Introduction
Most insects migrate at altitudes of a few hundred metres up to about two kilometres above the ground (Glick, Reference Glick1939; Johnson, Reference Johnson1969; Gatehouse, Reference Gatehouse1997), well above their ‘flight boundary layer’ – a (normally) shallow layer of the atmosphere extending up from the ground where the wind speed is less than an insect's air speed (Taylor, Reference Taylor1974). Insects flying at altitude should be regarded as active migrants because they have to sustain wing-beating to stay aloft (see below) and, due to the fast wind speeds usually encountered at these heights, they are capable of traversing tens or even hundreds of kilometres in just a few hours' flight (e.g. Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Smith, Riley, Pedgley and Woiwod2002a, Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Mouritsen, Hill, Riley, Sivell, Smith and Woiwod2008). Due to the difficulties inherent in observing small organisms at comparatively high altitudes, insects flying here are less widely studied than those flying near the ground. Nonetheless, many important insect pests are high-altitude migrants (Pedgley, Reference Pedgley1982, Reference Pedgley1993; Drake & Gatehouse, Reference Drake and Gatehouse1995; Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Chapman and Harrington2006); and it is, therefore, important that we gain a good understanding of their flight behaviour and its consequences.
Radar has been used to measure density-height profiles of migrating insects at many sites around the world, and some consistent patterns have been revealed (Drake, Reference Drake1984; Drake & Farrow, Reference Drake and Farrow1988; Drake & Rochester, Reference Drake and Rochester1994; Gatehouse, Reference Gatehouse1997; A.M. Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Reynolds and Riley2008). One frequently observed distribution is the concentration of insects into layers of great horizontal spatial extent, but restricted depth (~50–200 m), which often persist for several hours. These layers seem to be formed by insect migrants ascending after take-off (or perhaps descending later in their migratory journey), reaching particularly favourable attitudes and then maintaining flight there. Intense layering is particularly common when insects are migrating under the stable atmospheric conditions that exist in and above the night-time atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) during fair weather. In such conditions, insects apparently have excellent control over their flight altitude due to the weak vertical atmospheric motions (Wood et al., Reference Wood, Chapman, Reynolds, Barlow, Smith and Woiwod2006). Under these circumstances, insect migrants apparently select favourable altitudes at which to fly, such as in the zone of warmest air found at the top of a temperature inversion (which may facilitate prolonged flight if air temperatures are sub-optimal at other altitudes). In other cases, migrants may select the altitude of a nocturnal wind jet (thus maximising migration distances), which presupposes that they can somehow detect the presence of such wind-speed maxima (A.M. Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Reynolds and Riley2008).
Until now, most investigations of layering, both in the UK (D.R. Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Chapman, Edwards, Smith, Wood, Barlow and Woiwod2005, Reference Reynolds, Reynolds and Riley2008; Wood et al., Reference Wood, Chapman, Reynolds, Barlow, Smith and Woiwod2006) and elsewhere (Drake & Farrow, Reference Drake and Farrow1988; Drake & Rochester, Reference Drake and Rochester1994; Gatehouse, Reference Gatehouse1997; Feng et al., Reference Feng, Wu, Cheng and Guo2003, Reference Feng, Wu, Cheng and Guo2004, Reference Feng, Wu, Ni, Cheng and Guo2005), have been case studies of just one or a few nights only. However, to gain a clear picture of the frequency and scale of insect layering, and an understanding of the factors underlying layer formation, it is necessary to analyse data from long-term studies of insect density profiles. The only practicable way such data can be collected is by autonomously-operating entomological radar systems that provide continuous monitoring of aerial insect populations. We have been running such a system, comprising two vertical-looking entomological radars in southern UK, that has provided continuous data on vertical profiles of insect density since 1999 (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds and Smith2003).
In this paper, we take the first step towards producing a ‘climatology’ of insect layering at night (sensuDrake & Rochester, Reference Drake and Rochester1994) by providing quantitative answers to the following questions: (i) at what times of the day/night and at what altitudes do macro-insects fly? (ii) At what times and altitudes do intense layers of macro-insects most frequently occur? (iii) Which species are the most prevalent constituents of the nocturnal layers observed over the UK? Lastly, we aim to confirm that the nocturnal layers are due to active selection of flight height by the migrants and that they are not formed ‘passively’ due to the concentration of insects by atmospheric motion alone.
Radar studies elsewhere have frequently shown that the primary constituents of observed nocturnal layers are migratory noctuid moths, which are important agricultural pests (e.g. Chen et al., Reference Chen, Bao, Drake, Farrow, Wang, Sun and Zhai1989; Wolf et al., Reference Wolf, Westbrook, Raulston, Pair and Hobbs1990; Feng et al., Reference Feng, Wu, Cheng and Guo2003, Reference Feng, Wu, Ni, Cheng and Guo2005); and this is potentially the case in the present study. Climate change seems likely to increase the frequency of lepidopteran migration into Britain (Sparks et al., Reference Sparks, Dennis, Croxton and Cade2007), and a greater understanding of the mechanisms of flight-altitude selection by these migrants will be essential for the development of predictive models of pest immigration and outbreak management.
Materials and methods
Vertical-looking entomological radar
Continuous measurements of vertical profiles of insect abundance were obtained from two vertical-looking insect-monitoring radars (VLRs) (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds and Smith2003) situated at Malvern (Worcestershire) in west-central England, and at Harpenden (Hertfordshire) in east-central England (see details in D.R. Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Reynolds and Riley2008). The VLRs provide instantaneous vertical profiles in terms of (i) the number of individual targets, (ii) aerial density and (iii) a measurement of multi-target biomass (this is useful when densities are too high for individual targets to be resolved). Here, we are mainly considering macro-insect targets, with a mass greater than 15 mg, which were detected over the full height range of the radars (~150 m to 1.2 km above VLR). In this study, we analysed the data collected by both radars during the summer months (June–August) of four consecutive years (2000–2003, inclusive). Full details of the radars' operation are described elsewhere (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Smith, Woiwod, Reynolds and Riley2002b, Reference Chapman, Reynolds and Smith2003; D.R. Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Chapman, Edwards, Smith, Wood, Barlow and Woiwod2005, Reference Reynolds, Reynolds and Riley2008), and the following is therefore a brief summary.
Return signals were recorded from individual insect targets flying through one of the fifteen ‘range-gates’ (the sampling volumes), each of which are 45 m deep, separated by a 26 m non-sampled interval. Coverage above the radar was 180–1218 m at Malvern radar and 150–1188 m at Harpenden. Data were recorded during five-minute sampling periods, repeated every 15 minutes, 24 hours per day, thus producing 96 vertical profiles per day (or over a million remotely sensed aerial samples during the study period). Several parameters were extracted routinely from the raw data by the analysis program (Smith et al., Reference Smith, Riley and Gregory1993; Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Smith, Woiwod, Reynolds and Riley2002b) – particularly horizontal speed, displacement direction, body alignment and three radar back-scattering terms from which body mass and body shape are estimated.
The minimum detectable mass varies with altitude, such that a one-milligram insect barely registers in the lowest radar range-gate. This means that micro-insects, such as tiny Diptera, aphids and parasitic Hymenoptera, known to be hugely abundant at these heights (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Smith, Smith and Woiwod2004), are not detected. In Britain, the only insect orders that contain relatively abundant representatives of the migrant fauna, and which are large enough for detection by the radars throughout the sampling range, are certain families of the Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Neuroptera and Diptera.
Layer classification schemes
Previous case-study approaches for nocturnal layering events detected by the radars used a layer quality (LQ) classification scheme (see Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Chapman, Edwards, Smith, Wood, Barlow and Woiwod2005). Briefly, this consisted of seven possible categorizationes for each profile, the most pertinent to the present case being: LQ4 (a weak layer), LQ5 (an intermediately-pronounced layer), LQ6 (a pronounced layer) and LQ7 (a possible layer in conditions where high insect densities cause considerable inter-target interference).
In the present study, the above classification scheme was extended to produce a new aggregate index, the nocturnal layer quality (NLQ), which could represent the layer quality for a particular night (Wood, Reference Wood2007). To calculate the NLQ, the mean of all LQ values of 4, 5 and 6 was taken for the period 21:00–23:50 h UTC (all times in this paper are in UTC) resulting in a single value for 12 early evening profiles. NLQ values have a range between 0 and 6. If LQ=6 for all 12 profiles, then a value of NLQ=6 is returned; if LQ does not equal 4, 5 or 6 in any of the 12 profiles, then a value of NLQ=0 is returned. Mid-range NLQ values can, therefore, be produced either by temporally persistent layers of weak/intermediate sharpness or by very pronounced, but short-lived, layers.
Insect trapping
Data from the Rothamsted Insect Survey's (RIS) UK-wide light-trap and suction-trap network (Woiwod & Harrington, Reference Woiwod, Harrington, Leigh and Johnson1994) were used to ascertain which species of large nocturnally-migrating insects (in effect, noctuid moths) were most likely to be involved in the formation of nocturnal layers. The RIS light-trap network consists of standard Rothamsted traps (each fitted with a 200 W tungsten-filament (non-UV) light bulb: Williams, Reference Williams1948) distributed throughout the UK, which are emptied on a daily basis. For the purposes of this study, all the noctuids caught by all the RIS traps in England and Wales (~60 traps in use per year) during 2000–2006, inclusive, were identified to species. The RIS suction-trap network consists of towers 12.2 m tall that sample the insects flying directly above them (Macauley et al., Reference Macaulay, Tatchell and Taylor1988). The aphid portion of the samples are routinely extracted and identified, while all the other insects are stored in alcohol. For the purposes of this study, we had access to data on the identity and abundance of all the noctuid moths from the stored samples from 12 suction-traps distributed throughout England for the three years 2001, 2006 and 2007.
The fresh body weight and wing length (defined as thoracic centre to wing-tip) were measured for a range of moth species caught in a mercury-vapour (MV) light-trap at Rothamsted between 1999 and 2001. These measurements were required for comparison with radar-target-size distributions and for estimates of terminal velocities (see below).
We also attempted to identify the macro-insects detected by the radar directly by means of aerial trapping at 200 m above ground level (AGL) using a net suspended from the tethering line of a helium-filled blimp (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Smith, Smith and Woiwod2004). This work was carried out at Cardington airfield, Bedfordshire, approximately 40 km north of the Harpenden radar, for several weeks each summer during 1999–2007, inclusive. As the aerial net has a small aperture (0.64 m2), the method is more suited to sampling of small insects; but, when macro-insects are caught, this is indicative of very large numbers being airborne (e.g. Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Mouritsen, Hill, Riley, Sivell, Smith and Woiwod2008).
Terminal velocities
If the insects were to free-fall when they stopped flying, estimates of their terminal velocity (w T) will give some idea of how quickly a layer would be expected to dissipate. A basic fluid mechanic model was used to calculate fall speed (see Maryon, Reference Maryon1997; Wood, Reference Wood2007), with mass and insect cross-sectional area being the required variables. The cross-sectional area of the falling insect was calculated for the open- and closed-wing condition.
Results
Diel periodicity of insect activity
Daily patterns of insect activity at high altitudes throughout the study period were examined in detail, and some typical features of the vertical profile in insect numbers can be seen in the example (for 16 June 2000) presented here (fig. 1). Peaks of flight activity, particularly at the lowest altitudes covered by the radars, occurred around dawn (ca. 03:00–04:00) and dusk (ca. 20:00–22:00), associated with the synchronised take-off of large numbers of migrants (see also D.R. Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Chapman, Edwards, Smith, Wood, Barlow and Woiwod2005, Reference Reynolds, Reynolds and Riley2008; Wood et al., Reference Wood, Chapman, Reynolds, Barlow, Smith and Woiwod2006). As many as 70 macro-insect targets were detected per range-gate in a five-minute sample at this time.

Fig. 1. Time/height plot of insect numbers detected in a five-minute sample (see colour key) taken every 15 minutes on 16–17 June 2000 on the Malvern radar. This 24-h period shows many of the typical features in the vertical profile (see text). On 16 June, the end of civil twilight and sunrise were at 02:59 and 03:48, respectively; sunset and the end of civil twilight were at 20:31 and 21:20, respectively. No data was available for heights below 150 m above the radar.
Substantial dusk emigration in the summer quite often leads to the formation of layers aloft as the migrants ascend to particular altitudes and maintain flight there for extended periods of the night (Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Chapman, Edwards, Smith, Wood, Barlow and Woiwod2005; Wood et al., Reference Wood, Chapman, Reynolds, Barlow, Smith and Woiwod2006). Generally, in the UK, the ‘ascent phase’ profiles (which often show a semi-logarithmic decline in insect numbers with height) evolve directly into a nocturnal layering profile with a well-defined density maximum at a specific height. On this particular occasion (fig. 1), however, many of the dusk-only (crepuscular) fliers evidently descended back to the surface before the nocturnal layering event developed. Soon after 22:00 h, however, sample numbers reached 20–50 targets per range-gate at ~200–300 m AGL as an elevated layer formed. The layer rose steadily until, at midnight, it was centred at ~600 m AGL, where it persisted until dawn on 17 June. This occasion was somewhat unusual in that the migrants forming the layer flew all night, but moderately pronounced layering (see below) occurred on 30% of nights of the study period.
The other obvious feature in fig. 1 is the large amount of insect activity that occurred through the daytime, from 09:00 onwards. Daytime profiles of insect numbers varied considerably over both height and time – targets were present up to about 800 m, although the greatest counts were generally at the lowest observable altitudes. This build-up of insect activity was very probably associated with convective plumes in the daytime ABL (Drake & Farrow, Reference Drake and Farrow1988; Geerts & Miao, Reference Geerts and Miao2005; D.R. Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Reynolds and Riley2008).
Using data from the pooled four-year radar dataset, the mean number of insect targets per altitude band was plotted for the 736 summertime 24-h periods (fig. 2). The key difference between the example in fig. 1 and the pooled data displayed in fig. 2 is that, due to the absence of a consistent height for the nocturnal layering, this feature is not evident in the mean pattern; in fact, the greatest insect densities always occurred at the lowest observable heights.

Fig. 2. Time/height plot of insect numbers per five-minute sample (see legend for fig. 1), showing the pooled mean data for June–August 2000–2003, inclusive, for both the Malvern and Rothamsted radars. No interpolation was used for the contours.
The greatest numbers of insect targets during the 24-h period occurred during the dusk migration peak (mean of up to ~24 targets), while the lowest numbers occurred late in the night (about 01:00–02:30). The dawn activity peak was visible, but considerably less intense than the dusk one. Daytime activity generally started to build up between 06:00 and 07:00, although the largest numbers of daytime targets were observed between 11:00 and 14:30.
The greatest heights reached by insects occurred during the daytime (e.g. the ‘two target’ isopleth reached up to 850 m AGL between 09:00 and 10:00 (fig. 2)). At this time, air temperature constraints on flight height will be less severe than at night, and the ascent of many insects will be assisted by turbulent updraughts associated with the daytime convective boundary layer. The equivalent height was only 400 m for the dawn peak and 600 m for the dusk peak. The rate of decrease with altitude of insect numbers was greater at dusk than during the day.
Summation of insect numbers over all flight heights (fig. 3) clearly shows three of the four diurnal flight phases (i.e. dawn, daytime and dusk), but nocturnal activity is comparatively low. Of the months shown, July had the greatest daytime aerial activity and June the least. The mean maximum temperatures at screen level (ca. 1.5 m AGL) in the Midlands of the UK (UK Met Office website) were 19.3±1.1°C (95% C.I.), 20.7±1.1°C and 21.7±0.9°C for June, July and August, respectively. The coolest month (June) had the least flight activity in the middle of the day, while July and August with rather similar maximum temperatures had considerable overlap in daytime activity values. Presumably, other factors, such as timing of adult emergence and migration from continental Europe, may also influence the month-by-month variations in addition to the direct effect of temperature on flight activity.

Fig. 3. Confidence intervals (95%) for the total insect numbers in radar sampling profile (for every 15-minute interval throughout the 24-h period) for the months of June, July and August, averaged over the years 2000–2003, inclusive, for both radars (▪, June; ![]() , July;
, July; ![]() , August).
, August).
The daytime maximum in total insect numbers apparently occurred at 10:00–13:00 (fig. 3), before the part of the day that is usually the warmest (typically 12:00–15:00), but caution is required here because high levels of inter-target interference during very high-density insect activity may produce an apparent drop in analysable signals (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Smith, Woiwod, Reynolds and Riley2002b).
The dusk peak had very similar numbers of insect targets in June and July, but there was a slight reduction in August (mean ~70 targets). The progression of the timing of the dusk and dawn peaks towards mid-day from June to August illustrates the dependence of the peaks' timing on illumination (since the time of sunset and sunrise move closer to midday once the summer solstice has passed). This result thus indicates that the dawn and dusk activity peaks are initiated and terminated by particular light intensity thresholds that are reached progressively later in the morning, and earlier in the evening, as the season advances (Lewis & Taylor, Reference Lewis and Taylor1964).
Finally, we note that nighttime insect activity (after the dusk peak) is increased in August compared with June and July (fig. 3). The mean minimum temperatures at screen level (ca. 1.5 m AGL) in the Midlands of the UK (UK Met Office website) were 9.9±0.7°C (95% C.I.), 11.5±0.9°C and 12.0±0.5°C for June, July and August, respectively. There was thus no overlap in the confidence intervals for mean minimum temperatures for June compared with the warmer August nights, which may at least partly explain why there was greater nocturnal activity during August (fig. 3).
Periodicity of layering
The proportion of layering profiles in each LQ category that occurred throughout the day/night is shown in fig. 4. Weak and intermediate layers (LQ=4 or 5) were very frequent during the daytime. Examination of daily profiles indicates that some of this apparent layering was probably an artefact caused by multi-target ‘saturation’ effects reducing target numbers and resulting in gaps in the profile. In contrast, the analysis showed that nocturnal layers were more intense and stable than daytime ‘layers’, because LQ values of 5 and 6 peaked at night. The peak for both the intermediate and strong layers (30% and 11% for LQ values of 5 and 6, respectively) occurred at ~21:15, soon after the dusk activity peak. In fact, at 21:15, 60% of the profiles showed some degree of layering (defined as having an LQ value of 4–7), and layers became less common after this time. For the remainder of this study, we focus on the persistent and relatively stable nocturnal layers.

Fig. 4. Layering occurrence (%) in each 15-minute time interval throughout the 24-h period for June–August 2000–2003, inclusive, for both radars. Layer quality (LQ=4, 5 or 6) values indicate layers of increasing intensity (see text) (– – –, LQ=4; ![]() , LQ=5; —, LQ=6).
, LQ=5; —, LQ=6).
The altitude of nocturnal layers
For occasions when nocturnal layering was present (defined here as NLQ>1, which occurred on 30% of nights), the pooled vertical distribution data were examined to determine whether there was a preferential altitude for layering. Figure 5 shows that around three quarters of nocturnal layers detected by the radars (76% at Malvern, 73% at Rothamsted) occurred in range-gates 2–5, i.e. below 500 m AGL. (By definition, a layer cannot occur in range-gate 1 because layers are only recognised when there are reduced numbers in the gates both above and below it.) The peak in layering occurred in range-gate 3 (ca. 300 m AGL) at Malvern. However, at Rothamsted, most layering occurred at the lowest observable altitude (range-gate 2, ca. 240 m AGL).

Fig. 5. Altitude at which nocturnal (21:00–23:50 hours UTC) layers occur in the pooled data for June–August 2000–2003, inclusive, for both radars. See text for definition of a layer (![]() , Malvern; ▪, Rothamsted).
, Malvern; ▪, Rothamsted).
For the purposes of our study, a ‘critical region’ for the initiation of summertime nocturnal layers in Britain was, therefore, defined as occurring at: (i) altitudes between 200 and 500 m AGL, and (ii) times from 20:00–22:00. The meteorological conditions around 20:00, when many migrants are commencing flight, will be crucial in determining if a layer will be initiated or not. The end of the critical period was designated as 22:00, when the dusk peak will be long past and any layer going to develop will probably have formed. Thus, future research on the initiation of nocturnal insect layers could usefully be focused on this critical region.
Identity of species in nocturnal layers
Identification of radar-detected insects to species level can sometimes be achieved if ground-based trap data, or preferably high-altitude netting data (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Smith, Smith and Woiwod2004), are available to complement the analysis and provide an indication of the most likely candidate species (e.g. Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Smith, Riley, Pedgley and Woiwod2002a, Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Smith, Riley, Telfer and Woiwod2005, Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Brooks, Smith and Woiwod2006, Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Mouritsen, Hill, Riley, Sivell, Smith and Woiwod2008; Wood et al., Reference Wood, Chapman, Reynolds, Barlow, Smith and Woiwod2006). In the type of general analysis presented here, it is impossible to identify the majority of radar-detected insects to species level; but certain subsets of radar targets can, perhaps, be narrowed down to particular taxonomic groups, such as ‘noctuid moths’ (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) or ‘green lacewings’ (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). The first step is to compare radar target mass distributions with the masses of insect taxa known (from, say, trapping evidence) to be flight active at the relevant season and time of day. Figure 6 shows the frequency distribution of insect mass for all radar-detected insects (day-flying and nocturnal) during the summer months of 2000–2003 at both sites. As expected from aerial trapping evidence, there is a clear reduction in insect abundance as body mass increases, at least for the mass range shown here. It should be noted that the radar only detects insects larger than ~1 mg and that targets weighing a few milligrams are likely to be under-sampled (Smith et al., Reference Smith, Reynolds and Riley2000; Wood et al., 2008 unpublished data). Therefore, the dominance of the small day-flying insects will be, if anything, underestimated. By comparison, the mass distribution of night-flying insects during the same sample period is quite different, with the maximum abundance in the 80–160 mg size class (fig. 7). Leaving aside the uncertainties of under-sampling in the smallest size category (1–20 mg), it is very clear that large insects are proportionally much more abundant at night than during the day; and thus these large nocturnal insects are a major constituent of the nocturnal layers discussed here.

Fig. 6. Mass distributions of insects detected at all radar sampling heights, for all times of the day and night, during the months of June–August 2000–2003, inclusive, at both radar sites. Insects of mass below ~1 mg are not detected by the radar (see text).

Fig. 7. Mass distributions of insects detected at all radar sampling heights at night (defined as from one hour after sunset until one hour before sunrise) for the months of June–August 2000–2003, inclusive, at both radar sites.
Since virtually the only large nocturnal insects caught at high-altitude in the UK are noctuid moths (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Smith, Smith and Woiwod2004, Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Mouritsen, Hill, Riley, Sivell, Smith and Woiwod2008, and unpublished data), the rest of the analysis in this study will focus on this family. Table 1 lists the 25 most abundant species caught in the RIS national light-trap network during 2000–2006. It contains the well-known long-distance obligate migrant, Autographa gamma, and some resident species that are facultative migrants, such as Noctua pronuba and Xestia c-nigrum. The light-trap results are likely to reflect abundance rather than migration tendency; so, to determine which of these abundant species are most likely to be ascending to higher altitudes, we examined abundance data for noctuid moths caught in the 12.2 m suction-trap network and tabulated the 25 most abundant species (table 2) (see also Lewis & Taylor, Reference Lewis and Taylor1964, p. 444). The most common species, Amphipyra tragopoginis, is not migratory and its capture in large numbers at 12.2 m is curious, but it seems unlikely that it engages in high-altitude movement. (Taylor & Carter (Reference Taylor and Carter1961) found a continuously diminishing density with height, up to at least 17 m, in this species.) However, some of the other abundant species in the suction trap, such as N. pronuba, A. gamma, Agrotis exclamationis, X. c-nigrum, Phlogophora meticulosa and Agrotis segetum are known, or are strongly suspected, to be migratory (see Discussion). In these cases, capture at 12.2 m is consistent with migratory individuals ascending above their ‘flight boundary layer’ and potentially engaging in long-distance transport on the wind. Moth species with these characteristics are likely to be the dominant species in the layers.
Table 1. Summary of the catches of the 25 most abundant species of noctuid moth, from all English and Welsh RIS light-traps (ca. 60 traps in use per year) during 2000–2006, inclusive.

† Proportion with respect to the mean numbers of the 25 most abundant species.
Table 2. Summary of the catches of the 25 most abundant species of noctuid moth, from all English RIS suction-traps (11 or 12 traps in use per year) during 2001, 2006 and 2007.

† Proportion with respect to the mean numbers of the 25 most abundant species.
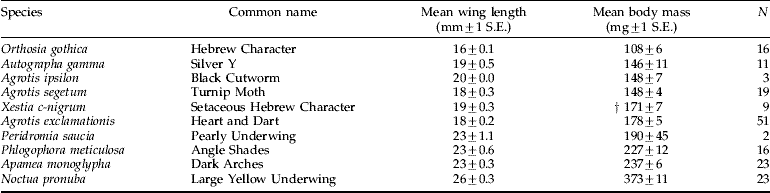
The mean body mass and wing length of noctuid moth species that are known to be migrants or were common in both suction-trap and light-trap catches are shown in table 3. The mass estimates of these migratory species are quite consistent with the mass distribution of large nocturnally-flying targets derived from the radar data, as discussed below.
Table 3. Mass and wing-lengths of abundant noctuid moth species caught in a mercury-vapour light-trap at Rothamsted, Harpenden, between 1999 and 2001. Listed are the ten species that are most likely to comprise nocturnal layers based on the ranking in both tables 1 and 2 and the reported high migratory propensity of the species (see text).
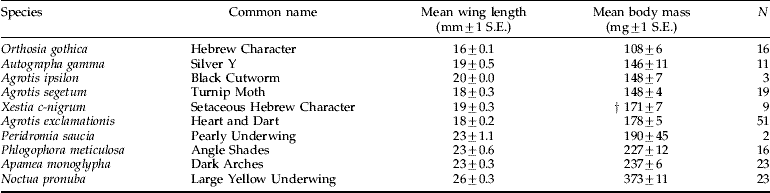
† Fresh masses of this species were not available, the mass value is an estimate based on equation 1 in the ‘Results’.
Insect sizes and terminal velocities
Figure 8 shows the relationship between body mass and wing-length for 209 individuals (of 17 noctuid species). The linear regression is given by:
where m is the mass of a noctuid moth, in mg, and l w is length of wing, in mm (R2=78%, P<0.001).
Values of cross-sectional area and insect mass were found to be closely correlated (for closed wings: R2=74%, P<0.001), and hence cross-sectional area can be estimated from mass for noctuid moths (Wood, Reference Wood2007). The terminal velocities (w T) for a range of noctuid moths were calculated (fig. 9) and found to be 10–12 m s−1 if wings were closed and 3–5 m s−1 if wings were open. The fitted lines can be used as an approximation to estimate terminal velocity from mass alone:
for closed and open wings, respectively, where m is mass in mg.
It is clear that the estimated terminal velocities of free-falling insects, of similar size to those comprising the nocturnal layers, are very large compared to the weak turbulent vertical motions that migrants will encounter when flying in the nocturnal atmospheric boundary layer in fair weather conditions (e.g. Stull, Reference Stull1997; Wood, Reference Wood2007).

Fig. 8. Body mass against wing-length for 209 noctuid moths of 17 species caught in a mercury-vapour light-trap at Rothamsted during 1999–2001, inclusive.

Fig. 9. Terminal velocity (calculated using a simple fluid dynamics model) against moth mass (see text).
Discussion
In the current study, we present the first systematic analysis of flight periodicity and altitude-selection in high-altitude migrant macro-insects, using data collected by continuously-operating insect-monitoring radars in over southern UK during the summer months of four consecutive years.
Daytime layers are reported infrequently in the radar entomology literature compared to nocturnal layers (but note Campistron, Reference Campistron1975; Smith et al., Reference Smith, Reynolds and Riley2000; Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Smith, Woiwod, Reynolds and Riley2002b). The daytime layers detected by our radars were not as temporally and spatially continuous as nocturnal layers, probably due to the influence of turbulence and updraughts in the convective boundary layer (Wood, Reference Wood2007). The processes involved in daytime layering clearly deserve further study; but, in this paper, we have concentrated on the more intense and persistent nocturnal layers.
In summertime in the UK, nocturnal layers were most frequent at 21:15, just after the ubiquitous dusk peak in insect density caused by mass take-off of migrants around dusk (ca. 20:45). This has been previously noted in case-study analyses (e.g. Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Chapman, Edwards, Smith, Wood, Barlow and Woiwod2005), but the present study has used a much more extensive dataset of archived radar records. Nocturnal layer concentrations tended to dissipate with time later in the night, particularly after midnight when insect aerial densities at all altitudes tend to become very sparse. Hence, although there are occasions in the UK when intense layering persists through the night, these appear to be due to particularly warm temperatures at layer altitude (Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Chapman, Edwards, Smith, Wood, Barlow and Woiwod2005) or perhaps to species with long migratory flight durations (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Mouritsen, Hill, Riley, Sivell, Smith and Woiwod2008). In the dataset analysed here, the least aerial activity was observed at about 02:30–02:45, following which activity peaked again between 03:30 and 03:45, due to the dawn take-off and emigration. There was a small peak in the frequency of layering at about 04:00, just after (and arising from) the dawn emigration. Dawn layering was generally short-lived; indeed, the period of the day with the least amount of layering was 05:15. Case studies of some rather striking and persistent post-dawn layers observed with our insect-monitoring radars are presented in D.R. Reynolds et al. (Reference Reynolds, Reynolds and Riley2008) ; but these layers are unusual, at least in the UK, and are not considered further here.
Nocturnal layers were observed mostly between altitudes of 200 and 500 m and were most frequent about 300–400 m AGL at both locations studied. There remains uncertainty about how much insect layering there was beneath the lowest radar-detection altitude, i.e. below about 150–180 m AGL. Most nocturnal layering followed from mass emigration at dusk (i.e. the dusk peak in insect numbers). Therefore, the ‘critical region’, in which meteorological variables might have a key influence on nocturnal layer initiation in southern Britain, was defined as the altitude band between 200 and 500 m AGL during the time period 20:00–22:00 hours. Estimates of terminal velocity show that insects constituting the layers must be maintaining their flight altitude by continuous wing-beating. Thus, nocturnal layers form due to the insects' response to atmospheric conditions, such as zones of warm air temperature or fast winds (Drake & Farrow, Reference Drake and Farrow1988; Reynolds et al., Reference Reynolds, Chapman, Edwards, Smith, Wood, Barlow and Woiwod2005; Wood et al., Reference Wood, Chapman, Reynolds, Barlow, Smith and Woiwod2006), and it is clear that they cannot be maintained simply by the action of atmospheric motions alone.
Comparison of the mass distribution of all radar-detected insects (fig. 6) with those detected solely at night (fig. 7) clearly shows that medium and large insects (those >40 mg) are much more common at night. As the only insects in this size category that have been caught in our high-altitude aerial netting at night are noctuid moths, we can confidently surmise that this taxon comprises the most important constituent of the nocturnal layers over the UK. The Noctuidae is the most speciose family of the macro-Lepidoptera, with around 400 species in the UK (Chinery, Reference Chinery1993), including some highly abundant species that are long-range migrants in Europe (e.g. Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Mouritsen, Hill, Riley, Sivell, Smith and Woiwod2008) and other continents (Riley et al., Reference Riley, Reynolds and Farmery1983; Fitt, Reference Fitt1989; Showers, Reference Showers1997; Feng et al., Reference Feng, Wu, Cheng and Guo2003, Reference Feng, Wu, Cheng and Guo2004, Reference Feng, Wu, Ni, Cheng and Guo2005). Two species that were highly abundant in the 12.2 m suction-trap catches, and that have also been caught flying at ~200 m AGL (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Smith, Smith and Woiwod2004, Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Mouritsen, Hill, Riley, Sivell, Smith and Woiwod2008), were A. gamma and N. pronuba. These species are known to be highly migratory (Hill & Gatehouse, Reference Hill and Gatehouse1993; Howard, Reference Howard1999; Hächler et al., Reference Hächler, Bloesch and Mittaz2002; Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Mouritsen, Hill, Riley, Sivell, Smith and Woiwod2008) and so are certain to be abundant constituents of the layers observed in this study. The body mass measurements of these species (table 3) indicate that A. gamma is probably responsible for many of the radar targets in the 80–160 mg size class in years when this species is abundant in Britain, while in other years species such as X. c-nigrum, Agrotis segetum and A. exclamationis may predominate in this size class. N. pronuba is probably responsible for the majority of targets in size class >320 mg (up to about 450 mg). The intermediate size class of 160–320 mg might well be composed of a number of species, including P. meticulosa, the heavier individuals of A. exclamationis, and perhaps Apamea monoglypha. These species have the migratory potential to cover hundreds of kilometres in a single flight (see Wood et al. (Reference Wood, Chapman, Reynolds, Barlow, Smith and Woiwod2006) for trajectory analyses of noctuid moth flight-paths) and, therefore, can easily fly to the UK from continental Europe. For examples, see Chapman et al. (Reference Chapman, Reynolds, Mouritsen, Hill, Riley, Sivell, Smith and Woiwod2008) for the migratory capabilities of A. gamma and French (Reference French1969) for the migration of Spodoptera exigua from North Africa to the British Isles. Precise prediction of the heights at which migratory noctuid moths concentrate under particular meteorological conditions will be essential for the production of accurate flight trajectory models, and so systematic studies of the factors involved in the selection of flight altitude will be invaluable for forecasting the migration pathways of pest species.
Acknowledgements
Some of this work was completed during funding from a BBSRC grant (BBS/S/L/2003/10273). Rothamsted Research receives grant-aided support from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC). We thank Met Office staff at Cardington for allowing us to run aerial netting operations on their site, Mr A.D. Smith for comprehensive radar engineering and other technical support, Mr Phillip Gould for identifying the moths and the Rothamsted Insect Survey for trap data.