformed (shortened) upper crust from the underlying, weakly deformed middle crust, and accommodates strain decoupling between the two crustal levels (Li et al. Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016). The occurrence of low-velocity reflectors between the middle and lower continental crust beneath the Yangtze Fold Zone may point to the existence of ductile shear zone or thin melt lenses at ~30 km depth (Li & van der Hilst, Reference Li and van der Hilst2010; Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Xie, Shen, Zheng, Yang, Shi and Ritzwoller2012; Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Wu, Gao, Fu, Sun, Wu and Ding2017). The intense crustal shortening structures within the Yangtze Fold Zone diminish abruptly towards the Sichuan Basin to the west (Fig. 2). Thus, the continental crust of the South China Block to the west of the Anhua–Xupu Fault (AXF) underwent significant shortening at upper and middle crustal depths during the Mesozoic.
The SE Yangtze and the entire Cathaysia block contain Middle to Late Jurassic plutons and their volcanic counterparts (Early Yanshanian episode; 165–153 Ma; Fig. 3), and Cretaceous plutons, bimodal volcanic rocks and clastic sedimentary sequences (Late Yanshanian episode; 145–87 Ma; Figs 2, 3). Different interpretations for the origins of the Early and Late Yanshanian magmatic episodes also exist (see Li, Reference Li2000, for an overview). We discuss the Jurassic–Cretaceous magmatism and extensional deformation in detail in the later parts of the paper. However, two important geological features regarding the Jurassic and Cretaceous tectonics of SE China are important to point out here: (1) In the published literature, the lack of an exposed Jurassic magmatic arc complex in SE China has always been interpreted against the palaeo-Pacific plate subduction beneath SE China during the early Mesozoic. However, recent drilling in the NE part of the South China Sea has recovered core samples of high-Mg diorite and granite rocks with ages between 198 and 195 Ma, representing calc-alkaline arc suites (CH Xu et al. Reference Xu, Zhang, Shi, Brix, Huhma, Chen, Zhang and Zhou2017). These Lower Jurassic calc-alkaline plutonic rocks have been interpreted to represent an Early Jurassic magmatic arc, which developed above a NW-dipping palaeo-Pacific oceanic slab (JH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018). The crystalline basement of the continental shelf in the northern South China Sea and the Taiwan Strait is thus likely to be composed of a subsided magmatic arc (Li et al. Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016; CH Xu et al. Reference Xu, Zhang, Shi, Brix, Huhma, Chen, Zhang and Zhou2017). (2) Strike-slip faulting and related deformation appear to have become increasingly important in SE China from the Late Jurassic through the Cretaceous. Palaeo-stress investigations in and around the Huangshan Basin in Anhui Province (south of the Yangtze River) have shown that a right-lateral strike-slip regime with nearly E–W compression and N–S extension predominated in the region from the late Middle Jurassic through the Late Jurassic (X Xu et al. Reference Xu, Tang and Lin2015). This stress regime was controlled by the subduction of the palaeo-Pacific slab beneath SE China. Then, a sinistral strike-slip regime with N–S compression and E–W extension predominated during the late Early Cretaceous, and it was induced by either the left-oblique subduction of the palaeo-Pacific slab or the oblique collision of the Philippine and SE China blocks in the Early Cretaceous (X Xu et al. Reference Xu, Tang and Lin2015). This left-lateral strike-slip tectonics in SE China played a significant role in the development of transtensional sedimentary basins in E and SE China (Y Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020, and references therein) and in the Korean Peninsula (DW Lee, Reference Lee1999) during the Late Cretaceous–Early Palaeogene, and then in the initial opening of the proto-South China Sea in the Palaeocene–Eocene (CY Huang et al. Reference Huang, Wang, Yu, You, Liu, Zhao, Shao, Zhong and Yumul2019).
3. Hainan Island: geological microcosm of Mesozoic SE China
3.a. Crustal architecture and geology of Hainan
Hainan Island is located in the continental shelf of southern China and adjacent to the Indochina Block in the west (Fig. 1). It is also tectonically situated within the NE–SW-trending South China Marginal Basin Rift System, which extends into the Taiwan Strait in the NE (Fig. 3). The basement rocks on Hainan are covered peripherally by Quaternary alluvium, and by Quaternary intra-plate basaltic lava flows in the northern part of the island (Fig. 4; Tian et al. Reference Tian, Yan, Huang, Dilek, Yu, Liu, Zhang and Zhang2020). Similar lava fields continue to the north on the Leizhou (Liuchow) Peninsula in mainland China, making up the Leiqiong volcanic field. The structural fabric of Hainan Island is defined mainly by NE–SW-oriented, oblique normal fault systems, forming locally well-developed horst blocks (Fig. 4). The inverted Baisha basin, which is composed of Cretaceous sedimentary and volcanic rock sequences in the west-central part of the island with a highest peak of 1417 m a.s.l., represents one of these fault blocks.
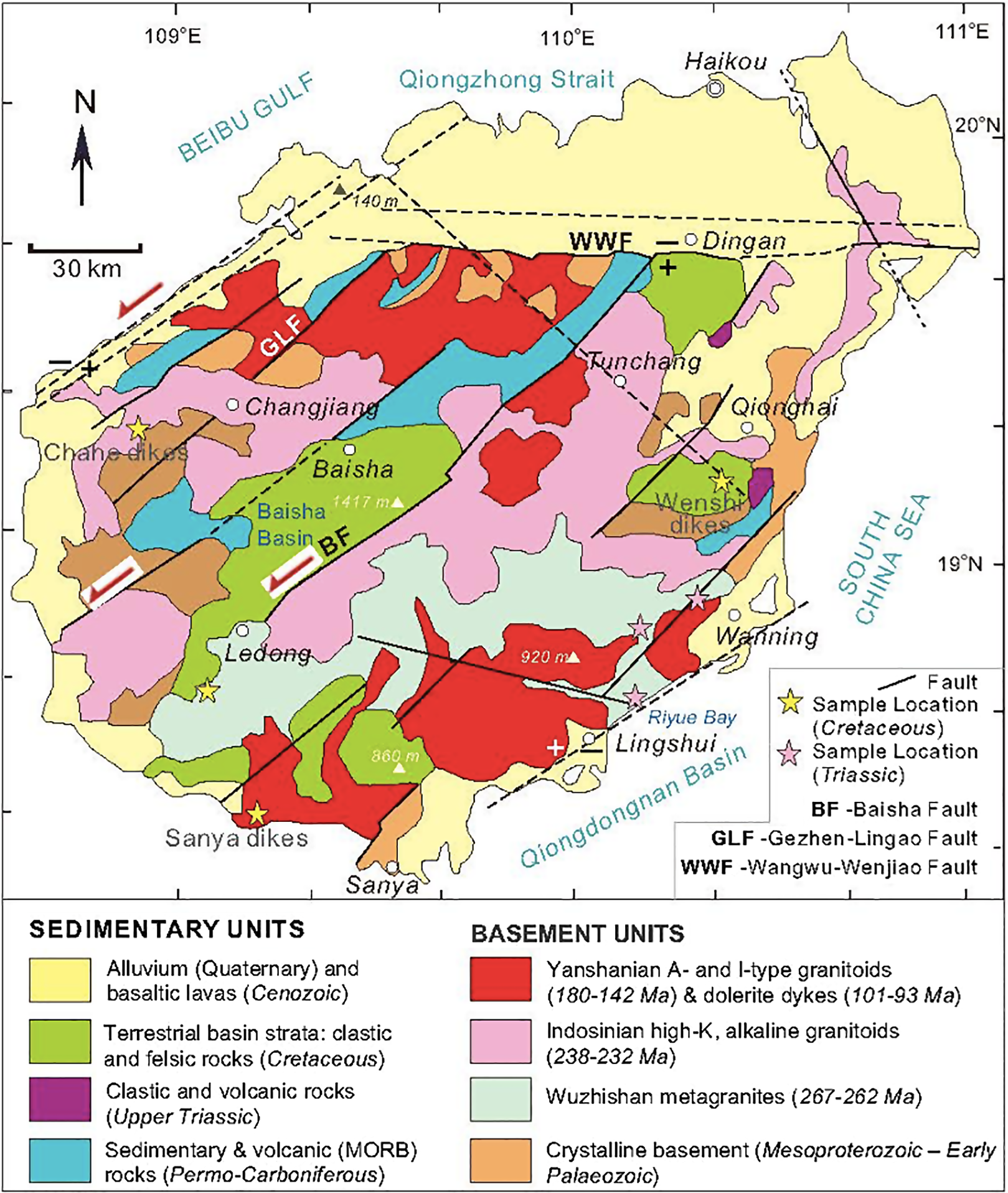
Fig 4. Geological map of Hainan Island, depicting the distribution of main fault systems, granitoid groups and sample locations for this study. Data are from XH Li et al. (Reference Li, Zhou, Chung, Ding, Liu, Lee, Ge, Zhang and Zhang2002), Ge, (Reference Ge2003), Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Li and Wang2006), Pedoja et al. (Reference Pedoja, Shen, Kershaw and Tang2008), Y Hu et al. (Reference Hu, Hao, Jia and Song2016), D Xu et al. (Reference Xu, Wang, Wu, Zhou, Shan, Hou, Fu and Zhang2017), Yao et al. (Reference Yao, Li, Li and Li2017), Tian et al. (Reference Tian, Yan, Huang, Dilek, Yu, Liu, Zhang and Zhang2020) and this study.
The crystalline basement in Hainan consists of metamorphosed Mesoproterozoic magmatic, volcanic and clastic rocks that are exposed mainly in the W-SW and E parts of the island (Fig. 4). Amphibolite-facies gneissic granitoids, gneiss and metaclastic rocks of the 1430 Ma Baoban Complex represent a Mesoproterozoic continental rift sequence (Yao et al. Reference Yao, Li, Li and Li2017). Greenschist-facies metasedimentary and metavolcanic rocks of the 1439 ± 9 Ma Shilu Group constitute the upper crustal volcanic–sedimentary units of this rift sequence (Yao et al. Reference Yao, Li, Li and Li2017). The unconformably overlying 1200–1000 Ma metamorphosed quartz–sandstones of the Shihuiding Formation make up foreland deposits. Metamorphosed Lower Palaeozoic sedimentary rocks are locally exposed both in the western and eastern parts of the island. These Mesoproterozoic crystalline and Lower Palaeozoic metasedimentary rocks are intruded by Permian (Wuzhishan), Triassic (Indosinian) and Jurassic–Cretaceous (Yanshanian) granitoids and are overlain by Lower and Upper Palaeozoic sedimentary–volcanic rock assemblages, and Upper Triassic clastic rocks (Fig. 4).
Permo-Carboniferous (333 Ma) metasedimentary and metavolcanic rocks with mid-ocean-ridge basalt (MORB) affinities in the west-central part of the island represent a major episode of continental rifting in its Palaeozoic tectonic history (Li et al. Reference Li, Zhou, Chung, Ding, Liu, Lee, Ge, Zhang and Zhang2002). Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Li and Wang2006) have demonstrated the occurrence of 267–262 Ma (Guadalupian), calc-alkaline metagranites (Wuzhishan orthogneiss) in east-central Hainan, which they have interpreted as the first major product of continental arc magmatism in SE China, developed above a NW-dipping subduction zone. These authors have also noted that this Permian, Andean-type arc magmatism was coeval with widespread crustal uplift along the coast of SE China that provided clastic sediments into terrestrial basins further inland. The timing of the Permian arc plutonism on Hainan is consistent with the findings of Zhang and co-workers in Anhui Province in SE China (FQ Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020) where Guadalupian (270–264 Ma) tuff deposits within the Gufeng Formation (Permian carbonate platform of SE China) represent the initial products of subaerial volcanism and magmatic arc construction in SE China during the Late Palaeozoic.
3.b. Mesozoic granitoids and associated intrusive rocks on Hainan
In this study, we have distinguished two major (early–Middle Triassic and Cretaceous) igneous events in the geological record of Hainan. Ge (Reference Ge2003) also reported the existence of Jurassic granitic intrusions (186 Ma) on Hainan Island. Triassic magmatic rocks include bimodal, high-K granites and hypabyssal dolerite, hornblende gabbro and syenite that are all alkaline to subalkaline in nature (Fig. 5). The distribution of these Triassic intrusions and their internal structural fabric are predominantly NE–SW oriented (Fig. 4). Contact relationships observed in the field suggest that the Xinglong granite intruded into the dolerite via magma stoping (Fig. 6a–c) and along extensional shear zones (Fig. 6d). These spatial relationships are best exposed below the river-bed dam in Dazhou Village, where irregular and anastomosing granite veins intrude the fine-grained dolerite and the larger outcrops of granite contain enclaves of dolerite. The dolerite rock is dark grey and displays an ophitic texture; it is composed mainly of plagioclase (70–60%), clinopyroxene (25–20%), amphibole (15–10%) and biotite (10–5%) (Fig. 7a). The Xinglong granite is red in both outcrop and hand sample and is coarse-grained. It is composed of plagioclase with microcline twinning (70–60%), quartz (25–20%), hornblende (10–5%) and biotite (10–5%) (Fig. 7b).
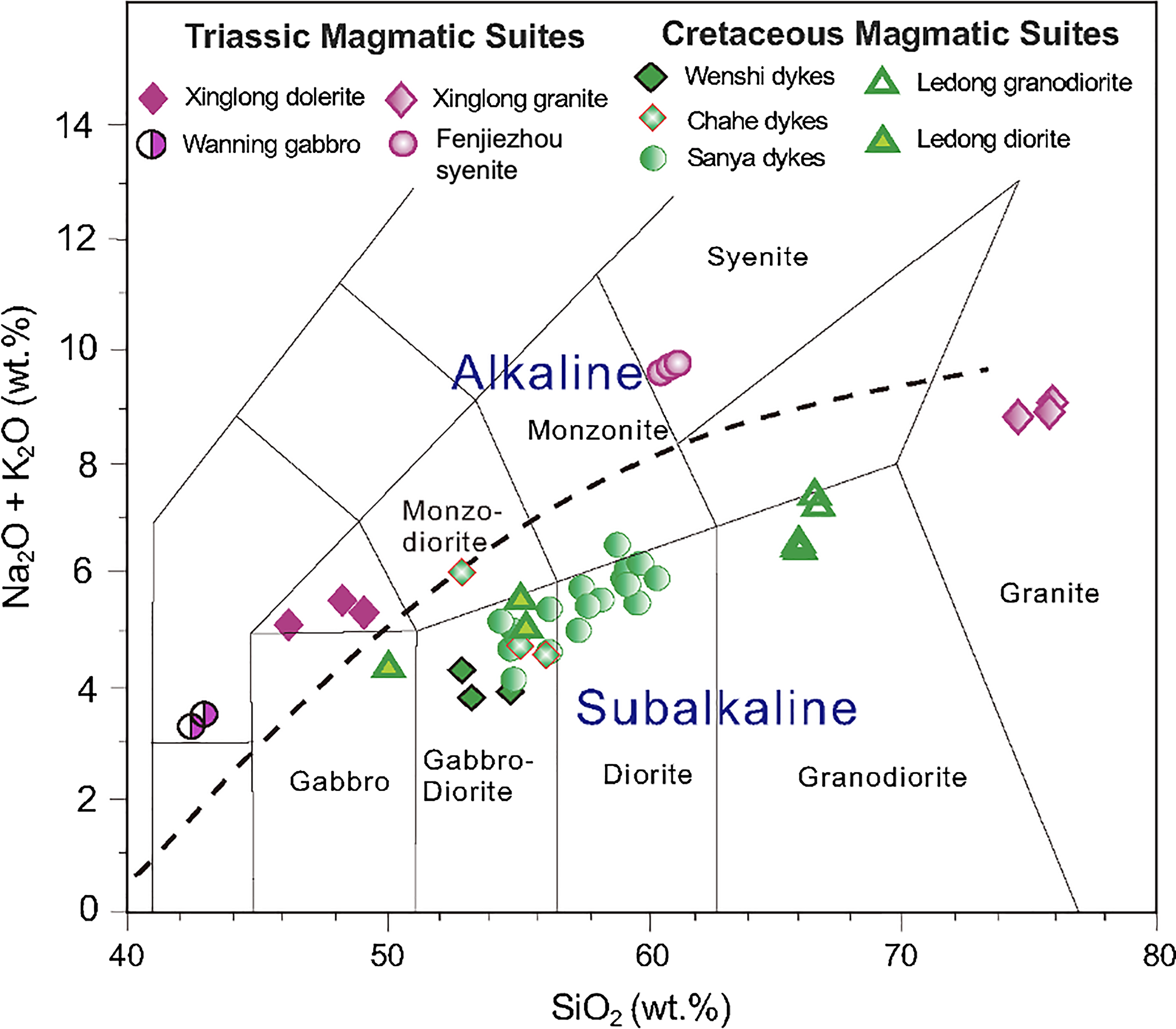
Fig 5. Total alkali vs SiO2 diagram for the Triassic and Cretaceous intrusive rock suites on Hainan Island (this study). FJZ = Fenjiezhou syenite. Alkaline–subalkaline boundary is from Le Bas et al. (Reference Le Bas, Le Maitre and Streckelsen1986).

Fig 6. Outcrop images of the primary intrusive relationships between the Triassic Xinglong granite and dolerite. (a–c) Xinglong granite is intrusive into the dolerite, forming jigsaw puzzle rafts of angular mafic rock pieces floating in the felsic rock, typical of magma stoping. (d) Syn-kinematic intrusion of the Xinglong granite along extensional shear zones in the dolerite.
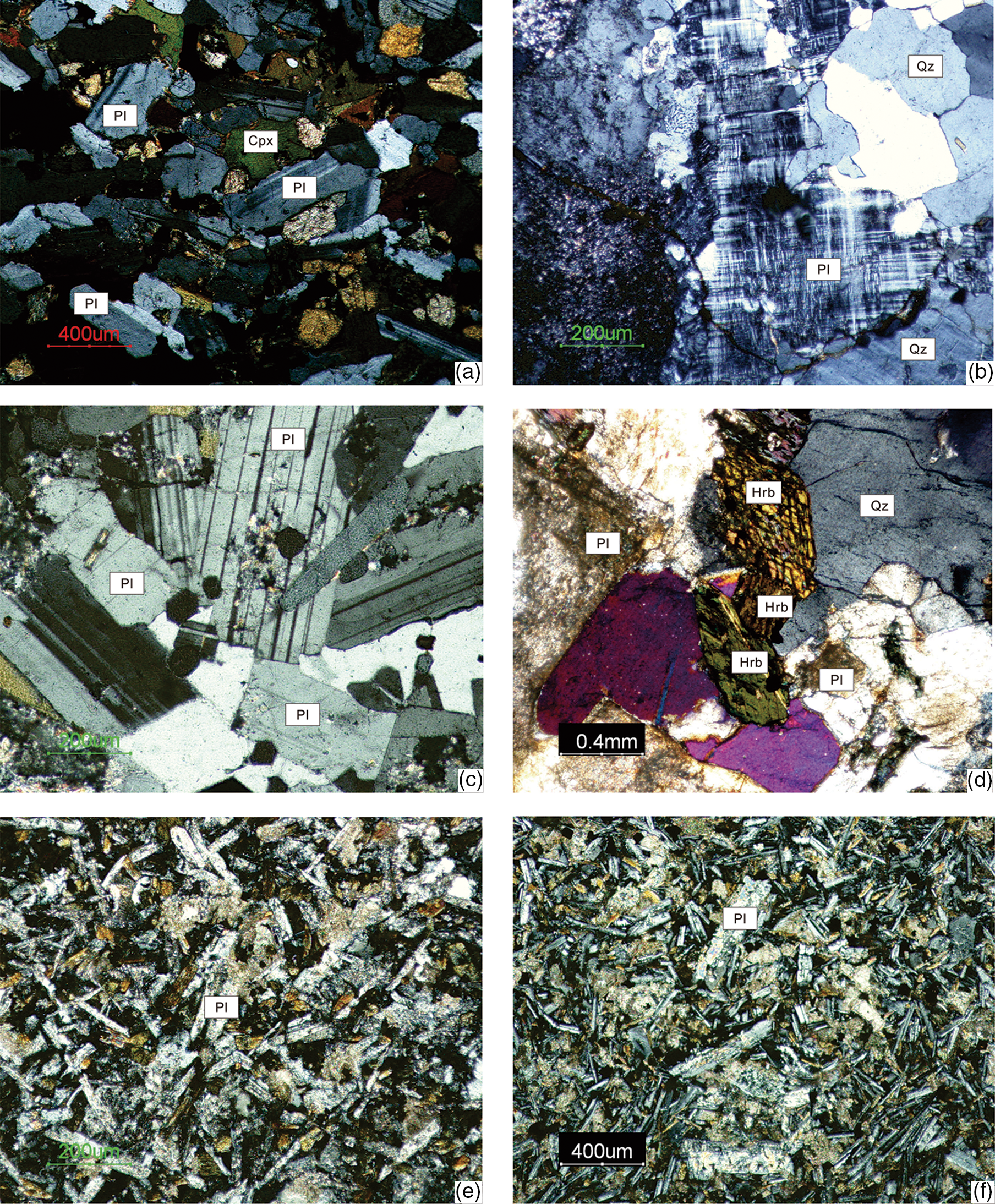
Fig 7. Microphotographs of representative samples from: (a) Xinglong dolerite; (b) Xinglong granite; (c) Wanning gabbro (coarse-grained) with euhedral to subhedral and prismatic plagioclase crystals with Carlsbad–albite twins; (d) Ledong diorite; (e) Wenshi dykes; (f) Sanya dykes. Key for acronyms: Cpx – clinopyroxene; Hrb – hornblende; Qz – quartz; Pl – plagioclase. See the text for descriptions of the mineralogy and textures of these rock samples.
The Wanning gabbro is exposed on the north side of the Wanning reservoir near Wanning City (Fig. 4) and is intrusive into ~251–234 Ma mylonitic gneissic granites. It is coarse-grained and composed predominantly of plagioclase (65–60%), hornblende (30–25%) and pyroxene (4–3%) (Fig. 7c). Accessory minerals include apatite, zircon and magnetite (2–1%). The Fenjiezhou syenite crops out on the small Fenjiezhou Island (or Boundary Island) in the Riyue Bay immediately to the SE of Hainan and is intrusive into Permo-Carboniferous metasedimentary rocks. It is composed of 75–70% feldspar, 10–5% albite, ~10% biotite and ~3% quartz.
Middle to Late Jurassic (180–142 Ma) granitoids (coexisting with minor dolerite, diorite and gabbro to syenite) and volcanic rock assemblages occur widely in NE–SW-trending belts in Hainan and SE China (Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010; Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Sun, Shen, Shu and Niu2006; Li & Li, Reference Li and Li2007). Jurassic granitoids have geochemical characteristics of I- and A-type granites, whereas the coeval syenites show incompatible trace-element patterns of ocean island basalt (OIB)-type melts (Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010; Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Sun, Shen, Shu and Niu2006). These Jurassic granite and syenite intrusions are spatially and temporally associated with alkaline basalts and bimodal (basalt–rhyolite) volcanic rocks (180–170 Ma).
Cretaceous magmatic rocks on Hainan occur as mainly NE–SW-striking doleritic dyke swarms in the Proterozoic metamorphic basement units and in the Triassic granitoids (Chahe dykes), in Lower Cretaceous sandstone-conglomerate units (Wenshi dykes) and in the Jurassic–Cretaceous granite suites (Sanya dykes) (Fig. 8). These dykes were intruded along NE–SW-oriented fault systems. Also part of the Cretaceous magmatic series is the Ledong diorite–granodiorite suite in the SW part of Hainan. Diorite occurs as enclaves within the granodiorite. The Chahe dykes occur in the west-central part of Hainan near the city of Changjiang, the Wenshi dykes occur in the east-central part near Wenshi Town in Qionghai City, and the Sanya dykes crop out along the Sanya City Highway in southern Hainan, west of the city of Sanya (Fig. 4). All dyke rocks are composed of dolerite with a diabasic texture and consist of plagioclase, pyroxene and hornblende with accessory minerals of apatite, zircon and magnetite (Fig. 7e–f).

Fig 8. Outcrop images of the Cretaceous Sanya dykes with their granitic host rock (Sanya granite) and the Cretaceous Wenshi dykes with their Cretaceous red sandstone host. Sanya dykes were emplaced along NE–SW-striking extensional fractures and fault systems that show consistently top-to-the west displacement and shearing.
3.c. Geochronology of Mesozoic intrusive rocks on Hainan
The hypabyssal dolerite and the Xinglong granite intrusions have U–Pb sensitive high-resolution microprobe (SHRIMP) zircon weighted mean 206Pb/238U concordia ages of 238 ± 2 Ma (MSDW = 0.69) and 234 ± 2 Ma (MSDW = 0.14), respectively (see Data Repository File #1 (in the Supplementary Material available online at https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016756820001211); Tang et al. Reference Tang, Chen, Dong, Yang, Shen, Cheng and Fu2013). SHRIMP zircon dating of the Wanning gabbro and Fenjiezhou syenite have weighted mean 206Pb/238U concordia ages of 240 ± 2 Ma and 231 ± 3.4 Ma, respectively (Tang et al. Reference Tang, Chen, Dong, Yang, Shen, Cheng and Fu2013). We interpret these ages as the timing of crystallization of the Wanning gabbro and hypabyssal dolerite, followed by the emplacement of the granite and syenite in the Middle to Late Triassic.
The dolerite dyke swarms display magmatic zircon ages between 101 ± 4 Ma and 93 ± 2 Ma (U–Pb SHRIMP dating), and inherited zircon ages of 238 ± 4 Ma and 237 ± 4 Ma (see Data Repository File #1 (in the Supplementary Material available online at https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016756820001211); Tang et al. Reference Tang, Chen, Dong, Yang, Shen, Cheng and Fu2013). Magmatic zircons represent the timing of a widespread NE–SW-dyking event in a regional, NW–SE-oriented extensional stress regime. Inherited zircon ages are identical to the ages of the Triassic dolerite and granite intrusions on Hainan, indicating that the Cretaceous magmas came up through these earlier-formed intrusive series. The Ledong granodiorite zircons have weighted mean 206Pb/238U concordia ages of 101 ± 0.9 Ma (see Data Repository File #1 (in the Supplementary Material available online at https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016756820001211); Tang et al. Reference Tang, Chen, Dong, Yang, Shen, Cheng and Fu2013), indicating contemporaneous emplacement of dolerite dykes and the Ledong granodiorite–diorite.
4. Geochemical and isotopic character of Mesozoic magmatic suites on Hainan and in SE China
The Mesozoic intrusive suites on Hainan are geochemically and isotopically distinct from each other, and the timing of their emplacement represents discrete tectonomagmatic episodes (Table 1). Triassic rock suites (Xinglong dolerite, Xinglong granite, Wanning gabbro and Fenjiezhou syenite) are predominantly alkaline in nature (Fig. 5). SiO2 contents of the Xinglong dolerite and granite show a bimodal distribution, ranging between 48.3 and 49.0 wt %, and 75.2 and 77.00 wt %, respectively. The Al2O3 content of the Xinglong dolerite is significantly higher than that of the Xinglong granite, and the alkali (Na2O + K2O) contents for both rock types are high (8.7–8.9 wt %). The Xinglong granite is high-K and has low rare earth elements (REE) concentration. It is strongly enriched in light REE (LREE), but weakly enriched in heavy REE (HREE) on a chondrite-normalized REE diagram (Fig. 9a). It also shows significant Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu* = 0.38–0.41) (Fig. 9a). On a MORB-normalized multi-element diagram, the Xinglong granite samples are characterized by enrichment in Y and Yb, and depletion in Sr, Ba, P and Ti (Fig. 9b). The Xinglong granite represents an I-type granite (Fig. 9). The slightly older, hypabyssal Xinlong doleritic rocks contain abundant amphibole, and are enriched in both LREE and large-ion lithophile elements (LILE; Rb, Ba, Th, K) (Fig. 9b). They are depleted in high-field strength elements (HFSE; Nb, Ta, Ti; Fig. 9b). The close association of these dolerite rock samples with the garnet–lherzolite melting curve on the Sm/Yb vs La/Yb and Sm/Yb vs La/Sm diagrams (Fig. 10) suggests that their magmas were derived from partial melting of lherzolitic peridotite of a continental mantle lithosphere in or near the garnet stability field. The slightly younger Fenjiezhou syenite (231 ± 3.4 Ma) is an A-type pluton, also showing LREE and LILE enrichments (Fig. 9a, b).
Table 1. Sr and Nd isotope ratios of the representative Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous intrusive suites in Hainan – SE China


Fig 9. (a) Chondrite–normalized REE diagram of representative Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous intrusions on Hainan and in SE China; (b) MORB–normalized multi–element diagram of representative Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous intrusions on Hainan and SE China. FJZ = Fenjiezhou syenite. Chondrite values are taken from Boynton (Reference Boynton and Henderson1984). MORB values are taken from Pearce (Reference Pearce and Thorpe1982, Reference Pearce, Hawkesworth and Norry1983). Data for the following intrusions are from Triassic Sheyang syenogranite (Zhu et al. Reference Zhu, Li, Xia, Xu, Wilde and Chen2017); Jurassic Chebu gabbro (He et al. Reference He, Xu and Niu2010; XH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010), Zhaibei granite (XH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010), Quannan syenite (XH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010) and Tabei syenite (XH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010); Cretaceous Jinjiang dykes (Z Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012), Yuebei dykes (Qi et al. Reference Qi, Hu, Liu, Coulson, Qi, Tian, Feng and Wang2012) and Matou monzogranite (Liu et al. Reference Liu, Qiu, Zhao and Yang2014).

Fig 10. (a) Plot of the Sm/Yb vs La/Yb compositional variations of the Xinlong dolerite and Wanning gabbro. Melting curves are from Xu et al. (Reference Xu, Ma, Frey, Feigenson and Liu2005); (b) plot of the Sm/Yb vs La/Sm compositional variations of the Xinlong dolerite and Wanning gabbro. Melting curves are from Aldanmaz et al. (Reference Aldanmaz, Pearce, Thirlwall and Mitchell2000). DMM = depleted MORB mantle, E-MORB = enriched mantle, N-MORB = normal MORB, PM = primitive mantle, WAM = Western Anatolian mantle, gt = garnet, sp = spinel. Ticks on the melting curves indicate the same percentages of melt fractions.
Cretaceous dykes and the coeval Ledong granodiorite are sub-alkaline in nature (Fig. 5), amphibole-rich (Fig. 7d) and show significant enrichment in LREE and LILE (Sr, K, Rb, Ba, Th) and depletion in HFSE in both chondrite-normalized and MORB-normalized multi-element diagrams (Fig. 9). We have plotted the Cretaceous Jinjiang and Yuebei dykes and the Cretaceous Matou monzogranite from mainland China on the chondrite-normalized and MORB-normalized multi-element diagram for comparison (Fig. 9a); these Cretaceous intrusive suites from SE China and our samples of the Cretaceous dyke swarms on Hainan display similar LREE and LILE enrichment patterns. These geochemical features are characteristic of magmas derived from partial melting of subduction-modified peridotites (Ulmer, Reference Ulmer2001).
Initial 87Sr /86Sr vus 143Nd/144Nd isotopic values of the representative rock suites (Fig. 11) show a well-defined pattern of a time-progressive evolution of melt sources from a highly enriched EMII-type mantle (for the Triassic magmatic series) toward a sub-arc type mantle field (for the Cretaceous dyke intrusions). Triassic granite–dolerite and gabbro–syenite rocks plot close to the EMII field, whereas the Jurassic gabbros and Cretaceous granitic plutons and dolerite–microgabbro dyke swarms plot within the sub-arc mantle field (Fig. 11). This trend reflects the geochemical evolution of the subduction-conditioned, subcontinental lithospheric mantle (SCLM) beneath SE China throughout the Mesozoic (Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Liang, Kröner, Cai, Shao, Wen, Jiang, Fu, Wang and Dong2015). Similar SCLM metasomatism and geochemical evolution patterns have also been documented from Mesozoic E-NE China (Liu et al. Reference Liu, Zou, Hu, Zhao and Feng2006; Zheng et al. Reference Zheng, Xu, Zhao and Dai2018, and references therein; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Li, Schertl and Feng2019).

Fig 11. Initial 87Sr/86Sr vs 143Nd/144Nd isotope diagram for the representative Mesozoic intrusive suites on Hainan and in SE China. BSE – bulk silicate earth; CA – calc-alkaline field; DM – depleted mantle; EMI – enriched mantle I; EMII – enriched mantle II; HIMU – high (238U/204Pb) mantle; LCC – lower continental crust; MORB – mid-ocean ridge basalt. Approximate fields of mantle reservoirs and MORB are from Zindler & Hart (Reference Zindler and Hart1986); the LCC are from Escrig et al. (Reference Escrig, Capmas, Dupre’ and Allegre2004).
5. Structural architecture and magmatic make-up of Mesozoic SE China
Figure 12 summarizes the Mesozoic regional geology, geochemical affinity and tectonic settings of magmatism on Hainan and in SE China. Also depicted in this diagram are the tectonostratigraphy and structural architecture of the Mesozoic sedimentary and volcanic rock sequences. The regional geology patterns and tectonostratigraphic units show a major change from contraction to extension in the Middle Mesozoic, attended by magmatism with different geochemical signatures.

Fig 12. Tectonostratigraphy, regional geology, structural architecture, geochemical affinity – isotopic signatures, and the inferred tectonic settings of Mesozoic tectonomagmatic suites on Hainan and in SE China. Interpreted melt sources and evolution patterns are also shown. Data for the Triassic geology and magmatism are from Li (2002), Xiao & He (Reference Xiao and He2005), Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Li and Wang2006), Li & Li (Reference Li and Li2007), Hu et al. (Reference Hu, Cawood, Du, Xu, Wang, Wang, Ma and Xu2017), Yao et al. (Reference Yao, Li, Li and Li2017) and this study. Data for the Jurassic geology and magmatism are from Ge (Reference Ge2003), TF Yiu et al. (Reference Yiu, Chu, Suga, Lan, Chung, Wang and Grove2017), Li et al. (Reference Li, Chen, Liu and Li2003), Jiang et al. (Reference Jiang, Jiang, Zhao and Ling2006), Zhou et al. (Reference Zhou, Sun, Shen, Shu and Niu2006), XH Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010), Guo et al. (Reference Guo, Chen, Zeng and Lou2012a, b), Yao et al. (Reference Yao, Li, Li and Li2017), Wei et al. (Reference Wei, Song, Hou, Chen, Faure and Yan2018), Ma et al. (Reference Ma, Wang, Huang and Xie2019), and this study. Data for the Cretaceous geology and magmatism are from Lapierre et al. (Reference Lapierre, Jahn, Charvet and Yu1997), Li (Reference Li2000), Guo et al. (Reference Guo, Chen, Zeng and Lou2012a, b), JH Li et al. (Reference Li, Zhang, Dong and Johnston2014), YZ Yang et al. (Reference Yang, Wang, Ye, Li, He, Siebel and Chen2017), Wang et al. (Reference Wang, Zhao, Huang, Xing and Wang2018), Gao et al. (Reference Gao, Wang, Tan and Li2019b), Tao et al. (Reference Tao, Pan, Liu, Jin, Jia and He2020), D Xu et al. (Reference Xu, Wang, Wu, Zhou, Shan, Hou, Fu and Zhang2017), Wang et al. (Reference Wang, Wang, Lia, Seagrenc, Zhang, Zhang and Qian2020) and this study.
5.a. Triassic geology and magmatism
Lower Triassic shallow marine rocks rest unconformably on the Permo-Carboniferous sedimentary and volcanic units. In the Zhejiang region, for example, the Lower Triassic Changxing Formation includes black bioclastic limestones with graded-bedding and cross-bedding features, characteristic of high-energy, shallow marine deposits, and the Lower Triassic Zhengtang Formation further south consists of clastic and carbonaceous turbiditic sequences; collectively, these two formations represent shelf-break and continental slope deposits, and are deformed by NW-vergent folds and thrust faults (Xiao & He, Reference Xiao and He2005; Chu et al. Reference Chu, Faure, Lin, Wang and Ji2012). These deformed Lower Triassic rocks are unconformably overlain by Upper Triassic lacustrine and terrestrial rocks that are interpreted as foreland basin (Li & Li, Reference Li and Li2007) or molasse deposits (Xiao & He, Reference Xiao and He2005).
Triassic sedimentary strata and some of the NW-vergent thrust faults are cross-cut by high-K, I-type granitoid, gabbro, syenite and hypabyssal dolerite intrusions (Fig. 12a). The negative ε Nd(T) values (−5.90 to −3.86) of the granite and dolerite rocks suggest partial melting of an enriched mantle source (EMII), accompanied by high-T crustal melting for the origin of their magmas (Fig. 11). Granitoid plutons and thrust faults become younger to the NW (249 to 217 Ma; Fig. 3), in the direction of thrusting, as documented by U–Pb zircon SHRIMP and 40Ar/39Ar mica ages of representative rocks (for a comprehensive age data table, see the data repository Files in Li & Li, Reference Li and Li2007). This early Mesozoic regional structure is known as the SE China Fold and Thrust Belt (Fig. 3; Xiao & He, Reference Xiao and He2005).
5.b. Jurassic geology and magmatism
Jurassic volcanic and sedimentary rock sequences in SE China rest unconformably on the folded–faulted Triassic foreland basin strata and deformed granitoids (Fig. 12b) or on the deformed Devonian to Carboniferous siliciclastic rock assemblages. The Jurassic magmatism produced A- and I-type granitoids, alkaline granites and syenites with minor gabbro, diorite, dolerite and lamprophyre dyke intrusions, which were emplaced along NE–SW-trending extensional fault systems (YH Jiang et al. Reference Jiang, Jiang, Zhao and Ling2006; XM Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Sun, Shen, Shu and Niu2006; C Guo et al. Reference Guo, Chen, Zeng and Lou2012; Quelhas et al. Reference Quelhas, Mata and Dias2020). These plutons locally intruded into thick sequences of basaltic, dacitic, rhyolitic volcanic rocks and alkaline basalts, which were also erupted within NE–SW-oriented grabens (Fig. 12b; Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010; C Guo et al. Reference Guo, Chen, Zeng and Lou2012; Wei et al. Reference Wei, Song, Hou, Chen, Faure and Yan2018). The Jurassic magmatism was hence associated with extensional deformation in a ~400 km wide belt, characterized by a Basin and Range-type crustal structure, which included lacustrine–playa lake deposits, evaporites and alluvial fan systems interspersed with bimodal volcanic sequences (see Wang & Shu (Reference Wang and Shu2012), and references therein, for an overview of the distribution of Mesozoic metamorphic core complexes in SE China, and Ni et al. (Reference Ni, Liu, Tang, Yang, Xia and Guo2013) for the occurrence of a metamorphic core complex in E China).
Jurassic granites have a relatively wide range of ε Nd(T) values (−6.55 to −0.78) and are geochemically similar to A-type granites (Fig. 11). However, geochemical compositions and isotopic fingerprints of these A-type granites display major differences, which appear to have resulted from isotopically distinct crustal domains within the South China Block, particularly in Cathaysia (Quelhas et al. Reference Quelhas, Mata and Dias2020). Syenites have high K contents (shoshonitic) and a large range of Nd–Sr isotopic compositions (ε Nd(T) = −3.54 to +3.44). Gabbros are geochemically analogous to intraplate transitional basaltic rocks and display a narrow range of ε Nd(T) values (−0.8 to +0.55). These geochemical and isotopic features suggest that magmas of the gabbros and syenites were derived from partial melting of a continental lithospheric mantle, which was modified by OIB-type (aesthenospheric) melts (Jiang et al. Reference Jiang, Jiang, Zhao and Ling2006), whereas the granites were produced by magmas that formed from partial melting of hornblende-bearing crustal rocks (Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Wartho, Clark, Li, Zhang and Bao2010; Yao et al. Reference Yao, Li, Li and Li2017; Quelhas et al. Reference Quelhas, Mata and Dias2020).
5.c. Cretaceous geology and magmatism
Cretaceous plutonic and volcanic rocks occur in a NE–SW-trending belt (Figs 2, 3). Granites and rhyolites within a 300 km wide zone adjacent to the modern coastline form coeval, felsic intrusive and extrusive assemblages with a minor occurrence of gabbros and basalts. Dominantly composed of high-K, I-type and A-type granites, the Cretaceous granitoids in SE China were emplaced in multiple episodes within discrete time windows (Li, Reference Li2000; XY Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Huang, Wang, Yu, Cao and Xie2019; X Zhao et al. Reference Zhao, Yu, Jiang, Mao, Yu, Chen and Xing2019). The 146–136 Ma and 132–123 Ma granites were intruded in southern Anhui, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and northern Jiangxi provinces (Gao et al. Reference Gao, Wang, Tan and Li2019b), whereas the 109–101 Ma high-K, calc-alkaline I-type granites were emplaced near the modern coastline of SE China (Z Li et al. Reference Li, Qiu and Xu2012). The younger, 97–87 Ma calc-alkaline I-type granites and some A-type granites were emplaced in coastal Fujian and eastern Taiwan (Li, Reference Li2000; X Zhao et al. Reference Zhao, Yu, Jiang, Mao, Yu, Chen and Xing2019). Cretaceous granites in Fujian, Guangdong and Zhejiang provinces that are closer to the present coastline are spatially associated with monzogranite, biotite granite, hornblende gabbro and syenite, and have I-type geochemical characteristics with enrichment in LREE and LILE, and relative depletion in HFSE (Fig. 9; Lapierre et al. Reference Lapierre, Jahn, Charvet and Yu1997; Guo et al. Reference Guo, Chen, Zeng and Lou2012a, b; Z Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012; Tao et al. Reference Tao, Pan, Liu, Jin, Jia and He2020). These rocks have a relatively narrow and homogeneous Sr–Nd isotopic compositional range, showing small negative ε Nd(T) values (−4.1 to −2.2) (Fig. 12c).
Cretaceous granitoids (132–123 Ma and 117 Ma) further inland in Hunan Province are high-K, calc-alkaline and weakly to strongly peraluminous in character, represented by two-mica or biotite monzogranites and minor granitoids. They display LREE enrichments and negative Ba, Sr, N, P and Ti anomalies, indicating strong subduction influence in their melt evolution (Ji et al. Reference Ji, Lin, Faure, Chen, Chu and Xue2017). Their negative zircon ε Hf(t) values (−12.5 to −3.6) and crustal Hf model (TDM) ages (1.4–2.0 Ga), combined with other geochemical features are interpreted to indicate partial melting of Neoproterozoic metapelitic rocks of the South China Block as their magma source (Ji et al. Reference Ji, Lin, Faure, Chen, Chu and Xue2017). Further to the E-NE in Jiangxi and Anhui provinces the Early Cretaceous granitoid plutons (i.e. Lingshan pluton in the Gan-Hang belt and Huayuan-gong granitoids in the Lower Yangtze River Belt) display A-type geochemical affinities with metaluminous to weakly peraluminous compositions, enriched Hf isotope ratios of zircon and a large range of high Y/Nb ratios (Yang et al. Reference Yang, Wang, Ye, Li, He, Siebel and Chen2017; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Zhao, Huang, Xing and Wang2018). Magmas of these A-type plutons were derived from mixing of aesthenospheric melts with magmas originated from partial melting of sedimentary rocks of a Mesoproterozoic crystalline basement (Yang et al. Reference Yang, Wang, Ye, Li, He, Siebel and Chen2017; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Zhao, Huang, Xing and Wang2018).
Cretaceous volcanic rocks near the coastal regions in SE China fall into two broad time intervals. The 143–124 Ma, acidic- to intermediate-composition volcanic rocks show variable enrichment in K, Rb, Ba, Th and Ce, and negative Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf and Yb anomalies. Geochemically, these volcanic rocks are similar to the age-equivalent, first and second episode, I-type granitic plutons in the region. This phase of volcanism in SE China also coincided with extensive ignimbrite flare-up episodes and with the formations of nested caldera complexes above large, overlapping silicic magma chambers near the modern shorelines in SE China (for example, in Fujian (Qiu et al. Reference Qiu, Wang and Zhou1999); in Western Guangdong (Geng et al. Reference Geng, Xu, O’Reilly, Zhao and Sun2006); in Jiangxi (Yang et al. Reference Yang, Jiang, Jiang, Zhao and Fan2011); and in Hong Kong (Sewell et al. Reference Sewell, Tang and Campbell2012)). Thus, it appears that the Early Yanshanian magmatic phase in SE China culminated in a ‘surge of pulsed supereruptions’ during the latest Jurassic – Early Cretaceous (Sewell et al. Reference Sewell, Tang and Campbell2012, p. 15), reminiscent in scale of the Yellowstone Caldera collapses in the Western USA during the Quaternary (Vazquez & Reid, Reference Vazquez and Reid2002). The 97–88 Ma bimodal volcanic rock suites exhibit significant negative Nb anomalies and negative ε Nd(T) values, suggesting that their magmas were derived from partial melting of an enriched lithospheric mantle source (Li, Reference Li2000; XY Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018).
Cretaceous volcanic rocks occurring further inland from the coastal regions are composed of tholeiitic and OIB-type basalts and minor alkaline rhyolites (YM Wu et al. Reference Wu, Guo, Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Alemayehu and Wang2020), interlayered with red sandstone, siltstone and mudstone, all deposited in NE–SW-oriented normal fault-bounded basins (Lapierre et al. Reference Lapierre, Jahn, Charvet and Yu1997; Y Wang et al. Reference Wang, Wang, Lia, Seagrenc, Zhang, Zhang and Qian2020). The geochemical and isotopic nature of these tholeiitic basalts suggests that their magmas were derived from a combination of aesthenospheric decompression melting and low-pressure, lower crustal melting in a continental setting (Fig. 12c). The 90 Ma Ji’an basalts in central Jiangxi Province have OIB-like geochemical signatures and display Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf isotopic compositions characteristic of a depleted aesthenospheric mantle, which was enriched by melts derived from dehydration of a subducted oceanic crust (Wu et al. Reference Wu, Guo, Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Alemayehu and Wang2020).
Syn-volcanic Cretaceous sedimentary rocks represent fluvial to lacustrine deposits, formed in a broad intracontinental rift system. This regional extensional structure represents the East China Rift System (Fig. 3; Tian et al. Reference Tian, Han and Xu1992). Cretaceous plutonic rocks and their volcanic counterparts within the East China Rift System represent the products of magmas, which were derived from partial melting of a subduction-metasomatized SCLM and which were variously affected by crustal contamination. NE–SW-running 101–93 Ma doleritic dyke swarms on Hainan reflect a discrete pulse of hypabyssal mafic magmatism during the Late Cretaceous, consistent with the geometry and kinematic evolution of the East China Rift System. Cretaceous mafic dyke intrusions with a predominant NE–SW orientation and age clusters of ~140 Ma, ~105 Ma and ~90 Ma also occur in Guangdong and Fujian, and display tholeiitic geochemical affinities (Li & McCulloch, 1998). These extensive NE–SW-striking doleritic dyke swarms near the coastal areas and the NE–SW-running East China Rift System point to a NW–SE-oriented tensile stress regime and the associated extensional deformation phase in SE China during the Cretaceous.
In summary, rifting, crustal subsidence, extensional doming and exhumation were widespread in the South China Block, particularly within Cathaysia during the Cretaceous (Figs 2, 3). The timing of the NW–SE-directed extension in Cathaysia has been constrained as 136–80 Ma based on thermochronological studies (Li, Reference Li2000; Zhou & Li, Reference Zhou and Li2000; Li et al. Reference Li, Zhang, Dong and Johnston2014). The results of these studies also indicate that the Cretaceous extensional tectonics and its attendant magmatism in Cathaysia migrated to the SE (oceanward in the present coordinate system) through time (Li, Reference Li2000; Li J et al. Reference Li, Zhang, Dong and Johnston2014, Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016; Yang et al. Reference Yang, Wang, Ye, Li, He, Siebel and Chen2017; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Zhao, Huang, Xing and Wang2018, Reference Wang, Wang, Lia, Seagrenc, Zhang, Zhang and Qian2020).
6. Crustal and mantle structure beneath modern SE China
The crustal make-up and architecture of SE China display major differences from north to south across the Jiang Shao Fault between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks (Figs 2, 3) and also from west to east within Cathaysia, as determined by combined gravity, P- and S-wave velocity, magnetotelluric, mass density and heat flow measurements (Ai et al. Reference Ai, Chen, Zeng, Hong and Ye2007; Lin et al. Reference Lin, Xing, Davis, Yin, Wu, Li, Jiang and Chen2018; YF Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Wang, Zhao and Jin2016; Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020). The results of recent geophysical studies have shown that both the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks consist of multiple accreted continental and oceanic terranes with significantly different lithologies and ages (Lin et al. Reference Lin, Xing, Davis, Yin, Wu, Li, Jiang and Chen2018; Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020). The Yangtze Block has an Archaean–Palaeoproterozoic crystalline basement and a Neoproterozoic fold-and-thrust belt in the SE (Jiangnan belt) that is widely interpreted to mark a collisional event (Li et al. Reference Li, Dong, Zhang, Zhao, Johnston, Cui and Xin2016). The Jiang Shao fault zone (Fig. 3) represents the tectonic boundary between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks. Cathaysia consists of West and East Cathaysia blocks, separated by a Mesozoic strike-slip shear zone (Lin et al. Reference Lin, Xing, Davis, Yin, Wu, Li, Jiang and Chen2018). The West Cathaysia Block has no cratonic basement and consists mainly of Neoproterozoic arc–back-arc ophiolites (according to the ophiolite classification scheme of Dilek & Furnes, Reference Dilek and Furnes2009, Reference Dilek and Furnes2011, Reference Dilek and Furnes2014) and metamorphic rocks, whereas the East Cathaysia Block has a cratonic basement and consists of Palaeoproterozoic metapelites, metaplutonic rocks, felsic metavolcanic rocks and migmatites (Lin et al. Reference Lin, Xing, Davis, Yin, Wu, Li, Jiang and Chen2018; K Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020). East Cathaysia also displays, in its SE part by the coast, widespread conductive anomaly and large depth-integrated conductance (K Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020), which points to high heat flow coinciding spatially with the distribution of Cretaceous mafic rocks.
The upper and middle crust in the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks are made of granite–granodiorite, bioite gneiss and granite gneiss (Zhao et al. Reference Zhao, Bai, Xu, Zhang and Badal2013). The lower crust in the Yangtze Block consists of biotite gneiss, monzonite gneiss, migmatite, paragranulite and amphibolite, whereas in the Cathaysia Block it is composed mainly of diorite, amphibolite, metabasalt, as well as metarhyolite, mica quartz schist and paragranulite (He et al. Reference He, Dong, Santosh and Chen2013; Zhao et al. Reference Zhao, Bai, Xu, Zhang and Badal2013; Stern et al. Reference Stern, Li and Keller2018; Gao et al. Reference Gao, Wang, Li and Tan2019a). The Cathaysian crust shows abrupt lateral and vertical variations in lithological units and structures, as observed on seismic profiles and magnetotelluric profiles, that most likely resulted from significant deformation and magmatic reworking, in addition to its accretionary history involving different lithospheric blocks (B Zhao et al. Reference Zhao, Bai, Xu, Zhang and Badal2013; L Zhao et al. Reference Zhao, Zhai, Zhou, Santosh and Ma2015). The average crustal thickness in Fujian Province in SE Cathaysia is ~31 km, and the Moho depth shallows gradually towards the northern South China Sea border (Zhang & Wang, Reference Zhang and Wang2007). The entire lithospheric thickness beneath SE China thins towards the South China Sea (Dong et al. Reference Dong, Wu, Zhang, Xu, Gao and Song2018), with the lithosphere–aesthenosphere boundary located at a depth of 60 to 70 km (Q Li et al. Reference Li, Gao, Wu, Guan, Ye, Liu, Hao, He, Li and Shen2013). Studies of mantle xenoliths recovered from the Cenozoic Xinchang basalts (Zhejiang Province) and Mingxi basalts (Fujian Province) in SE Cathaysia have shown that the Precambrian lithospheric mantle beneath this region was removed and replaced by hotter, younger and fertile mantle during the late Mesozoic lithospheric extension (CZ Liu et al. Reference Liu, Wu, Sun, Chu and Qiu2012, Reference Liu, Zhang, Liu, Sun, Chu, Qiu and Wu2017). This new lithospheric mantle was significantly modified by subduction–related metasomatic processes and upwelling asthenosphere in the latest Mesozoic (Y Xiao et al. Reference Xiao, Zhang, Su, Liang, Zhu and Sakyi2019).
Seismic tomography studies in SE China have shown high Vp–Vs anomalies and low Vp/Vs ratios in the mantle transition zone (MTZ) beneath the Yangtze Block, but low velocity anomalies (particularly very low Vs velocities) and high Vp/Vs ratios in the MTZ beneath the Cathaysia Block (Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Wang, Zhao and Jin2016). The large Vs anomalies in the Cathaysia MTZ may point to the existence of lower-viscosity partial melting products in the upper mantle of Cathaysia (Fig. 2); the high Vp–Vs anomalies in and across the MTZ of the Yangtze Block are likely to point to the existence of a cold slab (proto-Pacific ?) beneath Yangtze (Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Wang, Zhao and Jin2016). Seismic tomographic data also reveal that there are no detectable anomalies, signalling the existence of a subducted/accreted oceanic plateau or continental fragment beneath SE China (Li & van der Hilst, Reference Li and van der Hilst2010; Li et al. Reference Li, Gao, Wu, Guan, Ye, Liu, Hao, He, Li and Shen2013; Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Wang, Zhao and Jin2016).
Based on these crustal and mantle features of the Yangtze and Cathaysia continental blocks, we can make two major deductions: (1) towards the coastal areas in SE China and particularly in SE Cathaysia, depth to the aesthenosphere becomes shallow beneath the continental lithosphere as a result of significant lithospheric thinning and mantle upwelling in the Late Mesozoic. Furthermore, the continental crust becomes more mafic and magmatically reworked, as observed on magnetotelluric and seismic profiles (Zhao et al. Reference Zhao, Bai, Xu, Zhang and Badal2013; K Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020). Therefore, it appears that the continental lithosphere of SE China was significantly attenuated by the end of the Cretaceous; (2) the continental margin of SE China did not experience accretion of a large oceanic plateau or a microcontinent in the Mesozoic.
7. Geodynamic model
One of the fundamental questions about the Mesozoic tectonics of East Asia is when the subduction of the palaeo-Pacific oceanic plate beneath the Asian continent began. Although previous studies have suggested early Jurassic or later timing of this event, most recent geochemical, geochronological and structural investigations in NE and SE China show that onset of an active margin tectonics and the initiation of subduction of the palaeo-Pacific oceanic lithosphere beneath East China were under way by the early Triassic (Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Cao, Wilde, Zhao, Zhang and Wang2014; Sun et al. Reference Sun, Xu, Wilde, Chen and Yang2015; K Liu et al. Reference Liu, Gurnis, Ma and Zhang2017) and perhaps even earlier in the late Permian (Wang et al. Reference Wang, Li, Jian, Zhao, Xiong, Bao, Xu, Li and Ma2005; Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Li and Wang2006; Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Sun, Shen, Shu and Niu2006; Li & Li, Reference Li and Li2007; Z-X Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012; Duan et al. 2018; Shen et al. Reference Shen, Yu, O’Reilly and Griffin2018). Based on the findings of the work of FQ Zhang et al. (Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020), our work on Hainan (this study), and the findings of other recent studies (XH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012; Egawa, Reference Egawa and Itoh2013; Domeier & Torsvik, Reference Domeier and Torsvik2014; Shen et al. Reference Shen, Yu, O’Reilly and Griffin2018), we postulate a latest Permian – early Triassic start of an active margin tectonics that marked the beginning of the Pacific Rim of Fire in its western domain near the eastern margin of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean (Fig. 13a). Late Permian arc evolution associated with the westward subduction of the palaeo-Pacific oceanic plate has been documented from SE Japan (Hara et al. Reference Hara, Hirano, Kurihara, Takahashi and Ueda2018; Zhang X et al. 2018) and South Korea (K Yi et al. Reference Yi, Cheong, Kim, Kim, Jeong and Cho2012). In our geodynamic model, we envision the South China Block, consisting of the Yangtze and Cathaysia continents, situated in the upper plate of a W-NW-dipping palaeo-Pacific subduction zone (Fig. 13a), and far from the North China and Indochina blocks during the Late Permian (see the palaeogeographic reconstructions of Pangaea, Panthalassa, Palaeotethys and Neotethys in Domeier & Torsvik, Reference Domeier and Torsvik2014). The South China and Indochina blocks were separated from the rest of the Pangaea supercontinent by Palaeotethys during this time period.

Fig 13. Time–progressive tectonic evolution of Mesozoic SE China through a tectonic mode switch, controlled by slab dynamics of the downgoing palaeo-Pacific Plate and the mantle and upper plate responses to it. AP – accretionary prism; CC – continental crust; JSF – Jian Shao Fault; LM – lithospheric mantle. Data are from Xiao & He (Reference Xiao and He2005), Zhou et al. (Reference Zhou, Sun, Shen, Shu and Niu2006), Li & Li (Reference Li and Li2007), ZX Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012), Wang et al. (Reference Wang, Fan, Zhang and Zhang2013), Zhang et al. (Reference Zhang, Xu, Zhao and Badal2013), J Li et al. (Reference Li, Zhang, Dong and Johnston2014), JH Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018), N Tao et al. (Reference Tao, Li, Danisik, Evans, Li, Pang, Li, Jourdan, Yu, Liu, Batt and Xu2019), L Tao et al. (Reference Tao, Pan, Liu, Jin, Jia and He2020), Y Wang et al. (Reference Wang, Wang, Lia, Seagrenc, Zhang, Zhang and Qian2020) and YM Wu et al. (Reference Wu, Guo, Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Alemayehu and Wang2020).
Although the refined geodynamic model we present here for the Mesozoic evolution of SE China is mechanistically similar to that proposed earlier by Li & Li (Reference Li and Li2007) and ZX Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012), our explanation of the kinematics of plate motions, slab dynamics and modes of plate interactions are fundamentally different from their model. Both our model and the model by Li & Li (Reference Li and Li2007) and ZX Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012) infer a flat subduction of the palaeo-Pacific oceanic lithosphere in the Permo-Triassic (Fig. 13a). However, the model by Li & Li (Reference Li and Li2007) proposes an external cause, such as the subduction of a large oceanic plateau on the palaeo-Pacific plate, as the driving force for flat slab development. We find no geological or geophysical evidence in the extant literature (i.e. Li & van der Hilst, Reference Li and van der Hilst2010) for the collision or subduction of a large oceanic plateau along the SE China continental margin during the Permo-Triassic. We suggest that the initial flat subduction was due to a very large width of the subducting palaeo-Pacific slab, as discussed below.
7.a. Onset of active margin tectonics, flat-slab subduction and upper plate deformation
The Late Palaeozoic (Carboniferous to the earliest Permian) tectonics of E-SE China and its continental margin was largely dominated by extensive carbonate platform construction and passive margin development (FQ Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020, and references therein). This geological process was abruptly halted as the palaeo-Pacific oceanic plate foundered and began to subduct beneath continental Asia towards the end of the Palaeozoic (Fig. 13A). Passive margin transference into an active margin implies spontaneous subduction, but what causes this sudden passive margin collapse is not well understood, and the concept of subduction initiation is the subject of extensive interdisciplinary research (see Stern & Gerya, Reference Stern and Gerya2018, for an overview). Far-field stress influence (e.g. collision between the Indochina and Shibumasu blocks and the terminal closure of Palaeotethys), sudden acceleration of the palaeo-Pacific oceanic plate velocity against the Asian continent, and/or a collapse of an old fracture zone system near the Asian continental margin might have played a major role in spontaneous subduction initiation beneath the SE Asian continental margin at this time. Our study does not allow us to determine unequivocally the cause(s) of subduction initiation beneath East Asia in the latest Palaeozoic – early Mesozoic.
The research done by other geoscientists has shown, however, that active margin tectonics along the SE periphery of continental Asia persisted throughout the Mesozoic Era with changing slab geometry and dip angles (Zhou & Li, Reference Zhou and Li2000; XH Liet al. 2006, 2012; Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Sun, Shen, Shu and Niu2006; Li & Li, Reference Li and Li2007; ZX Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012; Zhu et al. Reference Zhu, Li, Xu and Wilde2013, Reference Zhu, Li, Xu and Wilde2014, Reference Zhu, Li, Xia, Xu, Wilde and Chen2017; JH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018). This convergent margin tectonics produced an intermittently active magmatic arc (ZX Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012; Duan et al. Reference Duan, Meng, Christie-Blick and Wu2018; JH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018) and a retroarc foreland basin system with a protracted, complex tectonic history of both extensional and contractional deformation history (Li & Li, Reference Li and Li2007; XH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012; ZX Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012, Reference Li, Zhang, Dong and Johnston2014; Pang et al. Reference Pang, Krapež, Li, Xu, Liu and Cao2014). Permian magmatic arc products are not exposed extensively in SE China, except on Hainan Island where Guadalupian calc-alkaline granites (Wuzhishan granites; et al. 2006) exist, and in Anhui Province where Guadalupian volcanic tuff deposits with calc-alkaline geochemistry are well preserved in the Permian sedimentary record (FQ Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020). However, the widespread occurrence of Permian detrital zircons in the Upper Permian through Jurassic sedimentary rock sequences in SE China has been interpreted to have sourced from a magmatic arc in the region (XH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012), including the proto-Japan arc (Duan et al. Reference Duan, Meng, Christie-Blick and Wu2018; Hara et al. Reference Hara, Hirano, Kurihara, Takahashi and Ueda2018; X Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Wu, Zhu, Zhang, Xing, Chen, Chen and Zhang2018; Wakita et al. Reference Wakita, Nakagawa, Sakata, Tanaka and Oyama2020).
We infer that an initially large width of the subducting palaeo-Pacific plate against the entire coast of East Asia resulted in flat subduction and resisted slab retreat (Fig. 14a). A global synthesis and three-dimensional modelling of 17 modern subduction zones and their kinematics suggest that the trench-parallel extent of a subducted slab (its width) may vary between 300 and 7000 km, and that it affects the slab dip angle and subduction partioning along a trench more than the age of the downgoing oceanic lithosphere (Schellart et al. Reference Schellart, Stegman, Farrington, Freeman and Moresi2010; Schellart, Reference Schellart2020). Very large widths of downgoing oceanic plates (8000 to >10 000 km) may resist slab retreat, have fast trench-normal subduction plate velocity and be pushed over by the continental upper plate, causing flat subduction. Conversely, small widths (~1500 km or less) result in slab-buoyancy-driven trench retreat, slow trench-normal subduction plate velocity (and small subduction partitioning – <0.5), and slab steepening with rollback (Schellart et al. Reference Schellart, Freeman, Stegman, Moresi and May2007; Schellart, Reference Schellart2020). The former configuration with flat slab leads into significant crustal shortening in the upper continental plate, as was the case in western North America during the Late Cretaceous – Early Eocene Sevier–Laramide orogeny due to the rapid Farallon plate motion caused by its enormous slab width (>10 000 km; Schellart et al. Reference Schellart, Stegman, Farrington, Freeman and Moresi2010). Subsequent segmentation of the Farallon plate into a series of smaller plates, such as the Juan de Fuca plate, with significantly reduced widths created slab rollback and upper plate extension during the Neogene (Mooney & Kaban, Reference Mooney and Kaban2010; YJ Wang et al. Reference Wang, Fan, Zhang and Zhang2013; Schmandt & Lin, Reference Schmandt and Lin2014).
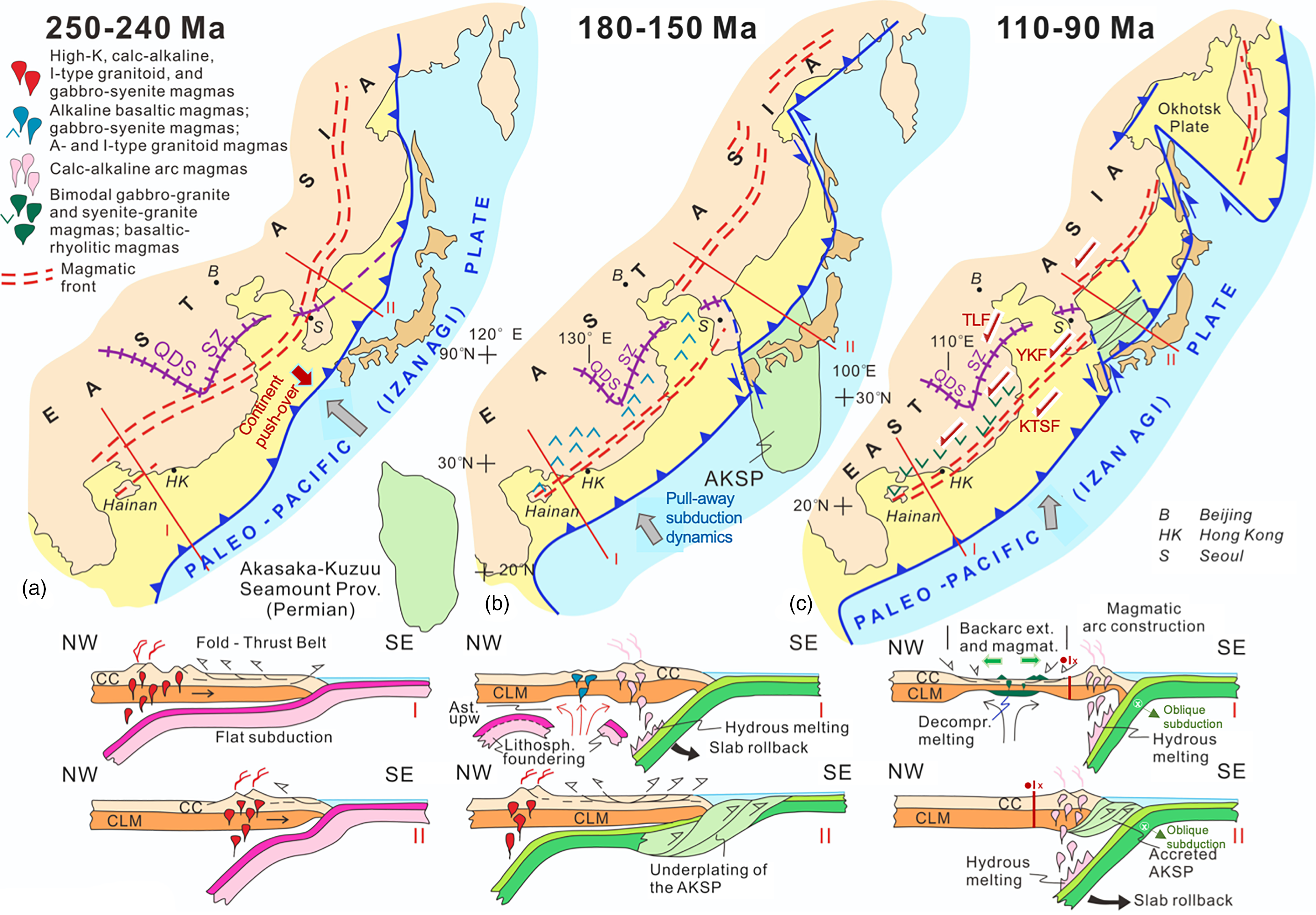
Fig 14. Geodynamic interpretation of subduction-related magmatism and its migration through time and space as a result of the slab geometry of the palaeo-Pacific (Izanagi) oceanic plate and active margin tectonics in East Asia. Broad time windows, keyed into those in Figure 13, include Early to Middle Triassic (250–240 Ma), Jurassic (180–150 Ma) and Albian–Cenomanian (110–90 Ma) in these inferred reconstructions. Outlines of the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin Island and the Kamchatka Peninsula are provided as reference in these reconstructions. The colour difference on land: buff colour = the Asian continent bounded by the modern shorelines; yellow colour = inferred continental crust along the active continental margin of Asia during Mesozoic times. Lines I and II refer to the tectonic profiles (shown below) across SE China and NE China – SE Russia, respectively. Distributions of major magmatic provinces with their characteristic geochemical affinities are depicted schematically in each reconstruction. QDS – Qinling–Dabie Suture; SZ – Sulu Suture Zone. Major sinistral fault systems that developed inboard of the magmatic arc system during the Late Cretaceous are shown tentatively: KTSF – Korea – Taiwan Strait Fault; TLF – TanLu Fault Zone; YKF – Yongdong–Kwangju Fault. Large grey arrows show the convergence direction of the palaeo–Pacific (Izanagi) oceanic plate with respect to Eurasia. Data are from Faure & Natal’in (Reference Faure and Natal’in1992), Maruyama et al. (Reference Maruyama, Isozaki, Kimura and Terabayashi1997), Lee (Reference Lee1999), WD Sun et al. (Reference Sun, Ding, Hu and Li2007), Hall (Reference Hall2012), ZX Li et al. (Reference Li, Li, Chung, Lo, Xu and Li2012), Wang & Shu (Reference Wang and Shu2012), Egawa (Reference Egawa and Itoh2013), Zahirovic et al. (Reference Zahirovic, Seton and Müller2014), Li & Li (Reference Li and Li2015), YQ Liu et al. (Reference Liu, Kuang, Peng, Xu, Zhang, Wang and An2015), SF Liu et al. (Reference Liu, Gurnis, Ma and Zhang2017), Tang et al. (Reference Tang, Xu, Wang and Ge2018), Zhao et al. (Reference Zhao, Yu, Jiang, Mao, Yu, Chen and Xing2019), Y Zheng et al. (Reference Zheng, Xu, Zhao and Dai2018) and Wakita (2020). See text for discussion of the model.
Flat subduction of the palaeo-Pacific plate beneath SE China resulted in push-over tectonics (v4 < v3 < v2 in Fig. 13a), characterized by slow retreat of the subduction hinge and rapid advancement of the continent over the trench. This plate interaction dynamics resulted in strong coupling between the two plates (Fig. 13a). The push-over geodynamic scenario caused landward-migrating shortening in the overlying continent and major crustal shortening (>300–km wide in the N–S direction) that manifested in the formation of the SE China Fold and Thrust Belt (Fig. 3; JH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018). As this flat subduction continued through time, thrust faulting and folding migrated inland (NW) until ~195 Ma. Flat subduction-induced edge flow and aesthenospheric uprising (Ballmer et al. Reference Ballmer, Conrad, Smith and Johnsen2015) led to enriched melts (EMII-type) and the necessary heat to cause partial melting of the lherzolitic subcontinental lithospheric mantle (Fig. 10) and the lower crust to produce high-K granites, syenites and mafic rocks (Fig. 12).
7.b. Slab foundering, trench retreat and upper plate extension
The flat geometry of the subducting palaeo-Pacific oceanic lithosphere for ~50 Ma during the Triassic led to its foundering and delamination, which in turn facilitated the initiation of slab-buoyancy-driven trench retreat and slab steepening in the Early Jurassic (Figs 13b, 14b). Accelerated subduction rate and subduction hinge retreat caused steepening of the downgoing slab, its rapid rollback, and slab segmentation (Fig. 13b). Segmentation of the subducting palaeo-Pacific slab resulted in a major decrease in slab width, which in turn led to pull-away subduction dynamics, causing strong decoupling of the upper and lower plates, and then lithospheric-scale extension and magmatism in the upper plate during the Cretaceous (Figs 13c, 14c). Aesthenospheric upwelling, replacing the delaminated lower plate, caused metasomatism of the continental mantle lithosphere by OIB-type melts. Partial melting of this modified mantle and the continental crust produced A- and I-type granitoids, syenites with OIB-like geochemical features, and both alkaline and bimodal volcanic rocks (Fig. 11; Yang et al. Reference Yang, Dilek, Weinburg and Liu2018; W Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Wu, Zhu, Zhang, Xing, Chen, Chen and Zhang2018; X Zhao et al. Reference Zhao, Yu, Jiang, Mao, Yu, Chen and Xing2019; this study). Slab-driven trench retreat and slab rollback resulted in upper plate extension, which produced NE–SW-trending, fault-bounded depocentres (grabens), fault-block ranges and metamorphic core complexes (Figs 12, 13b; Lin et al. Reference Lin, Faure, Monié, Schärer and Panis2008; Wang & Shu, Reference Wang and Shu2012; Li & Li, Reference Li and Li2015; JH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Wang, Lia, Seagrenc, Zhang, Zhang and Qian2020). Late Jurassic – Early Cretaceous SE China may have hence resembled the Cenozoic Basin and Range Province in Western North America (Dilek & Moores, Reference Dilek and Moores1999; XH Li, Reference Li2000; D Wang & Shu, Reference Wang and Shu2012) (see Section 8 for brief discussion of the Basin and Range tectonics and its analogy for Late Jurassic – Early Cretaceous SE China).
7.c. Slab segmentation and steepening, plate decoupling and continental back-arc extension
It has been well demonstrated that changes in rollback velocities along the strike of a subduction zone commonly lead to tearing and segmentation of the subducting lithospheric slab (Govers & Wortel, Reference Govers and Wortel2005; Schellart et al. Reference Schellart, Freeman, Stegman, Moresi and May2007; Rosenbaum et al. Reference Rosenbaum, Gasparon, Lucente, Peccerillo and Miller2008; Dilek & Altunkaynak, Reference Dilek, Altunkaynak, van Hinsbergen, Edwards and Govers2009). We think that the velocity of subduction rollback along the length of the palaeo-Pacific subduction system beneath the Asian continent became varied in time during the Jurassic, resulting in the development of sharp, hairpin-type cusps along its length (Maruyama et al. Reference Maruyama, Isozaki, Kimura and Terabayashi1997; Li & van der Hilst, Reference Li and van der Hilst2010; Hall, Reference Hall2012; Müller et al. Reference Müller, Seton, Zahirovic, Williams, Matthews, Wright, Shephard, Maloney, Barnett-Moore, Hosseinpour, Bower and Cannon2016; SF Liu et al. Reference Liu, Gurnis, Ma and Zhang2017; Zhou & Li, Reference Zhou and Li2017). Furthermore, the arrival of a large oceanic plateau at the palaeo-Pacific subduction trench, such as the Permian Akasaka–Kuzuu Seamount Province (Maruyama et al. Reference Maruyama, Isozaki, Kimura and Terabayashi1997), likely resulted in significant changes in along-strike slab subduction velocities and in slab tearing (Fig. 14c). Accreted fragments of this seamount province occur in the Kuzu area of Tochigi Prefecture in the central part of Honshu Island in Japan (Kobayashi, Reference Kobayashi2006). These developments in the palaeo-Pacific subduction dynamics caused slab segmentation and hence decreased slab width. The combination of decreased slab width, continued slab rollback and a more steeply dipping subduction zone in the Cretaceous produced an extended arc-trench and back-arc system in the upper plate (Figs 13c, 14c; Malinovsky et al. Reference Malinovsky, Golozoubov, Simanenko and Simanenko2008; J Deng et al. Reference Deng, Liu, Wang, Dilek and Liang2017; JH Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018; XY Li et al. Reference Li, Li, Suo, Dai, Guo, Ge and Lin2018, Reference Li, Li, Huang, Wang, Yu, Cao and Xie2019).
The southeastward-younging ages of the Cretaceous calc-alkaline rocks in E-SE China are consistent with this slab rollback interpretation. Slab dehydration triggered hydrous melting, which generated arc-like rocks in a magmatic belt close to the coastline (Figs 13c, 14c; Zhou et al. Reference Zhou, Liang, Kröner, Cai, Shao, Wen, Jiang, Fu, Wang and Dong2015). Aesthenospheric decompression melting and low-pressure lower crustal melting beneath the trench-distal back-arc setting formed crustally contaminated MORB-like tholeiitic basalts in an intracontinental extensional system (Fig. 12c; Sun et al. Reference Sun, Chen, Milan, Wilde, Jourdan and Xu2018; Tang et al. Reference Tang, Xu, Wang and Ge2018).
8. Basin and Range-style extensional tectonics: a recent analogue for Late Jurassic – Early Cretaceous SE China
8.a. Basin and Range tectonics of the Western US Cordillera
The Basin and Range geological province in western North America extends for ~2500 km from Canada in the north, through the Great Basin in the USA, to central Mexico in the south, and consists of NNW–SSE-oriented, fault-controlled basins (grabens and half-grabens) and mountain ranges (mostly horst blocks). The modern Great Basin is bounded to the west by the Sierra Nevada batholith and mountains in California and the Wasatch mountain range in Utah to the east, and by the Snake River Plain and the Mojave Block in the north and south, respectively. It is a unique physiographic province with a >600 km E–W width, mean elevation of 1500 m a.s.l. , average crustal thickness of 30 km and a closed, internal drainage system (Dilek & Moores, Reference Dilek and Moores1999). The temperature within its crust and upper mantle is higher than normal, as indicated by the high heat flow and the low seismic velocities in the underlying mantle.
The Basin and Range province behind (or to the east of) the Sierra Nevada magmatic arc was a high plateau with a thick crust (~60 km), supporting high topography (~3 km a.s.l.) in the Late Cretaceous – Palaeogene, after the Cordilleran orogeny (Dilek & Moores, Reference Dilek and Moores1999; Liu, Reference Liu2001; Best et al. Reference Best, Barr, Christiansen, Gromme, Deino and Tingey2009). Saline lakes were developed on this altiplano in the Eocene, reminiscent of today’s Tibetan plateau north of the Himalaya Mountains (Dilek & Moores, Reference Dilek and Moores1999). The Late Cretaceous – Palaeogene Laramide magmatism, which was associated with the flat Farallon slab, migrated eastward across the Great Basin (Dickinson, Reference Dickinson2006). However, by the Late Eocene – Oligocene the unusually thick crust and high topography of the Great Basin became unstable as the excess gravitational potential energy, thermal relaxation and enhanced radiogenic heating caused partial melting in the middle to lower crust that in turn resulted in the onset of orogenic collapse and extensional deformation (Liu, Reference Liu2001). This orogenic collapse also overlapped in time and space with re-migration of magmatism westwards across the Great Basin and towards the continental margin, as the segmented Farallon plate started dipping more steeply below the North American continent (Atwater & Stock, Reference Atwater and Stock1998; Dickinson, Reference Dickinson2006; Schellart et al. Reference Schellart, Stegman, Farrington, Freeman and Moresi2010; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Wu, Zhang, Fan, Zhang, Zhang, Peng and Yin2012). Aesthenospheric upwelling associated with the steeply dipping and fast-retreating, narrow Farallon slabs provided the necessary heat source for extensive crustal melting and induced thermal weakening, which collectively led to significant extensional deformation, crustal exhumation, and denudation of crystalline basement rocks forming metamorphic core complexes in the Great Basin during the Oligo-Miocene (Dilek & Moores, Reference Dilek and Moores1999; Dickinson, Reference Dickinson2006).
The Late Tertiary metamorphic core complexes in western North America are situated in the hinterland of the Late Jurassic – Early Eocene Sevier fold-and-thrust belt (Taylor et al. Reference Taylor, Bartley, Martin, Geissman, Walker, Armstrong and Fryxell2000), and stretch from the British Columbia (Canada) latitude in the north, through the Great Basin in the USA, to the Sonora Desert in northern Mexico. They are characterized by dome-shaped, highly deformed metamorphic and magmatic rocks in the footwalls of low-angle detachment faults, overlain by undeformed, terrestrial clastic rocks deposited in supradetachment basins and structural grabens. The exhumation of these metamorphic core complexes was synchronous with widespread outburst of commonly caldera-centred ignimbrite eruptions (Dilek & Moores, Reference Dilek and Moores1999). The ‘ignimbrite flare-up’ episode was coeval with the emplacement of metaluminous to mildly peraluminious granitoid plutons at depth and voluminous eruptions of rhyolitic, rhyodacitic ash-flow tuffs and high-K dacitic to andesitic lava flows (Best et al. Reference Best, Barr, Christiansen, Gromme, Deino and Tingey2009; Henry & John, Reference Henry and John2013). This volcanic phase was temporally associated with thin-skinned extensional deformation across the Great Basin that produced closely spaced, high-angle and shallow listric normal faults, and fault-bounded and strongly tilted stratigraphic–volcanic sequences (Proffett, Reference Proffett1977; Lipman, Reference Lipman1984; Johnson et al. Reference Johnson, Shannon, Fridrich, Chapin and Zidek1989; Bachl et al. Reference Bachl, Miller, Miller and Faulds2001). All these tectonic and magmatic events were largely a result of back-arc extension in the western North American Cordillera during the Mid-Cenozoic.
A second phase of the Basin and Range extension started around 18–16 Ma and developed block-faulting, regional subsidence and bimodal basaltic–rhyolitic volcanism (Dilek & Moores, Reference Dilek and Moores1999; Best et al. Reference Best, Barr, Christiansen, Gromme, Deino and Tingey2009). Eruption of alkaline basaltic lavas during this phase indicates the involvement of SCLM in the melt evolution. Strike-slip faulting in the western end of the Great Basin later in the Miocene shows that the mode of extensional deformation was largely controlled by transtension, rather than back-arc extension, as the San Andreas transform fault system replaced the active margin tectonics along the Pacific – North American plates (Atwater & Stock, Reference Atwater and Stock1998). Strain partitioning along and across the San Andreas transform fault system produced a series of NNW–SSE-striking, dextral transtensional fault systems (i.e. the Walker Lane Shear Zone), which have been accommodating ~25–15% of the Pacific – North American plate motion (Faulds et al. Reference Faulds, Henry and Hinz2005) and facilitating the N-NW motion of the Sierran – Great Valley block with respect to the Colorado Plateau (fixed North American plate) at an average rate of 15 mm a−1 since 10–8 Ma (Wernicke & Snow, Reference Wernicke and Snow1998).
8.b. Basin and Range analogue for Late Jurassic – Cretaceous SE China
There are many similarities between the Cenozoic geology and tectonics of the Western US Cordillera and the Late Jurassic – Cretaceous geology and tectonics of SE China, suggesting that similar geodynamic processes may have controlled their continental dynamics, specifically their tectonomagmatic and landscape evolution. Here, we draw some first-order parallels between these two continental regions, regarding the nature of major geological events and their consequences in a relative time frame.
(1) Both the Western US Cordillera and SE China experienced flat-slab subduction of oceanic plates against their continental margins that resulted in contractional deformation, which migrated inland through time.
(2) The onset of the following extensional deformation and attendant magmatism in both continental regions was associated with more steeply dipping and retreating oceanic slabs. It is inferred that this slab dynamics was a result of slab segmentation and hence major reduction in the widths of subducting slabs. Coeval magmatism migrated across the continental upper plates, towards the active margins, and produced bimodal volcanic rocks and granitoid intrusions, some of which resulted from partial melting of continental lower crust. This magmatism caused thermal weakening of the continental crust.
(3) Thermally weakened continental crust in the back-arc tectonic setting in both the Western US Cordillera and SE China subsequently underwent crustal exhumation and denudation of crystalline basement rocks. This process led to the development of metamorphic core complexes in the footwalls of low-angle detachment faults, which were onlapped by syn-extensional and terrestrial, supradetachment depocentres. This tectonic episode was also synchronous with the development of playa lakes within basins, separated by ranges, representing uplifted fault blocks. The landscape evolution in both regions was a manifestation of thin-skinned tectonics, with extensive alluvial fan system and internal drainage formation, and deposition of evaporites and lacustrine sediments.
(4) Spatially and temporally overlapped with metamorphic core complex formation was widespread eruption of rhyolitic, dacitic and andesitic tuffs and production of ignimbrites and ashfall deposits. In both SE China and in the Great Basin of the Western US Cordillera this unique magmatic event is known as ‘ignimbrite flare-up’, which was associated with the emplacement of shallow-level granitic plutons.
(5) Later-stage extensional deformation involved block-faulting, regional subsidence and bimodal (basaltic–rhyolitic) volcanism in both SE China and the Great Basin. Basaltic magmatism was a result of aesthenospheric decompression melting beneath significantly thinned continental lithosphere, and was locally fed by mafic dyke swarms, which were emplaced perpendicular to the regional tensile stress regimes.
(6) With the convergence direction of the subducting plates becoming more oblique with respect to the active margins of E-SE China and the Western US Cordillera through time, oblique subduction and the associated strain partitioning in the upper continental plates resulted in transtensional deformation. Major strike-slip fault systems developed, such as the Tanlu Fault in East China (Y Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Dilek, Zhang, Chen, Zhu and Hao2020) and the Walker Lane shear zone in western Nevada and eastern California (Faulds et al. Reference Faulds, Henry and Hinz2005), which strongly affected the crustal architecture of the continental margins in both regions.
This comparative summary shows that the time-progressive tectonic, magmatic and landscape evolution of Mesozoic SE China and the Cenozoic Western US Cordillera followed similar tectonic paths through time while undergoing similar geodynamic events. Although these two regions had significantly different geodynamic histories prior to the onset of flat-slab subduction along their continental margins, their SCLM and continental crust responded to the subducting slab dynamics and changing slab geometries in similar ways.
9. Conclusions
The geochemical fingerprints of magmatic rocks and the tectonic architecture of the continental crust on Hainan and in SE China in general were strongly affected by the motions of subducting plates and trench migration through time. A nearly complete record of the Triassic through Cretaceous igneous events, as discussed in this study, points to progressive melt evolution from alkaline through tholeiitic and OIB type, to magmas with calc-alkaline affinities, reflecting the changing character of the mantle source and slab dynamics beneath E-SE China. This magmatic progression overlapped with and followed a major tectonic switch from contractional deformation in the Triassic to lithospheric-scale extensional deformation during the Jurassic and Cretaceous. Our geodynamic model envisions a mode switch from a Laramide-type, flat-slab controlled contractional to a moderately-to-steeply dipping palaeo-Pacific slab geometry and Basin and Range-type extensional tectonics, reminiscent of the Late Cretaceous – Cenozoic North American Cordillera (Dilek & Moores, Reference Dilek and Moores1999; Dickinson, Reference Dickinson2006; Wells et al. Reference Wells, Hoisch, Cruz-Uribe and Vervoort2012, and references therein). This ‘push–pull geodynamics’ of Mesozoic E-SE China occurred during ~150 Ma of continuous convergence between the continental China and the oceanic palaeo-Pacific plate. Slab segmentation and fragmentation, which reduced the along-strike width of the subducting palaeo-Pacific plate, played a major role in the steepening and retreat of the downgoing oceanic slabs that in turn induced aesthenospheric upwelling, increasingly more mafic magmatism and lithospheric-scale thinning in the continental upper plate during the Middle Jurassic through Cretaceous.
The geology of Mesozoic E-SE China is a great natural laboratory to investigate the slab-controlled continental dynamics through time. Further systematic, precise geochronological and structural field studies of the Jurassic and Cretaceous magmatic rock suites, terrestrial basin deposits and extensional and strike-slip fault systems in SE China should further elucidate the validity of our analogy of its Basin and Range-type tectonic evolution during the Middle to Late Mesozoic.
Acknowledgements
Our fieldwork on Hainan Island was supported by research funds from the Second Institute of Oceanography to LM Tang. Y Dilek acknowledges field support by Zhejiang University for his research on Hainan Island. Formal reviews for the Geological Magazine by M Faure and WJ Xiao have helped us refine our interpretations and the model presented in this paper. Constructive and insightful reviews by Y Ogawa and Editor P Clift are gratefully acknowledged. We thank Susie (Bloor) Cox for her continued help and support, and Editor Peter Clift for his objective and constructive editorial handling of our paper.
Conflict of interest
None.
Supplementary material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016756820001211

















