Introduction
Numerous studies have found widespread and persistent cognitive deficits in schizophrenia patients across several domains including sustained attention, verbal memory, executive functioning and global performance Reference Sharma and Antonove(1,Reference Zakzanis, Leach and Kaplan2). Furthermore, cognitive impairment is considered a core characteristic of schizophrenia, is relatively independent of symptoms and is correlated with patient’s functional outcome (Reference Hoff and Kremen3–Reference Spaulding, Fleming, Reed, Sullivan, Storzbach and Lam5). For this reason, cognitive deficits may be of considerable prognostic value in schizophrenia, and routine cognitive assessment should be part of good clinical practice Reference Goldberg and Keefe(6).
The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) is a brief, standardised, cognitive screening instrument designed to assess global neuropsychological functioning that evaluates several domains of interest in schizophrenia: immediate memory, visuospatial/constructional ability, language, attention, delayed memory as well as a global measure (total scale) Reference Randolph(7).
Studies using RBANS reveal sensitivity to cognitive impairment typically associated with schizophrenia, has reasonable intraclass correlations, test-retest reliability and high correlations with more extensive assessments. Furthermore, RBANS performance has strongly correlated with functional outcome but has not always correlated with symptom severity Reference Gold, Queern, Iannone and Buchanan(8). Wilk et al. Reference Wilk, Gold, Humber, Dickerson, Fenton and Buchanan(9) reported RBANS normative data of out-patients diagnosed with a schizophrenia spectrum disorder (n = 575: 391 males, 184 females) recruited from two US mental health treatment facilities, and more recently, Loughland et al. Reference Loughland, Lewin, Vaughan, Sheedy and Harris(10) examined the impact of recruitment source differences by comparing the neuropsychological performance of an Australian community sample of people with schizophrenia from non-clinical settings (n = 285: 147 males, 138 females). RBANS was also sensitive in the detection of cognitive impairment in a psychiatric population of Swiss adolescents with psychotic symptomatology Reference Holzer, Chinet and Jaugey(11).
Most studies reviewed on cognitive performance in schizophrenia patients using RBANS have shown that memory is the more impaired domain followed by attention. However, visuospatial/constructional ability and language are shown to be only slightly or not impaired (Reference Gold, Queern, Iannone and Buchanan8–Reference Randolph, Tierney, Mohr and Chase12). Furthermore, schizophrenia patients have also been reported to have marked impairment relative to patients with bipolar disorder and other psychiatric conditions (Reference Randolph7–Reference Dickerson, Boronow, Stallings, Origoni, Cole and Yolken13).
Despite the suggested importance of taking into account cognitive deficits in the prognosis and treatment of schizophrenia patients, until now, no standardised assessment tool capable of briefly and accurately measuring this deficit has been available for Spanish clinicians.
The purpose of this study was to research the potential clinical usefulness of RBANS in Spanish population of patients with schizophrenia. The specific aims to research are as follows:
• To compare RBANS performance in a sample of schizophrenia patients with a group of non-psychotic psychiatric patients and a group of healthy control participants in order to evaluate its sensitivity and specificity to detect cognitive impairment in a Spanish sample of schizophrenia patients.
• To estimate the convergent validity of RBANS with a battery of neuropsychological tests, which tap into a group of cognitive domains usually considered sensitive to the cognitive impairment described in schizophrenia.
• To examine the relationship between RBANS and psychotic symptoms and clinical and demographic variables in patients with schizophrenia.
Methods
Participants
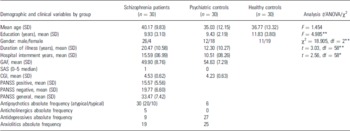
The sample consisted of a group of 30 patients with Diagnostic Statistical Manual IV-TR (14) diagnosis of schizophrenia and two control groups: 30 non-psychotic psychiatric patients and 30 healthy participants recruited from the community by advertisements and among hospital employees. The two groups of patients were all in-patients of the Psychiatric Hospital of Mérida, Spain, and were referred for a routine psychological assessment at the study centre. Written informed consent was obtained after a description of the study was provided to the participants. Ethical approval was obtained from the ‘Servicio Extremeño de Salud’ Research Ethics Committee. Corresponding to the schizophrenic spectrum disorders group, 20 patients were diagnosed with paranoid schizophrenia (67%), 9 residual (30%) and 1 disorganised (3%). The non-psychotic psychiatric control group consisted mainly of in-patients with affective, anxiety and personality disorders. Depression was diagnosed in 15 (50%) patients, anxiety disorder in 8 (27%), personality disorder in 6 (20%) and eating disorder in 1 (3%) patient. Tardive dyskinesia was an exclusion criterion for the schizophrenic group. Exclusion criteria for the psychiatric controls were a history of psychotic or manic symptoms, dementia or delirium. Exclusion criterion for normal controls was a history of psychiatric disorder. Exclusion criteria for all subjects were lifetime history of substance abuse, neurological disorders or other concomitant severe somatic disease (capable to interfere with cognitive functioning), intellectual or developmental disability and less than 6 years of education. All subjects were between 18 and 60 years of age, literate and had (corrected to) normal vision and hearing. Participants of both patient groups did not take any caffeine drink prior to the assessment. The characteristics of the sample are summarised in the Table 1.
Table 1 Demographic and clinical variables
PANSS, Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; SAS, Simpson-Angus Scale of Extrapyramidal Symptoms.
* p < 0.05
** p < 0.01.
Procedure
All participants received the experimental Spanish version of the RBANS (form A). RBANS is a cognitive screening test composed of 10 subtests that are combined to form five specific cognitive ability index scores: immediate memory, language, visuospatial/constructional ability, attention and delayed memory and a total scale score. Length of the battery to administer is less than 30 min Reference Randolph(7). RBANS was translated by the first two authors and by an English philologist who took into account several potential biases (word frequency, number of syllables and cultural adaptation for the short story to fit the cultural context of the Spanish population). Although Muntal et al. Reference Muntal, Dolors, Zaragoza, Aguilar and Haaland(15) are developing norms of RBANS for the Spanish population, they were not available when our study was performed. Therefore, the raw scores in this study were scaled using the US norms Reference Randolph(7).
In addition to RBANS, participants received a battery of standard neuropsychological measures of attention, memory, visuospatial and executive functioning. This battery consisted of tests that are considered sensitive to cognitive impairment characteristic of schizophrenia (Reference Sharma and Antonove1–Reference Kolb and Whishaw16). The administration time of the battery was approximately 90 min and incorporated the following tests: Stroop Colour-Word Test Reference Golden(17), Trail Making Test A and B Reference Reitan(18), Auditory Verbal Learning Test of the Complutense University TAVEC Reference Benedet and Alejandre(19), Rey-Osterreith Complex Figure Test Reference Rey(20), working memory index of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, third edition (WAIS III scale) Reference Weschsler(21) and speed of cognitive processing index of the WAIS III scale Reference Weschsler(21).
Furthermore, four scales of psychopathology and clinical status were administered: the Global Assessment of Functioning Scale (GAF) (14), the Clinical Global Impression Scale (CGI) Reference Guy(22), the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Reference Kay, Opler and Fiszbein(23) and Simpson-Angus Scale of Extrapyramidal Symptoms (SAS) Reference Simpson and Angus(24).
The assessment of the participants was conducted by two authors (J. C. S. and J. J. M.) with the assistance of two well-trained, supervised, advanced students of psychology from January 2004 to November 2004. Patients were clinically stabilised when they were assessed. First, RBANS and the four scales of psychopathology were administered, and then the neuropsychological test battery was administered the following day.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences for Windows (SPSS version 12.0). Data were initially examined for normality of distribution, and in cases where violations occurred transformations were performed. Descriptive statistics of demographic, clinical and cognitive characteristics of the samples were computed. We performed one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by ‘post hoc’ comparisons with the Tukey test to examine differences between groups in the five indexes and the total scale index of RBANS. Covariance analysis of RBANS by groups with educational level and gender as covariate variables was performed to study the potential influence of differences in education and sex in the three groups. ‘Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves’ (ROC curves) of total RBANS score between the three groups were computed to evaluate sensitivity and specificity. To summarise the data of the neuropsychological test battery, we transformed raw scores into z-scores using the Spanish norms provided by each test manual and created a composite z-score from the neuropsychological battery as a measure of global cognitive functioning. Individual z-scores were reduced by means of a principal components analysis (PCA) to determine how many discrete constructs were being assessed. Inter-test reliability analysis of RBANS was performed, and RBANS convergent validity with the neuropsychological test battery was assessed in schizophrenia patients using Pearson’s two-tailed test correlation and stepwise regression analysis. Pearson’s two-tailed correlation coefficients and regression analysis were calculated to study the relationship between RBANS and demographic and clinical variables. The pvalue for all analysis performed was set at 0.01.
Results
RBANS sensitivity, reliability and internal consistency
In RBANS, 70% of the schizophrenia patients had a total index score less than 75 (percentile rank <5) and 53% of the psychiatric controls scored less than 75. However, the percentage of the healthy controls that scored less than 75 was 0%. The difference between groups was highly significant (χ2 = 33.13, df = 2, p < 0.01). RBANS failure rate (% of cases with total index score less than 75) in the schizophrenia patients was significantly higher than that in the healthy controls (χ2 = 32.30, df = 1, p < 0.01). The area under the ROC curve was 0.956 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.906–1.000] (p < 0.001). Therefore, in the differential diagnosis between schizophrenia patients and healthy controls, we could propose a cut-off point of 82.5 with 80% sensitivity and 100% specificity.
However, the differences between patients with schizophrenia and psychiatric controls were not significant (χ2 = 1.76, df = 1, p > 0.05). The area under the ROC curve was 0.361 (95% CI 0.217–0.505) (p > 0.05).
The differences in the five means of RBANS index scores between groups were computed with ANOVA and subsequent post hoctests. They are summarised in Table 2. Schizophrenia patients and psychiatric controls performed significantly worse than healthy participants, and schizophrenia patients performed slightly worse than psychiatric controls, but the differences were not significant except for the immediate memory index in which the results approached significance (mean difference −9.367; p = 0.041). The lower index scores in patients with schizophrenia were observed in attention, immediate and delayed memory and the total scale. After covariate analysis to control effects of the educational level, the differences between groups in the five indexes remained significant (RBANS immediate memory, F = 30.49, p < 0.01; RBANS attention, F = 23.20, p < 0.01; RBANS language, F = 16.22, p < 0.01; RBANS visuospatial/constructional, F = 6.32, p < 0.01; RBANS delayed memory, F = 16.37, p < 0.01 and RBANS total, F = 37.28, p < 0.01). Group differences on RBANS total index score using gender as a covariate also remained significant (F = 46.82, p < 0.01).
Table 2 Differences in RBANS between groups (ANOVA and post hoctest)

H, Healthy participants; P, Psychiatric patients; S, Schizophrenia.
** p < 0.01.
Cronbach’s alpha for the total score and the five index scores in the global sample was 0.899, suggesting a high degree of internal consistency. Inter-item covariance mean was 188.674 (minimum 49.884, maximum 274.498). Inter-item correlations mean was 0.616 (minimum 0.331, maximum 0.889). The intraclass correlation coefficient for single measures was 0.596 (95% CI lower bound 0.511, upper bound 0.682, F = 9.865, p < 0.001). Cronbach’s alpha when one index of RBANS was not included in the calculus revealed the following results: when RBANS immediate memory was not included = 0.866, visuospatial = 0.899, language = 0.901, attention = 0.885, delayed memory = 0.884 and overall scale = 0.837.
Convergent validity
The neuropsychological battery included 10 selected variables. To condense data and determine how many discrete constructs were being assessed, we performed PCA. Components yielding eigenvalues greater than 0.70 were retained (the cut-off recommended by Jolliffe for defining a component) Reference Jolliffe(25), and varimax rotation was applied. The results of PCA yielded a four component solution. The resultant components were labelled as verbal memory [component (C) 1], executive functioning (C2), attention/speed of processing (C3) and visuospatial/constructional and visual memory (C4) (Table 3).
Table 3 PCA of the neuropsychological battery given to the whole sample (n = 90)

To study if RBANS assesses cognitive abilities similar to those assessed by the neuropsychological test battery in patients with schizophrenia, we examined the relationship between RBANS total scale index and the overall composite z-scores of the cognitive functions evaluated. The Pearson’s correlation value was 0.883 (p < 0.001). Furthermore, we performed the matrix correlations between the five RBANS indexes and the total index with the four cognitive components obtained in the PCA (Table 4). The results indicated that RBANS total score was highly correlated with the four cognitive areas (r = 0.883, p < 0.001). RBANS immediate and delayed memory indexes score were also strongly correlated with verbal memory (C1), executive functioning (C2) and attention (C3), with rvalues ranging from 0.787 to 0.570. The remaining correlations between RBANS indexes and components of the PCA of the neuropsychological battery were significant, with an rvalue ranging from 0.570 to 0.302 (p < 0.01).
Table 4 Pearson’s correlations between RBANS and PCA scores of the neuropsychological battery (n = 90)

C1, verbal memory; C2, executive functioning; C3, attention/speed of cognitive processing; C4, visuospatial/visual memory; CSUM, sum of components; npsy, neuropsychological.
** p < 0.01.
Given the high correlation between RBANS total score and many of the PCA component scores of the neuropsychological battery, we performed a stepwise regression analysis to specify which component scores contributed the most unique variance with RBANS total score. A three-variable solution emerged (F = 211.02, df = 1, p < 0.0001): the executive component entered in the equation first (F = 211.02, df = 1, p < 0.0001) with an R 2 of 0.70, the memory component entered the second (F = 176.371, df = 2, p < 0.0001), increasing the R 2 to 0.80, and the attention/speed of processing component entered the third (F = 141.88, df = 3, p < 0.0001), increasing the R 2 to 0.83. No other variables entered.
Relationship to demographic and clinical variables
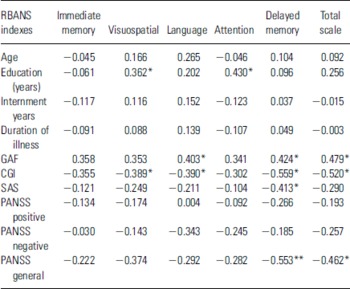
To examine the impact of age, education, duration of illness, global functioning and symptoms, two-tailed Pearson’s correlations were calculated between these clinical and demographical variables and the six RBANS index scores (Table 5). Only the attention and visuospatial/constructional indexes of RBANS correlated moderately with years of education in patients with schizophrenia (p < 0.05), suggesting a relationship between cognitive performance and educational achievement. As regards to the relationship between RBANS and the global functioning of patients with schizophrenia, we observed correlations (p < 0.05) between the CGI and four indexes of RBANS, including the total scale. Moreover, the GAF correlated with three RBANS indexes (p < 0.05). The relationship between scores on the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for the schizophrenia group revealed a strong negative correlation between the PANSS general psychopathology scale and delayed memory (p < 0.01) and the total RBANS index (p < 0.05). Simpson-Angus Scale of Extrapyramidal Symptoms (SAS) was correlated with delayed memory index of RBANS (p < 0.05). To examine how much variance in RBANS total index is explained by schizophrenia patient’s age, educational level, illness length, years of internment and by clinical variables such as CGI, GAF and PANSS (positive, negative and general scales), we used stepwise regression analysis, and only the CGI entered in the model (R 2 = 0.271, F = 10.400, p = 0.003). Thus, the rest of the predictive clinical and demographical variables were not significant and they were excluded.
Table 5 Correlations between RBANS and demographic and clinical variables in schizophrenia patients

PANSS, Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; SAS, Simpson-Angus Scale of Extrapyramidal Symptoms.
* p < 0.5
** p < 0.01.
Moderator variables
Group differences in medication were tested by chi-squared tests. No difference was found between the schizophrenia groups with normal RBANS performance (NP = total index score equal or greater than 75) and poor RBANS performance (PP = total index score less than 75) in relation to the number of subjects that took atypical (in the NP group 5 and in the PP group 15), or typical antipsychotics (NP 4, PP 6, χ2 = 0.71, df = 1, p = 0.33), antidepressants (NP 2, PP 7, χ2 = 0.37, df = 1, p = 0.44), nor in the number of patients that took anticholinergics (NP 0, PP 5, χ2 = 3.47, df = 1, p = 0.14) or anxiolitics (NP 4, PP 15, χ2 = 1.97, df = 1, p = 0.16). Therefore, the differences in cognitive functioning between normal and low performance groups in RBANS probably cannot be explained by differences in medication.
Effects of nicotine consumption on cognitive functioning were analysed with Pearson two-tails correlations, and we did not find association between the daily number of cigarettes smoked and the performance in RBANS total index score 0.229 (p = 0.224).
Discussion
This study suggests that the Spanish experimental version of RBANS is a useful screening tool for assessing neuropsychological status, with high sensitivity to cognitive impairment frequently observed in schizophrenia patients. However, RBANS did not discriminate between the cognitive impairment found in patients with schizophrenia and in-patients with other severe non-psychotic psychiatric conditions. Dickerson et al. Reference Dickerson, Boronow, Stallings, Origoni, Cole and Yolken(13) reported significant differences between patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in RBANS performance. Both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder were associated with significant cognitive impairment, but those in schizophrenia were more severe. Our results showed a similar trend, but the difference in RBANS performance between the schizophrenia patients and the non-psychotic psychiatric patients were not significant. Probably, illness severity of non-psychotic group and the small sample sizes of our study may explain the differences between the two findings.
Nevertheless, in concordance with the main trend of data reported by previous studies on RBANS (Reference Gold, Queern, Iannone and Buchanan8–Reference Hobart, Goldberg, Bartko and Gold26), our results point out that the RBANS, a brief and easily administered battery of cognitive tests, showed good sensitivity, solid internal consistency and convergent validity with a more complex battery of neuropsychological tests, sensitive to cognitive impairment usually detected in patients with schizophrenia.
The cognitive domains of Spanish in-patients with schizophrenia that were most impaired on RBANS were attention, immediate and delayed memory and total scale. Thus, our results were similar to those of the main neuropsychological studies on cognitive functioning that report memory dysfunction as a central feature of schizophrenia spectrum disorders Reference Zakzanis, Leach and Kaplan(2). Moreover, the overall performance of Spanish patients on RBANS appears to be more impaired in comparison with Wilk’s et al. Reference Wilk, Gold, Humber, Dickerson, Fenton and Buchanan(9) normative data (composed of 458 of out-patients and 117 of in-patients) and even more markedly in comparison with Loughland’s et al Reference Loughland, Lewin, Vaughan, Sheedy and Harris(10) sample from a schizophrenia patients recruited from a non-clinical setting. Therefore, RBANS total scale is consistently reported to be impaired, and it may be a sensitive simple measure in the screening of cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia patients (Reference Gold, Queern, Iannone and Buchanan8–Reference Hobart, Goldberg, Bartko and Gold26). Likewise, visuospatial/constructional and language scales were only slightly impaired in the Spanish sample. The composition of our sample of more chronic in-patients, with less education and probably with more serious deficit in their cognitive functioning may explain the differences in impairment severity with previous normative studies.
RBANS performance was not clearly associated with symptoms and clinical status of the schizophrenia patients. We can only report a moderate correlation between RBANS performance and rather broad and general clinical parameters such as the illness severity, reflected in the CGI-Schizophrenia Scale and also in the General Scale of the Positive and Negative Schizophrenia Syndrome Scale (PANSS). These results may be interpreted as a negative association between the overall performance in RBANS and the general level of illness severity in patients with schizophrenia. Previous studies reviewed did not report consistent results in the relationship between symptoms and neuropsychological functioning (Reference Gold, Queern, Iannone and Buchanan8–Reference Hughes, Kumari and Soni27). Cognitive impairments have been found to persist in schizophrenia, whereas symptoms tend to change over the course of illness, and a causal relationship between the course of symptoms and neuropsychological functioning has not yet been found Reference Hughes, Kumari and Soni(27).
It is important to consider some limitations in this pilot study such as the differences in educative level between the three samples, the heterogeneity of psychiatric group, the lack of Spanish norms and, in general, the small sample size. Another methodological problem comes from possible learning effects. Although the verbal and visual stimulus of RBANS and the battery of neuropsychological tests are different, both batteries tap similar cognitive domains. Because they were administered in a short-time interval (24 h) and the administration procedure was not counterbalanced, carry over and learning effects cannot be ruled out. Moreover, RBANS was originally developed for assessing dementia Reference Randolph(7). Therefore, the battery may not necessarily have high specificity for cognitive impairment in schizophrenia in the differential diagnosis with other psychiatric and neurological disorders. Instruments designed specifically for people with schizophrenia that include explicit testing of frontal functions might have higher accuracy (Reference Goldberg and Keefe6–Reference Pino, Guilera, Gómez, Rojo, Vallejo and Purdon29).
To our knowledge, this is the first RBANS research with psychiatric patients in a Spanish population. Despite the limitations previously reported, our preliminary data point out that RBANS appears to be a useful screening measure of cognitive functioning in patients with schizophrenia, especially in clinical settings. The battery is sensitive to the cognitive deficits usually observed in schizophrenia patients of different languages and cultural backgrounds, and it has been shown to have a high degree of internal consistency and convergent validity with larger batteries of neuropsychological tests.
Acknowledgements
Part of this study was supported by grant SCSS0404 from the Health Authorities of the ‘Junta de Extremadura’, Spain. The authors thank Dr Pedro Reyes from the English Language Department of the University of Extremadura, Spain, for his collaboration in the Spanish translation of RBANS.